Who Invented the Lathe? Discover the Fascinating Origins of this Essential Tool

The lathe is an essential tool used in various industries, from woodworking to metalworking. It is a machine that rotates a workpiece on its axis, allowing for precision shaping and cutting. But have you ever wondered who was the genius behind the invention of this indispensable tool?
The origins of the lathe can be traced back to ancient times, where it was first developed by the Egyptians around 1300 BC. However, the basic concept of rotating a workpiece to shape it can be found even earlier in ancient Mesopotamia. These early lathes were operated by hand or using a bow, and they were primarily used for woodworking.
It wasn’t until the Middle Ages in Europe that the lathe began to evolve into a more sophisticated machine. The addition of a foot pedal allowed for more control, and the invention of the screw-cutting lathe in the 16th century revolutionized the manufacturing industry. This new type of lathe enabled the production of standardized screws and threads, which played a crucial role in industrialization.
One of the most significant advancements in lathe technology came in the 19th century with the invention of the power lathe. This innovation replaced manual labor with steam, water, or electric power, greatly increasing the efficiency and productivity of the lathe. In the 20th century, further advancements transformed the lathe into the computer numerical control (CNC) lathe, capable of high-precision and automated machining.
Today, the lathe continues to be an essential tool in various industries, and its origins can be traced back thousands of years. From its humble beginnings in ancient Egypt to its modern, high-tech iterations, the lathe has played a crucial role in shaping our world.
The Origins of the Lathe: Unveiling its Inventor
Often considered one of the most important tools in the history of machinery, the lathe has a long and fascinating history. It is an essential tool in various industries, including woodworking, metalworking, and even pottery. But who exactly invented this versatile machine?
The Ancient Origins
The exact origins of the lathe are difficult to trace, as evidence suggests that simple versions of this machine were used as far back as ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia. These early lathes were operated by hand and were primarily used for shaping wood.
However, it was during the time of the Ancient Greeks that the lathe truly began to take shape as a more sophisticated tool. The Greek mathematician and engineer, Heron of Alexandria, described a lathe powered by a pulley system in the 1st century AD. This innovation allowed the lathe to be operated more efficiently and with increased precision.
Medieval Europe and the Renaissance
During the Middle Ages and the Renaissance period, the lathe continued to evolve and improve. In medieval Europe, craftsmen started using foot-powered lathes, which allowed them to work with metal as well as wood. This opened up new possibilities for creating intricate designs and detailed work.
Leonardo da Vinci, the renowned Italian polymath of the Renaissance, made significant contributions to the development of the lathe. He designed and built several lathes, including a spring pole lathe that utilized a bent springy pole to power the cutting tool.
The Industrial Revolution and Modern Advances
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries brought about major advancements in lathe technology. Steam power became a popular method for driving lathes, greatly increasing their productivity and efficiency.
In the 19th century, Henry Maudslay, an English engineer, made significant improvements to lathe design, introducing features such as the screw cutting mechanism and carriage. These innovations revolutionized metalworking and set the stage for the modern lathe.
Today, the lathe has become an indispensable tool in numerous industries and continues to evolve with the advent of computer numerical control (CNC) technology. CNC lathes are capable of performing complex operations with high precision, making them an essential part of modern manufacturing processes.
While it may not be possible to pinpoint a single inventor of the lathe, its origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations and the innovative minds of the ancient Greeks and Renaissance pioneers. Their contributions have shaped the lathe into the versatile and powerful machine that it is today.
The Ancient Beginnings: Unraveling the Origins
The lathe is an ancient tool that has been essential to human civilization for centuries. While its exact origins are still a matter of debate, evidence points to its existence in ancient civilizations around the world.

The Ancient Egyptians
One of the earliest known examples of a lathe-like tool comes from ancient Egypt. The Egyptians used a simple two-person lathe called a bow lathe, which consisted of a bow-shaped wooden frame and a cord. By wrapping the cord around a workpiece and pulling on the bow, the Egyptians were able to rotate the workpiece and shape it using cutting tools.
The bow lathe was primarily used for woodworking and creating intricate designs on furniture and other wooden objects. The Egyptians were skilled craftsmen and used the lathe to create ornate and detailed pieces that showcased their exceptional craftsmanship.
The Ancient Greeks
The ancient Greeks also had their own version of the lathe, known as the potter’s wheel. This specialized lathe was used for shaping clay pottery. Similar to the bow lathe, it relied on manual force to rotate the workpiece. By spinning the wheel with their hands, potters were able to shape and mold the clay into various forms.
The potter’s wheel was a significant advancement in pottery making and allowed for the production of uniform and symmetrical vessels. It revolutionized the art of pottery and greatly influenced ceramic traditions in many cultures.
The Ancient Romans
The Romans further advanced the lathe by introducing more sophisticated designs and mechanisms. They developed the horizontal lathe, which featured a horizontal bed and a hand crank or treadle for rotation. This innovation allowed for increased control and precision in shaping workpieces.

With the introduction of the horizontal lathe, the Romans were able to produce a wide range of items, including furniture, architectural details, and even weapons. Their mastery of the lathe contributed to their reputation as skilled artisans and craftsmen.
Overall, the origins of the lathe can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Greece, and Rome. These early versions of the lathe laid the foundation for its evolution into the essential tool it is today, serving as a testament to the ingenuity and creativity of our ancestors.
The Genius Behind the Invention: Pioneering Minds
The invention of the lathe was a result of the innovative thinking and ingenuity of several individuals throughout history. These pioneers played a crucial role in developing and refining the lathe into the powerful and versatile tool it is today.
Leonardo da Vinci
One of the earliest recorded individuals to contribute to the development of the lathe was the legendary Italian polymath, Leonardo da Vinci. In the late 15th century, da Vinci conceptualized and designed a machine that closely resembled a lathe. His design included a tool support system that allowed for precise cutting and shaping of materials.
Thomas Blanchard

Another key figure in the history of the lathe is American inventor Thomas Blanchard. In the early 19th century, Blanchard made significant improvements to the lathe, making it more efficient and practical for industrial use. He invented the “copying lathe,” which could reproduce wooden parts with remarkable accuracy and speed.
Henry Maudslay
English engineer Henry Maudslay is widely regarded as one of the most influential figures in the development of machine tools, including the lathe. In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, Maudslay made significant advancements in lathe technology, such as the introduction of the screw-cutting mechanism. His work laid the foundation for the industrialization of manufacturing processes.
Richard Roberts
English engineer Richard Roberts further refined the lathe in the 19th century by introducing the slide rest. This innovation allowed for greater precision and control in shaping materials, making the lathe an even more valuable tool for various industries.
Modern Innovators
In recent times, many inventors and engineers have continued to push the boundaries of lathe technology. With advancements in computer numerical control (CNC) technology, lathes can now be controlled with incredible precision and automation. This has further expanded the capabilities of the lathe, making it an essential tool in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing.

Conclusion
The invention of the lathe was the result of the collective efforts of many brilliant minds throughout history. From da Vinci and Blanchard to Maudslay and Roberts, these pioneers paved the way for the development of a tool that has revolutionized the way we shape and create objects. Today, the lathe continues to evolve, with modern innovators pushing the boundaries of what is possible. The lathe is truly a testament to human ingenuity and the power of innovation.
Evolutionary Leaps: Advancements throughout History
1. The Handheld Lathe
The evolution of the lathe can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where the first known form of a lathe emerged. This primitive lathe was handheld, with the operator using a bow-shaped tool to create rotational motion. This innovation allowed craftsmen to shape wood and other materials, laying the foundation for all future lathe designs.
2. The Treadle Lathe
As human ingenuity progressed, so did the design of the lathe. In ancient Rome, the treadle lathe was introduced. This design utilized foot power to rotate the workpiece, freeing up both hands of the operator for more precise control of the cutting tool. The treadle lathe revolutionized woodworking, enabling craftsmen to create intricate designs and symmetrical patterns.
3. The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution marked a significant turning point in the development of the lathe. The introduction of steam power and manufacturing techniques led to the creation of larger and more powerful lathes. These lathes were capable of handling larger workpieces and performing more complex operations. The Industrial Revolution also saw the introduction of automatic lathes, which could replicate the same motions over and over again, increasing productivity and efficiency.
4. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Lathes
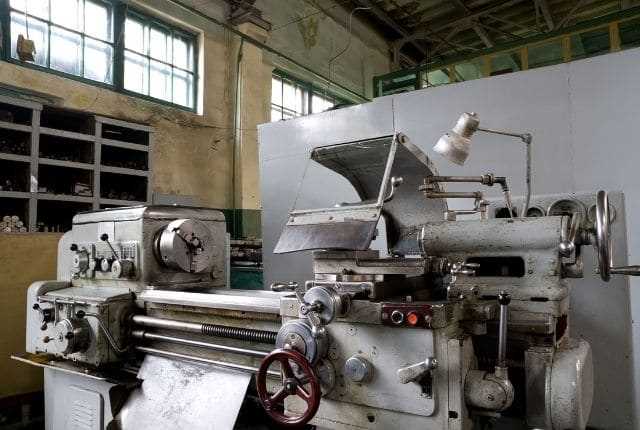


In the second half of the 20th century, computer technology revolutionized the lathe once again. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) lathes were developed, allowing for precise control of cutting tools and the ability to create complex shapes with ease. CNC lathes can be programmed to perform a wide range of operations, making them indispensable in modern manufacturing industries.
5. Advanced Materials and Automation
Today, lathe technology continues to advance. The use of advanced materials, such as ceramics and composites, has expanded the capabilities of lathes. These materials require special tools and techniques to shape, pushing the boundaries of what is possible with lathe technology. Additionally, automation has become increasingly common in lathe operations, with robots and programmable machines taking over repetitive tasks, increasing productivity and reducing human error.
Conclusion
The lathe has come a long way from its humble beginnings as a handheld tool. Throughout history, we have witnessed incredible advancements in lathe technology, from the handheld lathe to the CNC lathe of today. These innovations have shaped our world, enabling the creation of intricate designs, precise components, and the manufacturing of advanced materials. As technology continues to progress, we can only imagine what the future holds for this essential tool.
Industrial Revolution Impact: Revolutionizing Manufacturing
The Industrial Revolution, which took place from the 18th to the 19th century, had a profound impact on the manufacturing industry. It brought about significant changes in the way goods were produced and transformed the economic landscape of the world.
The Rise of Factories
One of the most notable impacts of the Industrial Revolution was the rise of factories. Before this period, manufacturing was primarily done in homes or small workshops using hand tools. However, with the development of new machines and technologies, large factories emerged. These factories, equipped with specialized machinery and powered by steam engines, allowed for mass production on a scale never seen before.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
The introduction of machinery in manufacturing led to a significant increase in efficiency and productivity. Machines such as the steam engine, spinning frame, and power loom revolutionized textile production, enabling the production of fabrics on a much larger scale. With the use of machines, tasks that were previously done manually could now be completed more quickly and with greater precision.
Improvements in Transportation
The Industrial Revolution also brought improvements in transportation, which further revolutionized manufacturing. The invention of the steam engine made it possible to transport goods and materials over long distances more efficiently and quickly. This led to the expansion of markets and the ability to access raw materials from distant locations, spurring industrial growth.
Division of Labor
Another significant impact of the Industrial Revolution was the division of labor. Instead of one person completing all the tasks required in the production process, work was divided into specialized tasks performed by different workers. This division of labor increased productivity and allowed for the production of goods in larger quantities.
Growth of Urban Centers
The Industrial Revolution also resulted in the growth of urban centers. As factories emerged and industrialization progressed, people moved from rural areas to cities in search of employment opportunities. This led to the rapid expansion of urban areas and the rise of industrial cities.
Conclusion
The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on manufacturing, revolutionizing the way goods were produced. The rise of factories, increased efficiency and productivity, improvements in transportation, division of labor, and growth of urban centers were some of the notable effects of this transformative period. These changes laid the foundation for the modern manufacturing practices we see today.
Lathe in the Modern World: Ubiquitous Applications
1. Manufacturing Industry
In the modern manufacturing industry, lathes are an essential tool for producing a wide range of products. They are used for tasks such as shaping and finishing parts, creating symmetrical shapes, and producing precision components. Lathes play a vital role in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing.
2. Woodworking
Lathes are widely used in the woodworking industry for various purposes. They can be used to turn wooden bowls, vases, furniture legs, and other decorative or functional wooden items. Woodturning lathes allow craftsmen to shape wood with precision and create intricate designs.
3. Metalworking
Metals lathes are commonly used in metalworking industries to create precision components for various applications. They can be used to turn and shape metal parts, cut threads, and produce smooth finishes on metal surfaces. Metal lathes are crucial in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and machinery manufacturing.
4. Jewelry Making
Lathes are also used in the jewelry making industry to create intricate designs on metal pieces. Jewelry lathes allow craftsmen to shape precious metals, create custom settings for gemstones, and produce detailed engravings on jewelry pieces.
5. Education and Training
Lathes play a significant role in technical education and vocational training programs. Students learn how to operate a lathe as part of their training in various fields such as machining, woodworking, metalworking, and jewelry making. Lathes provide hands-on experience and help students develop essential skills for future careers.
6. DIY and Hobbyist Projects
Lathes are not only used in professional settings but also popular among DIY enthusiasts and hobbyists. Many hobbyists and DIYers have their small lathes for woodworking, metalworking, or other creative projects. Lathes provide them with the ability to create customized and unique items.
7. Artistic and Sculptural Applications

Lathes are used by artists and sculptors to create unique and intricate artistic pieces. Artists can shape various materials such as wood, metal, and even ceramics using lathes, allowing them to bring their creative visions to life.
8. Scientific and Research Applications
In scientific and research contexts, lathes are used for precision machining and fabrication of specialized components and instruments. They are crucial for producing experimental setups, prototypes, and custom equipment required for scientific experiments and research projects.
9. Medical Field
While not as commonly associated with lathes, they are used in various medical applications. Lathes are used for machining and shaping medical implants, prosthetics, and other specialized medical devices. They ensure the precise and accurate production of custom-made components for patient care.
10. Industrial Maintenance and Repair
Lathes are also utilized in industrial maintenance and repair operations. They are used to repair and overhaul machinery, equipment, and various mechanical components. Lathes enable skilled technicians to restore damaged or worn-out parts, ensuring the smooth operation and longevity of industrial assets.
In summary, lathes have found widespread applications in various industries, hobbies, and creative fields. Their versatility and precision make them an indispensable tool in the modern world, contributing to the production of countless essential products and enabling creative expression.
Precise Craftsmanship: Fine-tuning Techniques
When it comes to using a lathe, precision is of the utmost importance. The ability to fine-tune and perfect a piece of work is what separates true craftsmen from amateurs. Here are some of the most essential techniques for achieving precise craftsmanship on a lathe:
1. Tool Selection
Choosing the right cutting tools is crucial for achieving precise cuts on a lathe. Different materials and shapes require specific tools, so it’s essential to have a well-rounded selection. Some common lathe cutting tools include gouges, chisels, parting tools, and skew chisels.
2. Focusing on Measurements
Accurate measurements are essential for achieving precise craftsmanship. Whether it’s the length, diameter, or depth of a piece, taking precise measurements and consistently referring to them throughout the turning process is crucial. This ensures that the finished product meets the desired specifications.
3. Speed and Feed Rates
Adjusting the speed and feed rates on a lathe can greatly affect the quality and precision of the work. Different materials require different speeds and feed rates to achieve the desired finish. It’s important to experiment and find the optimal settings for each specific project.
4. Tool Rest Positioning
The position of the tool rest greatly influences the stability and control of the cutting tool. Adjusting the tool rest position allows the craftsman to find the most comfortable and effective position for achieving precise cuts. It’s important to experiment with different tool rest positions to find what works best for each individual.
5. Finishing Techniques
After the initial shaping and cutting is complete, the final finishing touches are crucial for achieving precise craftsmanship. Sanding, polishing, and applying a finish can greatly enhance the appearance and quality of the piece. It’s important to take time and pay attention to detail during this final stage.
6. Regular Maintenance and Sharpening
A well-maintained lathe and sharp cutting tools are essential for achieving precise craftsmanship. Regularly cleaning, lubricating, and inspecting the lathe will ensure optimal performance. Sharpening the cutting tools when necessary will guarantee clean and precise cuts.
7. Patience and Practice
Above all, achieving precise craftsmanship on a lathe requires patience and practice. It takes time and dedication to develop the skills and techniques needed to produce high-quality work. Through trial and error, a craftsman can continually refine their skills and achieve greater precision.
By utilizing these fine-tuning techniques, craftsmen can take their lathe work to the next level. The ability to achieve precise craftsmanship not only results in visually appealing pieces but also ensures the functionality and longevity of the work. With practice and attention to detail, anyone can become a master of the lathe.
Expanding Frontiers: Lathe in Contemporary Industries
Introduction
The lathe, a versatile and essential tool, has been a cornerstone of manufacturing and machining for centuries. While its origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations, the applications and advancements of lathe technology have expanded significantly in contemporary industries. This article explores how the lathe continues to play a pivotal role in various sectors, revolutionizing manufacturing processes and contributing to technological advancements.
1. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry heavily relies on lathes for the production of precision components. Lathes are utilized to manufacture various engine parts, such as cylinders, pistons, and crankshafts. The ability to produce accurate and high-quality components ensures the efficiency and reliability of automobiles, contributing to advancements in fuel efficiency, performance, and safety.
Moreover, lathes are used in the production of wheels and other rotating components, contributing to the overall aesthetics and functionality of vehicles. The use of computer numerical control (CNC) lathes enables automation and increases productivity in the automotive manufacturing process.
2. Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, lathes play a crucial role in the production of aircraft components. These components often require high precision and intricate designs. Lathes are used to manufacture engine parts, landing gear components, turbine blades, and other critical components. The ability to produce complex parts to exact specifications ensures the safety and functionality of aircraft.
The aerospace industry also benefits from the advancements in lathe technology, such as the use of multi-axis CNC lathes. These machines allow for the production of complex geometries and reduce manual labor, leading to increased efficiency and reduced production costs.
3. Medical Industry
Lathes have found applications in the medical industry, particularly in the production of prosthetics and medical implants. The precision and customization capabilities of lathes enable the production of accurate and well-fitting prosthetic limbs, dental implants, and joint replacements. The use of CNC lathes allows for the production of complex and personalized medical devices, improving the quality of life for patients.
4. Electronics Industry
The electronics industry utilizes lathes for the production of precision components, such as connectors, switches, and pins. These components are crucial for the functionality of various electronic devices, from smartphones to computers. Lathes enable the manufacturing of intricate designs and precise dimensions, ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic devices.
The miniaturization of electronic components has also been made possible through advancements in lathe technology. CNC precision lathes can produce tiny components with high accuracy, contributing to the development of smaller and more advanced electronic devices.
Conclusion
The lathe continues to evolve and adapt to the changing needs of contemporary industries. From the automotive and aerospace sectors to the medical and electronics industries, lathes play a crucial role in manufacturing precision components. The advancements in lathe technology, such as CNC capabilities, have revolutionized manufacturing processes and contributed to technological advancements. As industries continue to push the boundaries of innovation, the lathe is expected to remain an essential tool in the ever-expanding frontiers of manufacturing and machining.
Revolutionary Innovations: Future Prospects and Trends
1. Artificial Intelligence and Automation
The future of lathes lies in the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation technologies. AI can be used to optimize the performance and efficiency of lathes by analyzing data, making real-time adjustments, and predicting maintenance requirements. Automation, on the other hand, can enable lathes to perform tasks without human intervention, leading to increased productivity and reduced labor costs.
2. Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT can revolutionize the way lathes are operated and monitored. By connecting lathes to the internet, manufacturers can collect data on machine performance, energy usage, and inventory levels in real time. This data can then be used to optimize production processes, reduce downtime, and improve overall efficiency. Additionally, the IoT can enable remote monitoring and control of lathes, allowing operators to manage multiple machines from a centralized location.
3. Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, has the potential to disrupt traditional machining processes, including lathe operations. With 3D printing, complex parts can be produced directly from a digital model, eliminating the need for multiple machining operations. This can lead to cost savings, reduced material waste, and shorter lead times. As 3D printing technology continues to advance, it is expected to play a significant role in the future of lathes.
4. Advanced Materials
The demand for lathes that can handle advanced materials, such as composites and exotic alloys, is growing. These materials offer unique properties, but they also present challenges in terms of machining. Future lathe innovations will focus on developing cutting tools, coatings, and machining techniques that can effectively handle these materials. This will allow manufacturers to expand their capabilities and meet the evolving needs of various industries.
5. Green Manufacturing
Sustainability is becoming an increasingly important aspect of manufacturing. Future lathe innovations will focus on reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste generation, and improving overall environmental performance. This can be achieved through the use of energy-efficient components, recycling and reusing materials, and implementing eco-friendly machining processes. Green manufacturing practices will not only help protect the environment but also enhance the reputation and competitiveness of lathe manufacturers.
FAQ
When was the lathe first invented?
The lathe is one of the oldest tools in human history. It was first invented around 1300 BC in ancient Egypt.
Who invented the lathe?
The exact inventor of the lathe is unknown, but it is believed to have been invented by ancient Egyptians.
What were the early lathes used for?
Early lathes were primarily used for woodworking, shaping objects such as bowls, cups, and furniture legs.
How did the lathe evolve over time?
Over time, the design of the lathe evolved to include more features and functionalities, such as the addition of a motor, automatic feeding mechanisms, and the ability to create more precise and complex shapes.
Who improved the lathe during the Industrial Revolution?
During the Industrial Revolution, the lathe was improved by various inventors and engineers, such as Henry Maudslay and Joseph Whitworth, who introduced new concepts and techniques to make the lathe more efficient and versatile.
What are some modern applications of the lathe?
Modern lathes are used in a wide range of industries, including metalworking, woodworking, and manufacturing. They are used to create components for machinery, furniture, instruments, and much more.
What are the different types of lathes available today?
There are several types of lathes available today, including engine lathes, turret lathes, and CNC lathes. Each type has its own specific features and is used for different applications.







