What is a Lathe Machine: A Comprehensive Guide

Lathe machine is a versatile tool that is used in various industries for shaping and cutting materials. It is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece on its axis to perform various operations such as cutting, drilling, sanding, and turning. The lathe machine has been a fundamental tool in the manufacturing industry for centuries, and its usage has evolved over time.
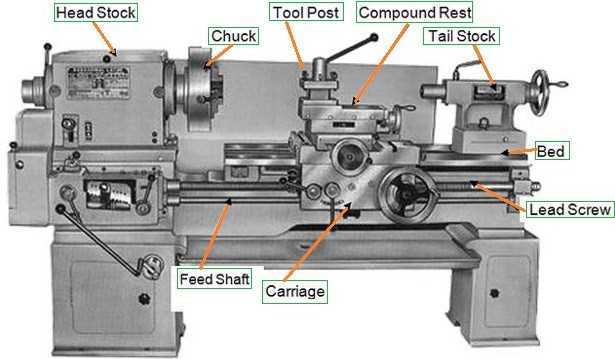
The lathe machine consists of several important components, including the bed, headstock, tailstock, tool post, and carriage. The bed is the base of the machine and provides support to all the other components. The headstock houses the main spindle, which holds the workpiece and rotates it. The tailstock supports the other end of the workpiece and can be adjusted to accommodate different lengths. The tool post holds the cutting tools, and the carriage moves along the bed, allowing the cutting tools to come into contact with the workpiece.
One of the key advantages of using a lathe machine is its ability to create complex shapes and contours. By using different cutting tools and adjusting the position of the workpiece, operators can create a wide range of shapes and sizes. This makes the lathe machine an essential tool in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and furniture manufacturing.
“The lathe machine has revolutionized the way we manufacture products. Its versatility and precision make it a valuable tool in the industry.”
Understanding the Basics of Lathe Machine
What is a Lathe Machine?
A lathe machine is a tool used in the machining industry to shape and cut various types of materials, such as wood, metal, and plastic. It is a versatile machine that can perform a variety of tasks, including turning, facing, drilling, knurling, and threading.
Parts of a Lathe Machine
A lathe machine consists of several key components:
- Bed: The bed is the foundation of the lathe machine and provides a rigid support for all the other parts.
- Headstock: The headstock is located at one end of the lathe machine and houses the main spindle. It is responsible for rotating the workpiece.
- Tailstock: The tailstock is located at the opposite end of the headstock and provides support to the other end of the workpiece. It can be moved along the bed to adjust the length of the workpiece.
- Carriage: The carriage is the part of the lathe machine that holds and moves the cutting tool. It can move along the bed and has various mechanisms for controlling the tool’s movement.
- Chuck: The chuck is a device mounted on the spindle that holds the workpiece securely in place.
- Tool Post: The tool post is located on the carriage and holds the cutting tool. It can be adjusted to achieve the desired cutting depth and angle.
- Feed Mechanism: The feed mechanism allows for the controlled movement of the carriage and cutting tool along the workpiece.
How Does a Lathe Machine Work?
A lathe machine works by rotating the workpiece against a fixed cutting tool. The cutting tool is held in the tool post, which can be adjusted to achieve the desired cutting depth and angle. As the workpiece rotates, the cutting tool removes material to shape or cut the workpiece. The movements of the carriage and tool post are controlled by various mechanisms, allowing for precise and accurate machining.
Types of Lathe Machines
There are several types of lathe machines, including:
- Bench Lathe: A small lathe machine mounted on a bench or table.
- Engine Lathe: A larger lathe machine used for machining heavy and long workpieces.
- Turret Lathe: A lathe machine with a rotating tool turret that allows for multiple cutting operations without the need for manual tool changes.
- CNC Lathe: A computer-controlled lathe machine that can perform complex operations with high precision and accuracy.
- Speed Lathe: A simple lathe machine designed for light-duty tasks and high-speed operations.
Applications of Lathe Machines
Lathe machines are used in various industries for a wide range of applications, including:
- Manufacturing of cylindrical or spherical objects, such as tubes, shafts, and screws.
- Turning and shaping of wood to create furniture, musical instruments, and other wooden products.
- Machining of metal parts for automotive, aerospace, and machinery industries.
- Fabrication of plastic components, such as bottles, containers, and fittings.
Conclusion
A lathe machine is a versatile tool used in the machining industry for shaping and cutting various types of materials. Understanding the basics of a lathe machine, including its parts, working principles, types, and applications, is essential for anyone involved in machining operations.
Common Applications of Lathe Machine
1. Metalworking
One of the most common applications of a lathe machine is in metalworking. With a lathe machine, operators can perform various metalworking tasks such as turning, facing, drilling, boring, grooving, threading, and more. The ability to shape and form metal parts accurately and efficiently makes the lathe machine indispensable in the manufacturing industry.
2. Woodworking

In addition to metalworking, lathe machines are also extensively used in woodworking. They are used to shape and carve wooden objects such as furniture legs, spindles, bowls, vases, and more. The lathe machine’s precision and versatility allow woodworkers to create intricate designs and achieve smooth finishes on their projects.
3. Glassworking
Lathe machines are also used in glassworking to create various glass objects and components. Glassblowers use lathe machines to shape molten glass into different forms such as vases, cups, and bottles. The rotating motion of the lathe machine allows the glassblower to work on the glass evenly and achieve precise shapes.
4. Prototyping
Lathe machines are widely used in prototyping applications, where engineers and designers create a physical model or a working prototype of a product. The lathe machine can accurately shape a wide range of materials, allowing designers to test and refine their designs before mass production.
5. Repair and Maintenance
Lathe machines are also used in repair and maintenance work. They allow operators to repair and fabricate damaged or worn-out parts, saving time and money compared to ordering new parts. Whether it’s repairing mechanical components or restoring antique objects, the lathe machine is a valuable tool in the repair and maintenance industry.
6. Education and Training
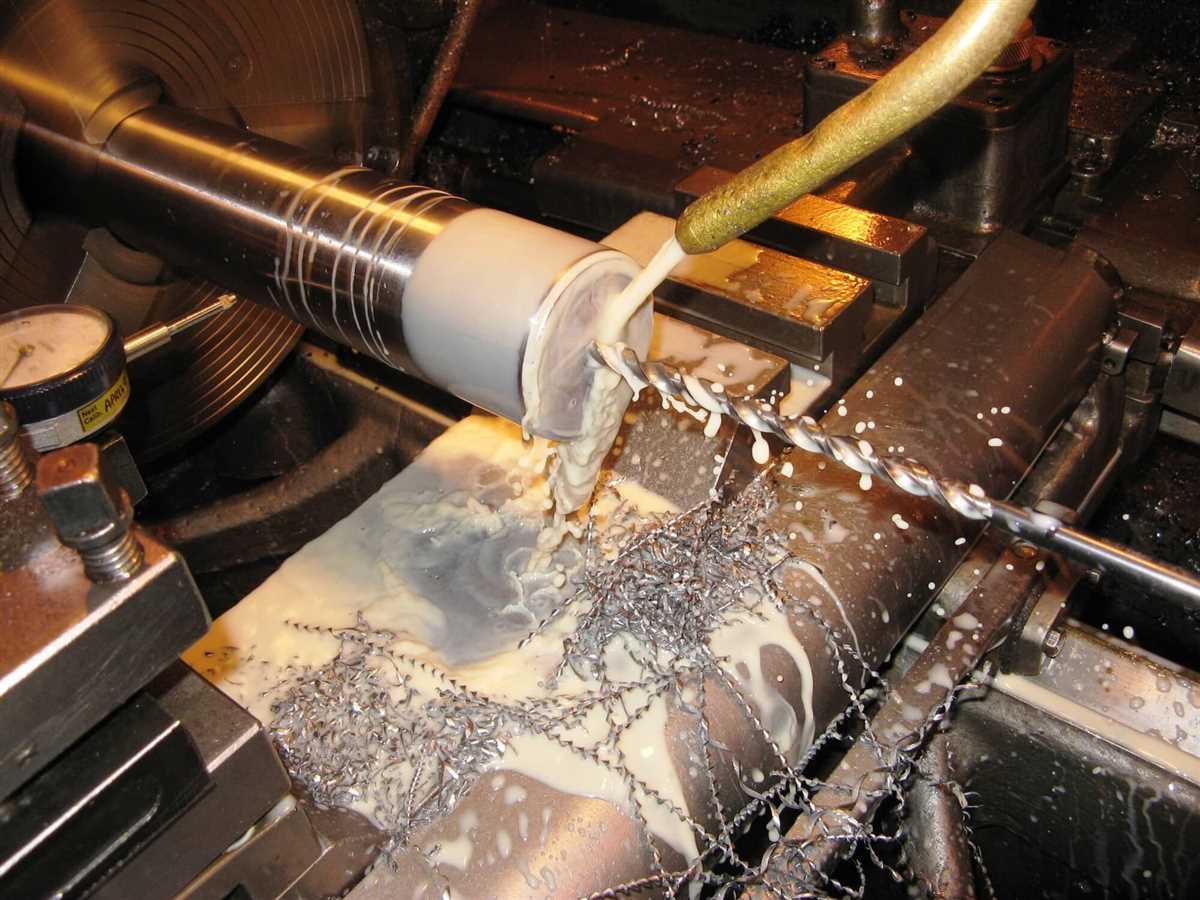

Lathe machines are extensively used in educational institutions and training centers to teach students the fundamentals of machining and metalworking. Students can learn how to operate a lathe machine, perform various operations, and gain hands-on experience in manufacturing processes. The lathe machine plays a vital role in training the next generation of machinists and engineers.
7. Jewelry Making
Lathe machines are also used in jewelry making to create intricate metal designs. Jewelers use the lathe machine to turn precious metals into rings, bracelets, pendants, and other jewelry items. The lathe machine’s precision and control allow jewelers to create precise and detailed designs that can be customized to meet the customer’s requirements.
8. Musical Instrument Making
Lathe machines are essential in the production of musical instruments. They are used to shape and fine-tune various components of instruments such as guitar necks, drums, and brass instruments. The lathe machine’s ability to create consistent and accurate shapes contributes to the quality and performance of musical instruments.
9. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry extensively uses lathe machines to fabricate and repair various engine and mechanical components. From turning brake rotors to machining engine cylinders, the lathe machine plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving vehicle performance and safety.
10. Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, lathe machines are used to manufacture critical components for aircraft and spacecraft. These machines are used to create precise and robust parts that meet the high standards and specifications of the aerospace industry. From turbine blades to engine components, the lathe machine’s accuracy and reliability are vital in aerospace manufacturing.
Types of Lathe Machines
A lathe machine is a versatile equipment used in various industrial applications. These machines are designed to perform different tasks and come in different types based on their characteristics and functionalities.
1. Engine Lathe
The engine lathe is the most common type of lathe machine used in workshops and industries. It is versatile and can perform a wide range of machining operations, such as turning, facing, drilling, and threading. This type of lathe machine is usually used for small to medium-sized workpieces.
2. Bench Lathe
Bench lathes are smaller in size compared to engine lathes and are commonly used in small workshops or for DIY projects. They are lightweight and portable, making them suitable for hobbyists and beginners. Bench lathes are ideal for smaller workpieces and are mainly used for tasks such as polishing, grinding, and drilling.
3. Speed Lathe
Speed lathes are designed to operate at high speeds and are mainly used for tasks such as polishing and light-duty work. They are lightweight, compact, and have a simple design. Speed lathes are ideal for small-sized workpieces and are commonly used in workshops, jewelry making, and watch repair.
4. Turret Lathe
Turret lathes are a type of lathe machine equipped with a turret, which holds multiple tools that can be easily indexed and selected for different machining operations. These machines are highly efficient and are used for mass production of identical workpieces. Turret lathes are mostly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
5. CNC Lathe
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathes are modern lathe machines that are controlled by a computer program. These machines offer high precision and automation, allowing for complex machining operations. CNC lathes are widely used in industries where precision and efficiency are crucial, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical.
6. Automatic Lathe
Automatic lathes are specialized machines that are capable of automatically feeding and ejecting workpieces. These machines are highly automated and can perform a wide range of machining operations without manual intervention. Automatic lathes are commonly used for mass production of small-sized components in industries such as electronics and watchmaking.
7. Vertical Lathe
Vertical lathes, also known as vertical turning lathes or VTLs, are used for machining large and heavy workpieces. These machines have a vertical spindle orientation and can perform tasks such as turning, drilling, milling, and grinding. Vertical lathes are commonly used in industries such as aerospace, power generation, and heavy machinery.
8. Special Purpose Lathe
Special purpose lathes are designed for specific machining tasks or industries. These lathes can be customized or modified to meet the specific requirements of the application. Examples of special purpose lathes include wheel lathes used for machining railway wheels and gap bed lathes used for machining long and large diameter workpieces.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are various types of lathe machines available, each designed for specific applications and machining operations. The choice of lathe machine depends on factors such as the size and complexity of the workpiece, required precision, and production volume. Understanding the different types of lathe machines can help in selecting the appropriate machine for a specific task or industry.
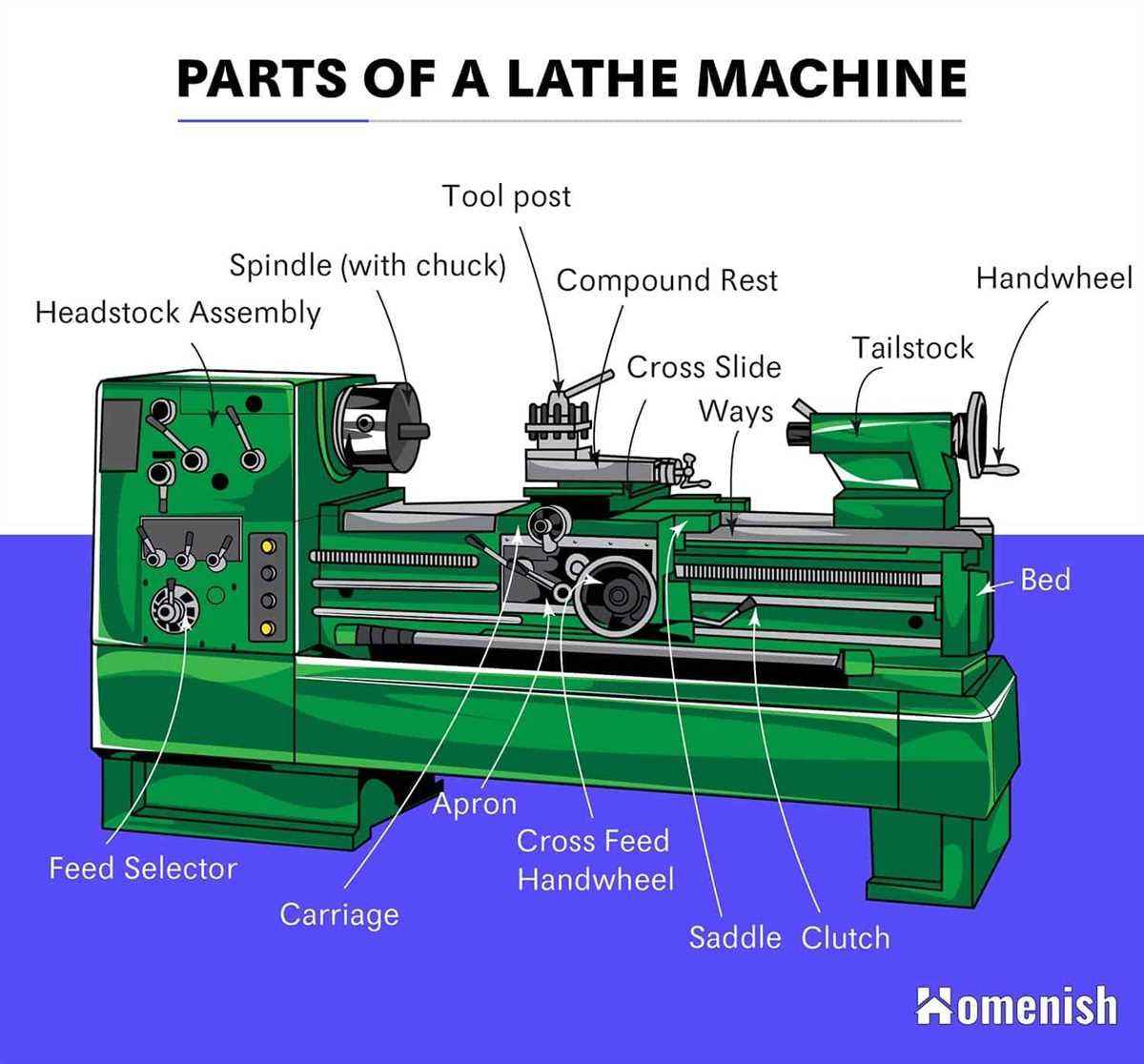
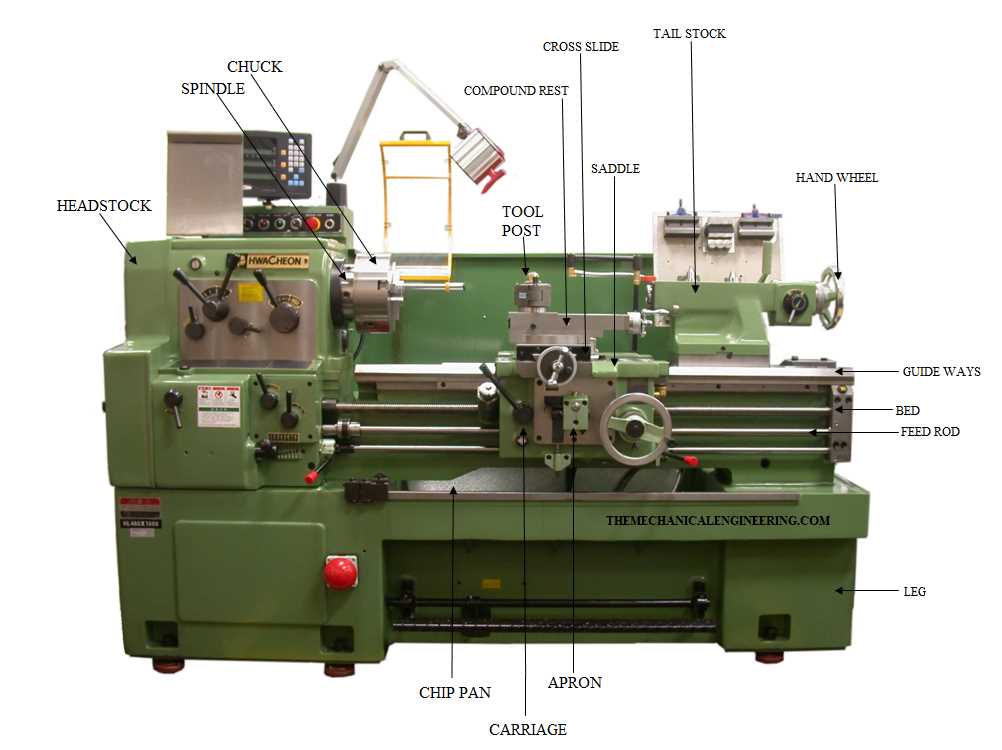
Components of a Lathe Machine
1. Bed
The bed is the main component of a lathe machine and provides a rigid and stable base for all other components. It is usually made of cast iron and supports the headstock, tailstock, and carriage.
2. Headstock
The headstock is located on the left side of the lathe machine and holds the main spindle. It contains the gears, pulleys, and other mechanisms to transmit power from the motor to the spindle. The headstock also houses the chuck, which is used to hold the workpiece.
3. Tailstock
The tailstock is located on the right side of the lathe machine, opposite the headstock. It can be moved along the bed using a handwheel and is used to support the opposite end of the workpiece. The tailstock may include a lever to lock it in position and a drill chuck for drilling operations.
4. Carriage
The carriage is mounted on the bed and can be moved along it using a handwheel or a powered feed mechanism. It consists of the saddle, cross-slide, and toolpost. The carriage is responsible for controlling the cutting tool and moving it across the workpiece.
5. Saddle
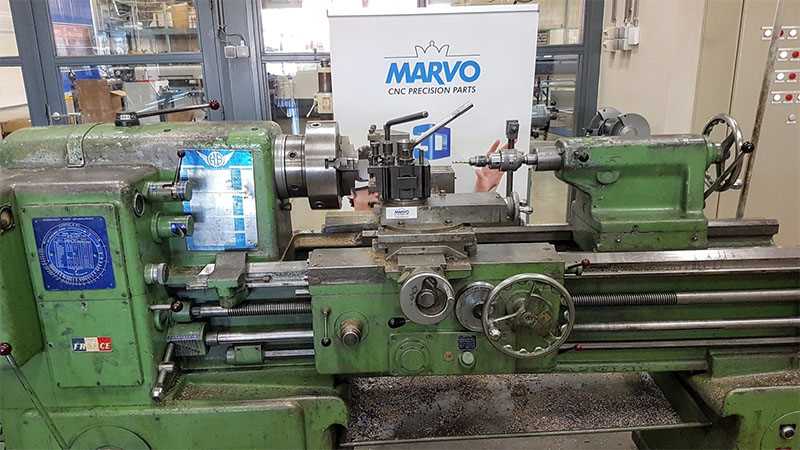

The saddle is the part of the carriage that holds the cross-slide and moves along the length of the bed. It can be locked in position to provide stability during machining operations.
6. Cross-Slide
The cross-slide is mounted on the saddle and can be moved perpendicular to the length of the bed. It holds the cutting tool and allows for precise control over its position relative to the workpiece.
7. Toolpost
The toolpost is mounted on the cross-slide and holds the cutting tool. It can be adjusted vertically and horizontally to position the tool at the desired height and angle.
8. Spindle
The spindle is the rotating component that holds and drives the workpiece. It is located in the headstock and can be controlled to rotate at different speeds.
9. Chuck
The chuck is attached to the spindle and used to hold the workpiece securely. It can be adjusted to accommodate different sizes and shapes of workpieces.
10. Apron
The apron is located below the carriage and contains various mechanisms for controlling the movement and feed of the carriage. It includes the feed rod, half-nuts, and feed mechanism.
11. Lead Screw
The lead screw is a long, threaded rod located inside the lathe bed. It is used in conjunction with the half-nuts and feed rod to control the longitudinal movement of the carriage and provide automatic feed.
12. Tailstock Quill
The tailstock quill is a movable component of the tailstock that can be extended or retracted to support different lengths of workpieces. It can be locked in position using a lever.
13. Controls and Accessories
In addition to the main components, a lathe machine may include various controls and accessories. This can include dials and levers for adjusting the speed and direction of rotation, coolant systems for lubrication and cooling, and additional tooling for specialized operations.
Conclusion
A lathe machine consists of several key components that work together to perform various machining operations. Understanding these components is essential for effectively operating and utilizing a lathe machine.
Working Principle of Lathe Machine
A lathe machine works on the principle of rotation. It rotates the workpiece against a cutting tool to remove material and shape the workpiece into the desired form. The workpiece is mounted on a spindle, and the cutting tool is positioned either by hand or by a computer-controlled system.
Step 1: Mounting the workpiece
The workpiece, which can be a metal or wood material, is mounted securely on the spindle of the lathe machine. The spindle rotates at a high speed, allowing the cutting tool to come into contact with the workpiece.
Step 2: Tool positioning
The cutting tool is positioned either manually by an operator or automatically by a computer-controlled system. The tool is adjusted according to the desired shape and size of the workpiece. The cutting tool can be moved horizontally, vertically, or at an angle to achieve different cuts and shapes.
Step 3: Rotation and cutting
Once the workpiece and cutting tool are properly positioned, the lathe machine is turned on, and the spindle starts to rotate. The cutting tool comes into contact with the rotating workpiece, removing material and shaping it. The cutting tool may move along the length of the workpiece or stay stationary while the workpiece rotates.
Step 4: Finishing and polishing

After the desired shape is achieved, the cutting tool is removed, and the workpiece is inspected. If necessary, additional finishing and polishing processes may be applied to improve the surface smoothness and remove any imperfections.
Overall, the working principle of a lathe machine involves the rotation of the workpiece and the controlled movement of the cutting tool to shape and form the workpiece into the desired shape and size.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Lathe Machine
Advantages:
- Versatility: Lathe machines are versatile tools that can be used for various machining operations such as turning, facing, boring, threading, and more. They can handle a wide range of materials including wood, metal, and plastic.
- Precision: Lathe machines are known for their high precision and accuracy. They can be used to create intricate and detailed designs with tight tolerances. This makes them suitable for applications that require precise machining.
- Efficiency: Lathe machines are efficient in terms of material removal and production rate. They can remove material quickly and effectively, making them ideal for high-volume production.
- Wide range of sizes: Lathe machines are available in various sizes, ranging from small benchtop models to large industrial ones. This allows users to choose the right machine for their specific needs and available space.
- Easy to operate: Lathe machines are relatively easy to operate, especially with modern advancements in technology. They can be manually operated or computer-controlled, depending on the complexity of the machining task.
Disadvantages:
- High cost: Lathe machines can be expensive, especially the larger and more advanced models. This can be a significant investment for small businesses or hobbyists.
- Requires skill and experience: While lathe machines are relatively easy to operate, they still require a certain level of skill and experience to achieve optimal results. Improper use can lead to costly mistakes or accidents.
- Space requirements: Lathe machines require a dedicated space in a workshop or factory. Their size and weight can make it challenging to accommodate them in small or crowded workspaces.
- Limited to cylindrical shapes: The main drawback of lathe machines is that they are primarily designed for machining cylindrical shapes. Other complex shapes may require additional equipment or different machining methods.
- Tooling and setup time: Changing the tooling or setting up a lathe machine for a different machining operation can be time-consuming. This can affect the overall productivity and efficiency of the machining process.
Tips for Using a Lathe Machine Safely
- Wear proper protective gear: Always wear safety goggles or a face shield to protect your eyes from flying debris. Additionally, wear ear protection and gloves to safeguard against loud noise and potential injuries.
- Secure the workpiece: Make sure the workpiece is securely clamped or held in place using a chuck or a faceplate. This will prevent the workpiece from moving or being thrown off the lathe during operation.
- Familiarize yourself with the machine: Before operating the lathe machine, read the user manual and understand the functions and controls. Be aware of the emergency stop button and ensure it is easily accessible.
- Check for damaged tools or accessories: Prior to using the lathe, inspect the tools, cutting bits, and accessories for any signs of damage. Replace any worn out or broken parts to prevent accidents or poor results.
- Maintain a clean work area: Keep your work area clean and free from clutter. Remove any chips or debris from the lathe bed, carriage, and tool rest to prevent accidents or interference with the machine’s operation.
- Avoid loose clothing or jewelry: Do not wear loose clothing, long sleeves, or dangling jewelry while operating the lathe machine. Loose clothing or jewelry can get caught in the rotating parts and cause serious injuries.
- Use the appropriate cutting tools: Select the right cutting tools and ensure they are properly sharpened and secured in the tool post. Dull or improperly secured tools can cause the workpiece to vibrate or result in poor cutting performance.
- Start with lower speeds: When starting a lathe machine, begin with lower speeds and gradually increase the speed as needed. This will help maintain control of the workpiece and reduce the risk of accidents.
- Never leave the machine unattended: Always stay close to the lathe machine while it is in operation. Never leave it unattended, even for a short period. Accidents can happen quickly, and immediate action may be required to prevent further damage or injuries.
- Learn proper cutting techniques: Take the time to learn and practice proper cutting techniques. This includes correct tool angles, feed rates, and depth of cut. Using improper techniques can result in poor cutting performance or damage to the machine.
By following these safety tips, you can help ensure a safe and enjoyable experience when using a lathe machine. Always prioritize your safety and take the necessary precautions to minimize the risk of accidents or injuries.
Maintenance and Care of Lathe Machine
Regular Cleaning

One of the most important aspects of maintaining a lathe machine is regular cleaning. Cleaning the machine helps to prevent the build-up of dust, debris, and metal shavings, which can affect the machine’s performance.
Use a brush or compressed air to remove the chips and dust from the machine’s surfaces, gears, and crevices. Make sure to clean the chuck, tool post, and tailstock as well.
Lubrication
Lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation of a lathe machine. Regularly lubricate the moving parts of the machine, including the headstock, tailstock, and carriage.
Use the recommended lubricants and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for lubrication. Make sure to clean the parts before applying lubricants to remove any dirt or debris that might be present.
Check and Adjust the Alignment
Regularly check the alignment of the lathe machine to ensure that it is functioning properly. Use a dial indicator to check the alignment of the tailstock, headstock, and carriage.
If any misalignment is detected, make the necessary adjustments to bring the machine back into alignment. This will help to prevent accidents and ensure accurate machining.
Inspect Belts and Pulleys
Inspect the belts and pulleys of the lathe machine for any signs of wear or damage. Replace any worn or damaged belts and adjust the tension of the belts if necessary.
Make sure that the pulleys are clean and properly aligned. Misaligned pulleys can cause unnecessary strain on the belts and affect the machine’s performance.
Keep the Workspace Clean
Maintaining a clean workspace is important for the overall care of the lathe machine. Remove any clutter or unnecessary items from the area around the machine.
Keep the floor swept and free from oil, coolant, or metal chips. This will help to prevent accidents and ensure that the machine operates in a safe and efficient manner.
Follow Safety Guidelines
Always follow the safety guidelines provided by the manufacturer when using and maintaining a lathe machine. Wear appropriate safety gear, such as safety glasses and gloves, to protect yourself from potential hazards.
Regularly inspect the machine for any safety issues and address them immediately. Familiarize yourself with emergency shutdown procedures in case of any unforeseen incidents.
Conclusion
Maintaining the lathe machine properly is essential for its longevity and optimal performance. Regular cleaning, lubrication, alignment checks, inspection of belts and pulleys, keeping the workspace clean, and following safety guidelines are crucial steps in the maintenance and care of a lathe machine.
FAQ
What is a lathe machine used for?
A lathe machine is used to shape wood, metal, or other materials by rotating them against a cutting tool. It is commonly used for turning, drilling, cutting, knurling, facing, and threading operations.
How does a lathe machine work?
A lathe machine works by rotating the workpiece on its axis, while a cutting tool is moved in various ways to shape the material. The movement of the cutting tool can be controlled manually or through automated systems.
What are the different types of lathe machines?
There are several types of lathe machines, including engine lathes, bench lathes, toolroom lathes, turret lathes, and CNC lathes. Each type is designed for specific applications and offers different features and capabilities.
What safety precautions should be taken when using a lathe machine?
When using a lathe machine, it is important to wear protective equipment such as safety glasses and gloves. The work area should be well-lit and free from clutter. The machine should be properly maintained and operated according to the manufacturer’s instructions. It is also important to be aware of the potential hazards and follow proper safety procedures.
Can a lathe machine be used for woodworking?
Yes, a lathe machine can be used for woodworking. It allows for the shaping and turning of wooden objects such as bowls, spindles, and furniture legs. However, it is important to use the appropriate cutting tools and techniques for woodworking projects.
Video











