How to Measure CFM of an Air Compressor: A Step-by-Step Guide

Knowing how to measure the CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) of an air compressor is essential for anyone working with pneumatic tools or equipment. CFM is a key metric that determines the air volume or flow rate produced by the compressor. This measurement is crucial for selecting the right compressor for a specific application or determining if an existing compressor can meet the demands of a particular tool or equipment.
To measure the CFM of an air compressor, you will need a few tools and follow a step-by-step process. The first step is to ensure that the compressor is properly set up and connected to the tool or equipment you are planning to use. This includes checking the pressure gauges, hoses, and fittings for any leaks or damage.
Next, you will need to attach a flow meter or an anemometer to the end of the hose or fitting that connects to the tool or equipment. This device will measure the air velocity or speed at the outlet, which is crucial for calculating the CFM. Make sure to position the flow meter or anemometer correctly and securely to get accurate readings.
Once everything is set up, you can start the compressor and let it run for a few minutes to stabilize the air flow. During this time, you should make sure that the tool or equipment is not in use to avoid any interference with the measurements. Once the air flow has stabilized, you can record the air velocity or speed using the flow meter or anemometer.
Finally, you can use a simple formula to calculate the CFM based on the recorded air velocity or speed. The formula involves multiplying the cross-sectional area of the outlet by the air velocity or speed. The result will give you the CFM of your air compressor. Remember to convert any measurements to consistent units, such as cubic feet per minute, if necessary.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can accurately measure the CFM of your air compressor and ensure that it meets the requirements of your pneumatic tools or equipment. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions when choosing or evaluating air compressors for various applications, ultimately improving the efficiency and effectiveness of your work.
Understanding CFM and Its Importance in Air Compressors

The term CFM stands for cubic feet per minute, and it is a unit of measurement that is crucial in the world of air compressors. CFM is used to measure the airflow rate or volume of air delivered by an air compressor. This measurement is important because it determines the compressor’s ability to power various tools and equipment.
In simple terms, CFM indicates how much air an air compressor can deliver within a minute. The higher the CFM rating of a compressor, the more air it can provide. This is important because different tools and applications require different amounts of airflow. A higher CFM rating is necessary for tools that demand a large volume of air, such as sandblasters or industrial spray guns, while a lower CFM rating may be sufficient for simpler tasks.
Knowing the CFM rating of an air compressor is crucial because:
- It helps to ensure that the compressor can provide sufficient air to power the tools or equipment being used. If the compressor’s CFM rating is too low for the application, it may result in reduced performance or even damage to the tools.
- It allows for proper matching of the compressor to the tools and equipment. Different tools have different CFM requirements, and using a compressor with a mismatched CFM rating can lead to inefficiency or inadequate performance.
- It helps in determining the correct pipe and hose size for the air compressor system. Adequate CFM flow is necessary for efficient operation, and using undersized pipes or hoses can result in pressure drops and decreased performance.
Overall, understanding CFM and its importance in air compressors is essential for selecting the appropriate compressor for your specific needs and ensuring optimal performance of your tools and equipment.
Gather the Required Tools and Equipment
Before you can measure the CFM of an air compressor, you will need to gather the necessary tools and equipment. Here is a list of what you will need:
- Anemometer: This device measures air velocity and will be used to calculate the CFM.
- Pressure gauge: You will use this gauge to measure the air pressure in the compressor tank.
- Stopwatch: This will be used to measure the time it takes for the tank to fill up.
- Tape measure: You will need this to measure the dimensions of the air compressor’s tank.
- Calculator: You will use a calculator to perform the necessary calculations to determine the CFM.
Once you have gathered all of the required tools and equipment, you will be ready to move on to the next steps in measuring the CFM of your air compressor. Make sure that all tools are in good working condition and properly calibrated to ensure accurate measurements.
Check for Air Leaks
Air leaks in an air compressor system can significantly affect its CFM (cubic feet per minute) output. It’s important to regularly check for air leaks to ensure that your compressor is operating efficiently.
Step 1: Visual Inspection
Start by visually inspecting all the fittings, hoses, and connections in your air compressor system. Look for any signs of air leakage, such as hissing sounds, bubbles, or oil stains. Pay close attention to connections and joints, as these are common areas for leaks to occur.
Step 2: Soap and Water Test
If you suspect an air leak but can’t visually identify it, you can perform a soap and water test. Mix a solution of water and dish soap, then apply it to the suspected leak areas. If there is a leak, you should see bubbles forming. Take note of the location of the leaks for further inspection.
Step 3: Check Seals and Gaskets
Seals and gaskets are another common source of air leaks. Inspect these components for any signs of wear or damage. Replace any worn or damaged seals and gaskets to ensure a proper seal and prevent air leakage.
Step 4: Inspect the Air Pressure Regulator
The air pressure regulator is responsible for controlling the pressure in the system. If it is not functioning properly, it can lead to air leaks. Inspect the regulator for any visible damage or signs of wear. If necessary, replace the regulator to ensure proper functioning and prevent air leakage.
Step 5: Conduct a System Pressure Test
If you have gone through the above steps and still suspect air leaks, you can conduct a system pressure test. Close all the valves and create pressure in the system with the compressor. Then, monitor the pressure gauge for any drop in pressure. If the pressure drops, it indicates the presence of air leaks. Take note of the drop in pressure and inspect the system further to locate and fix the leaks.
By regularly checking for air leaks and addressing them promptly, you can maintain the efficiency and CFM output of your air compressor system. Regular maintenance and inspections will ensure that your compressor operates at its optimal capacity and extends its lifespan.
Prepare the Air Compressor for Measurement

1. Make sure the air compressor is turned off
Before you start measuring the CFM of an air compressor, it’s important to ensure that the machine is turned off. This will prevent any accidents or injuries that may occur while taking measurements.
2. Disconnect any accessories or attachments
Remove any hoses, tools, or attachments that may be connected to the air compressor. These accessories can affect the airflow and accuracy of the CFM measurement, so it’s best to measure the CFM with only the bare compressor unit.
3. Empty the air tank
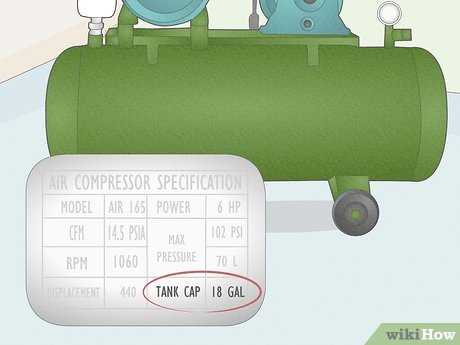
If the air compressor has an air tank, you will need to drain it completely before measuring the CFM. This is important because the CFM measurement is based on the airflow rate and pressure, and having any remaining air in the tank can affect the accuracy of the measurement.
4. Clean the intake filter
Check and clean the intake filter of the air compressor. A clogged or dirty filter can restrict airflow and affect the CFM measurement. Remove any dust or debris from the filter to ensure accurate measurements.
5. Ensure the pressure gauge is working properly
Check the pressure gauge on the air compressor to ensure it is functioning correctly. A faulty or inaccurate pressure gauge can lead to incorrect CFM measurements. If necessary, calibrate or replace the gauge before proceeding.
6. Position the airflow measurement device
Place the airflow measurement device, such as a CFM meter or an anemometer, near the outlet of the air compressor. This device will measure the volume of air flowing out of the compressor and provide the CFM reading.
Select the Appropriate Measurement Method
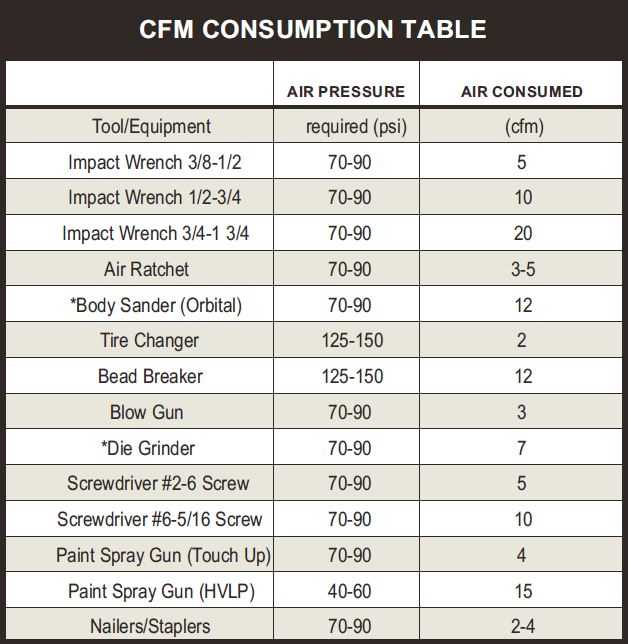
When it comes to measuring the CFM of an air compressor, it’s important to select the appropriate measurement method. There are several methods to choose from, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Pitot Tube Method: This method involves using a pitot tube, which is a hollow tube with a pressure gauge, to measure the velocity pressure of the air. The velocity pressure can then be used to calculate the CFM of the air compressor. This method is accurate and reliable, but it can be time-consuming and requires specialized equipment.
- Anemometer Method: An anemometer is a device that measures the speed of airflow. This method involves using an anemometer to measure the velocity of the air being produced by the air compressor. The velocity can then be used to calculate the CFM. This method is relatively easy to use and does not require specialized equipment, but it may not be as accurate as other methods.
- Orifice Plate Method: The orifice plate method involves installing an orifice plate, which is a flat disc with a hole in the center, in the air line of the compressor. The pressure difference across the orifice plate can then be used to calculate the CFM. This method is popular because it is simple and inexpensive, but it may not be as accurate as other methods.
When selecting the appropriate measurement method, consider factors such as the level of accuracy required, the equipment and resources available, and the time and effort needed to perform the measurement. It may be helpful to consult with experts or refer to industry standards to ensure that the chosen method is suitable for your specific needs.
Conduct the CFM Measurement
Once you have gathered all the necessary tools and prepared the air compressor for testing, it’s time to conduct the CFM measurement. Here are the step-by-step instructions:
Step 1: Position the Measurement Device
Place the measurement device, such as an anemometer or flow hood, in the designated position to capture the airflow from the compressor. Ensure that the device is positioned properly and securely to obtain accurate readings.
Step 2: Start the Air Compressor
Turn on the air compressor, allowing it to run at its maximum output. This will provide the most accurate measurement of CFM. Make sure to adjust any control settings or valves to maintain a consistent output throughout the measurement process.
Step 3: Record the Measurements
Using the measurement device, record the airflow readings at various points around the compressor outlet. Take multiple readings to ensure accuracy and consistency. Note down the CFM values obtained at each measurement point.
Step 4: Calculate the Average CFM
Once you have recorded all the measurements, calculate the average CFM by adding up the individual CFM values and dividing by the total number of measurements taken. This will give you a more reliable and representative measurement of the air compressor’s CFM.
By following these steps, you will be able to accurately measure the CFM of your air compressor, which is essential for choosing the right equipment and ensuring optimal performance in various applications.
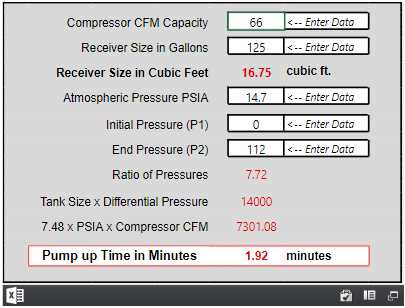
Calculate the Actual CFM
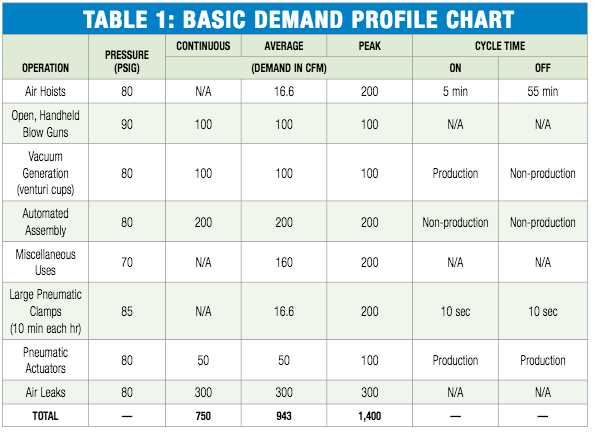
To calculate the actual CFM (cubic feet per minute) of an air compressor, you will need to measure a few variables and perform some calculations. The actual CFM represents the true output of the compressor, taking into account factors such as ambient conditions and pressure drop.
Step 1: Measure the Time
Start by measuring the time it takes for the air compressor to fill up a known volume of air. Make sure the tank is empty before starting the measurement. Note down the time taken in seconds.
Step 2: Measure the Tank Volume

Determine the tank volume in gallons or cubic feet. This information is often provided by the manufacturer or can be measured directly by calculating the dimensions of the tank. Note down the tank volume for later use in the calculations.
Step 3: Calculate the Fill-Up Rate
Divide the tank volume by the time taken to fill it up. This will give you the fill-up rate in gallons per second or cubic feet per second.
Step 4: Convert to CFM
To convert the fill-up rate to CFM, multiply it by an appropriate conversion factor. For example, if the fill-up rate is in cubic feet per second, you can use the conversion factor of 60 to convert it to CFM.
Note: It is important to note that the actual CFM may vary depending on factors such as temperature, humidity, and altitude. These factors can affect the performance of the air compressor and should be taken into account when calculating the actual CFM.
Compare the CFM Measurement with the Manufacturer’s Rating
Once you have measured the CFM of your air compressor, it is important to compare this measurement with the manufacturer’s rating. The manufacturer’s rating can usually be found on the air compressor’s label or in the user manual. The rating represents the maximum CFM that the air compressor is capable of producing.
To compare the CFM measurement with the manufacturer’s rating, you will need to ensure that the measured CFM is equal to or greater than the manufacturer’s rating. If the measured CFM is lower than the manufacturer’s rating, it indicates that the air compressor may not be delivering the expected performance.
If the measured CFM is significantly lower than the manufacturer’s rating, there may be potential issues with the air compressor, such as leaks or mechanical problems. In such cases, it is recommended to troubleshoot and address the underlying problem before further use.
However, it is important to note that there may be some small variations between the measured CFM and the manufacturer’s rating. These variations can occur due to factors such as temperature, humidity, and altitude. Therefore, it is advisable to consider these factors and make allowances for any slight differences when comparing the CFM measurement with the manufacturer’s rating.
FAQ:
What is CFM and why is it important to measure it in an air compressor?
CFM stands for cubic feet per minute and it is a measurement of the volume of air that an air compressor can deliver. It is important to measure CFM because it helps determine how well an air compressor can power tools and other equipment.
What tools do I need to measure the CFM of an air compressor?
To measure the CFM of an air compressor, you will need a stopwatch or a timer, a pressure gauge, and a calculator.
How do I measure the CFM of an air compressor?
To measure the CFM of an air compressor, you can follow these step-by-step instructions:
Can I use a handheld anemometer to measure the CFM of an air compressor?
No, a handheld anemometer is not suitable for measuring the CFM of an air compressor. It is designed to measure wind speed and is not accurate for measuring the volume of air flow.
Why is it important to measure the CFM of an air compressor before buying it?
Measuring the CFM of an air compressor before buying it is important because it helps ensure that the air compressor has enough power to handle the tools and equipment you plan to use with it. If the CFM is too low, the air compressor may not be able to provide enough air flow for your needs.
Video:











