Understanding the Process of Turning in a Lathe Machine

The process of turning in a lathe machine is a fundamental operation in the field of manufacturing. It involves removing material from a workpiece to give it the desired shape, size, and finish. This process is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and machining.
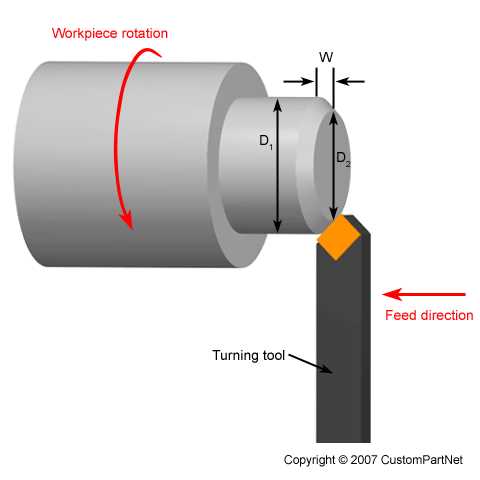
Turning is typically performed using a lathe machine, which consists of a rotating spindle that holds the workpiece and a cutting tool that is fed into the workpiece to remove material. The workpiece is rotated at a high speed while the cutting tool moves along the axis of the workpiece. This allows for precise control over the dimensions and surface finish of the final product.
During the turning process, the cutting tool makes contact with the workpiece, causing it to remove material in the form of chips. The cutting tool can be made from various materials, such as high-speed steel or carbide, depending on the requirements of the application. It is important to select the appropriate cutting tool for the specific material being turned to ensure optimal results.
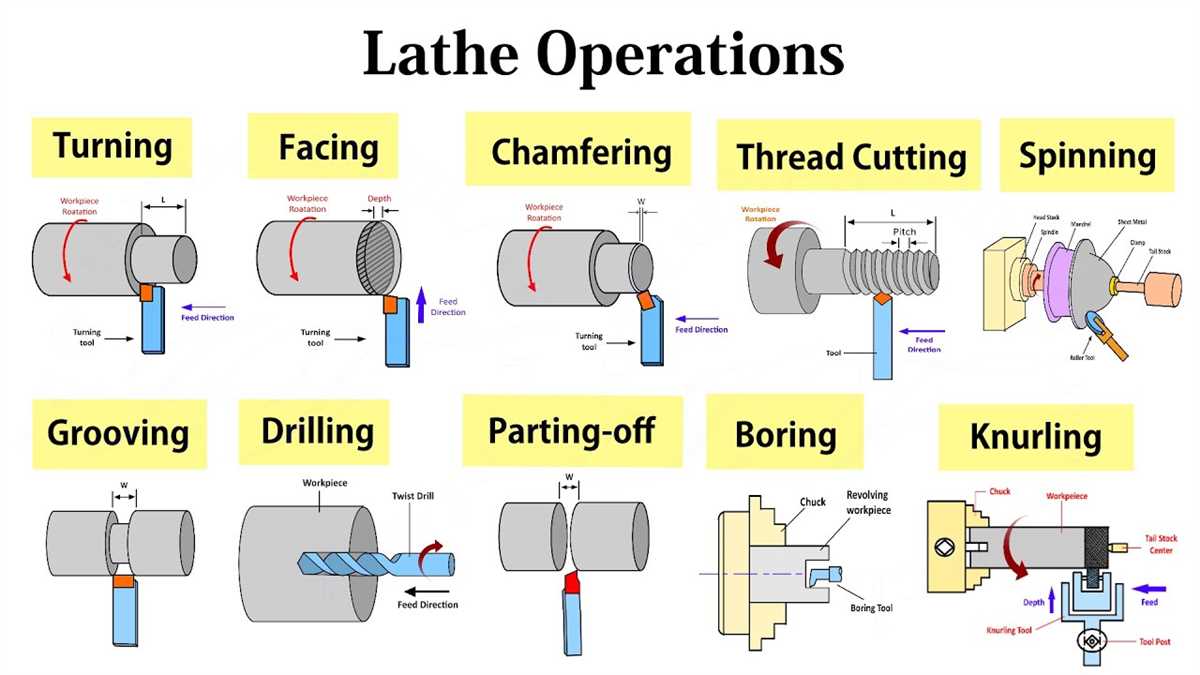
There are different types of turning operations that can be performed on a lathe machine, including facing, turning, grooving, and threading. Each operation requires a specific tool and technique to achieve the desired result. Additionally, the operator must have a good understanding of the machine and its controls to ensure safe and efficient operation.
In conclusion, turning in a lathe machine is a crucial process in the manufacturing industry. It allows for the creation of complex shapes and precise dimensions in a variety of materials. By understanding the process and selecting the appropriate tools, operators can produce high-quality parts that meet the requirements of their customers.
Basics of Lathe Machine
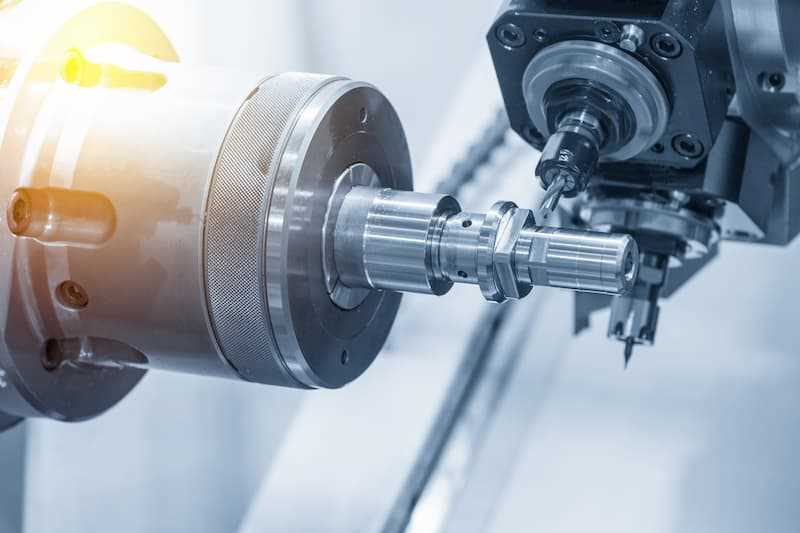

A lathe machine is a versatile tool used in various industries for shaping and machining different materials. It is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece on its axis to perform various operations such as cutting, drilling, facing, turning, and threading. Lathe machines can be both manually operated and computer-controlled (CNC).
Components of a Lathe Machine
A lathe machine consists of several main components:
- Bed: It is the base of the lathe machine on which all other components are mounted. It provides rigidity and stability to the machine.
- Headstock: It is located on one end of the bed and houses the main spindle. The spindle rotates the workpiece.
- Tailstock: It is located on the other end of the bed and supports the workpiece with a center. It can be adjusted for different lengths of workpieces.
- Toolpost: It holds various cutting tools that are used to shape and machine the workpiece.
- Carriage: It moves along the bed and holds the toolpost and cutting tools. It can be manually or automatically controlled.
- Feed Mechanism: It controls the movement of the carriage and the cutting tool along the workpiece.
- Chuck: It is used to hold and rotate the workpiece. Different types of chucks are available for different workpiece shapes and sizes.
- Spindle Motor: It provides the power to rotate the main spindle and the workpiece.
Types of Lathe Machines
There are several types of lathe machines available, each designed for specific applications:
- Engine Lathe: This is the most common type of lathe machine used for general-purpose machining.
- Gear Head Lathe: This type of lathe machine has a built-in gear mechanism for changing spindle speeds.
- Turret Lathe: It is a specialized lathe machine with a turret that holds multiple tools. It is used for high-volume production.
- CNC Lathe: These are lathe machines controlled by computer programs, allowing for precise and complex machining.
- Speed Lathe: This type of lathe machine operates at a high speed and is used for light-duty operations like polishing and sanding.
Applications of Lathe Machine
Lathe machines are widely used in various industries due to their versatility. Some common applications include:
- Turning and facing operations
- Drilling and boring holes
- Threading and tapping
- Cutting external and internal grooves
- Making cylindrical and conical shapes
- Surface finishing and polishing
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of lathe machines is essential for anyone working in the machining industry. With their wide range of applications and capabilities, lathe machines play a crucial role in shaping and machining various materials.
Types of Lathe Machines
There are various types of lathe machines available in the market, each designed for specific applications and requirements. Some of the common types of lathe machines include:
- Engine Lathe: This is the most common type of lathe machine and is used primarily for cylindrical turning. It features a horizontal bed and can handle a wide range of workpieces.
- Turret Lathe: Turret lathes are equipped with a turret tool post that holds multiple cutting tools. This allows for quick tool changes and reduces setup time, making turret lathes ideal for mass production.
- Gap Bed Lathe: Gap bed lathes have a removable section in the bed, which allows for the turning of larger diameter workpieces. The gap bed lathe is versatile and can handle both large and small jobs.
- Speed Lathe: Speed lathes are designed for high-speed turning operations. They are compact and often used for tasks such as polishing, grinding, and finishing workpieces.
- CNC Lathe: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) lathes are automated machines that use computer programming to control the cutting process. CNC lathes offer high precision and are suitable for complex and intricate work.
Each type of lathe machine has its own advantages and is suited for specific applications. The choice of lathe machine depends on factors such as the size and type of workpiece, production volume, and required precision.
It is important to understand the capabilities and limitations of each type of lathe machine before selecting the most suitable one for a specific machining task.
Components of a Lathe Machine
A lathe machine is a versatile tool used in various metalworking operations. It consists of several components that work together to perform turning operations.
1. Bed
The bed is the base of the lathe machine. It provides support and stability to all the other components. It is usually made of cast iron and has a flat and rigid surface. The bed is designed to absorb vibrations and ensure accurate machining.
2. Headstock
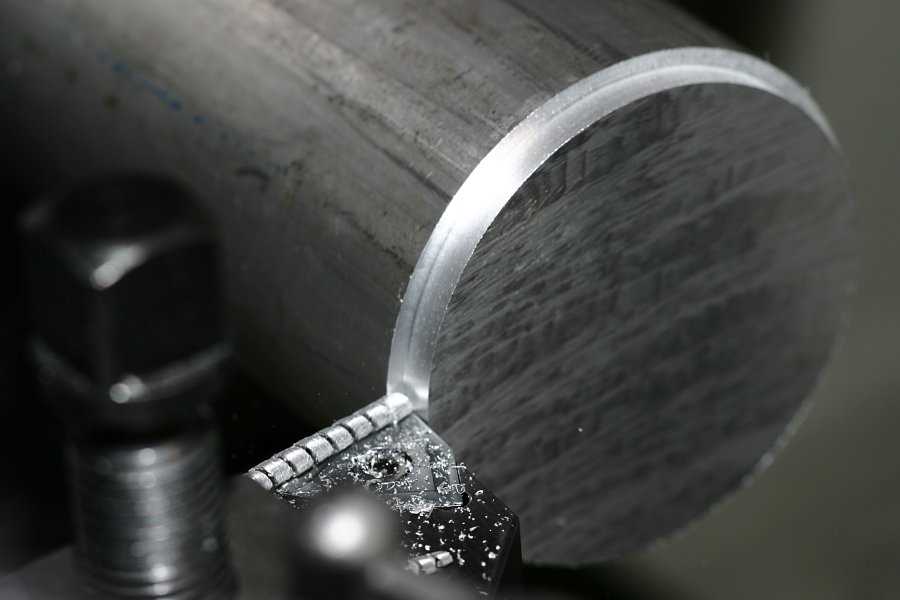

The headstock is located at one end of the lathe machine’s bed. It supports the main spindle, which holds the workpiece and rotates it during machining. The headstock also houses various gears and mechanisms for controlling the speed and direction of rotation.
3. Tailstock
The tailstock is located at the opposite end of the lathe machine’s bed. It provides support to the other end of the workpiece and can be moved along the bed to adjust the length of the workpiece. The tailstock also contains a spindle that can be extended or retracted to hold the workpiece firmly.
4. Carriage
The carriage is the component that moves along the bed in a longitudinal direction. It consists of several parts, including the saddle, cross-slide, and compound rest. The carriage holds the cutting tool and controls its movement, allowing precise cutting and shaping of the workpiece.
5. Chuck
A chuck is a device used to hold the workpiece securely in place during machining. It is mounted on the spindle in the headstock and can be adjusted to accommodate different sizes and shapes of workpieces. Chucks can be either three-jaw or four-jaw, depending on the requirements of the operation.
6. Tool Post
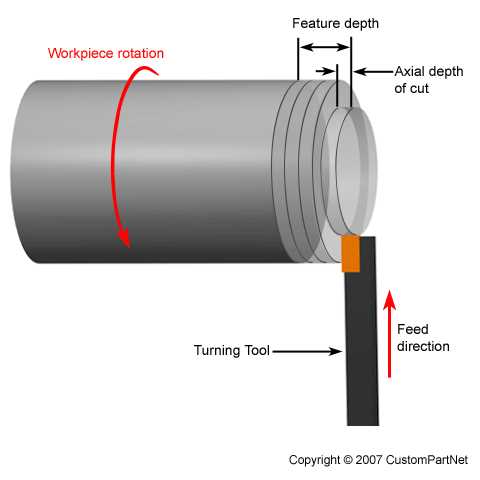
The tool post is a component mounted on the carriage that holds the cutting tool. It allows for quick and easy interchangeability of cutting tools, enabling different machining operations to be performed without the need for extensive reconfiguration.
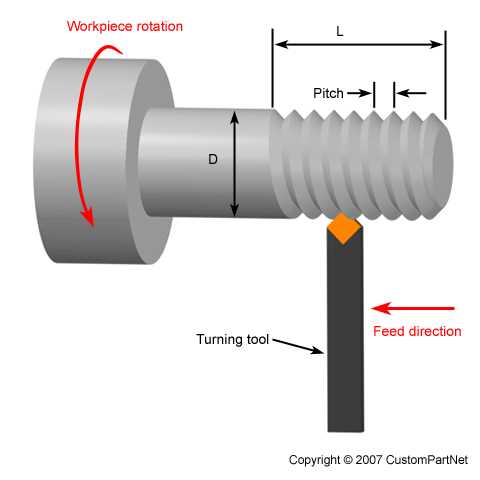
7. Apron
The apron is a component located on the front of the carriage. It houses various controls and mechanisms for controlling the movement of the carriage and the cutting tools. The apron also contains the feed and threading mechanisms, allowing for automatic feed rates and thread cutting.
8. Feed and Lead Screw
The feed and lead screw are components responsible for controlling the movement of the carriage and the cutting tool. The feed screw moves the carriage along the bed, while the lead screw controls the longitudinal movement of the cutting tool. These screws are typically powered by gears and can be adjusted to achieve different feed rates and thread pitches.
9. Electrical Control Panel
The electrical control panel contains the switches, knobs, and buttons used to control and operate the lathe machine. It houses the main power switch, motor controls, speed controls, and various safety features. The control panel allows the operator to set and adjust the parameters of the machining operation.
10. Motor
The motor is the power source of the lathe machine. It provides the rotational power needed for the spindle, feed and lead screws, and other moving parts. The motor is typically located inside the headstock and can be powered by electricity or other energy sources.
In conclusion, a lathe machine consists of various components that work together to perform turning operations. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate and efficient machining. Understanding the function and interaction of these components is essential for successfully operating a lathe machine.
Turning Process in a Lathe Machine
Introduction
In the manufacturing and machining industries, the process of turning is a fundamental operation that involves the removal of material from a workpiece to produce a cylindrical shape. This operation is typically performed using a lathe machine, which is a versatile and widely used tool in the industry.
The Lathe Machine
A lathe machine consists of several key components, including the bed, headstock, tailstock, carriage, and tool post. The workpiece is mounted on the spindle, which is driven by the motor in the headstock. The tool post holds the cutting tool, which is used to remove material from the workpiece.
The Turning Process
The turning process involves several steps, which are as follows:
- Workpiece Setup: The workpiece is securely mounted on the spindle using appropriate chucks or fixtures.
- Tool Selection: The cutting tool is selected based on the desired shape, material of the workpiece, and the desired surface finish.
- Speed and Feed Rate Selection: The appropriate speed and feed rate are determined based on the material being turned and the desired cutting conditions.
- Tool Positioning: The tool post is adjusted to position the cutting tool at the desired depth and angle relative to the workpiece.
- Cutting Operation: The lathe machine is started, and the cutting tool is brought into contact with the rotating workpiece. The tool is then fed into the workpiece to remove material and create the desired shape.
- Finishing: Once the desired shape is achieved, finishing operations such as chamfering, grooving, or thread cutting may be performed.
- Checking and Quality Control: The workpiece is inspected to ensure it meets the required specifications and quality standards.
- Workpiece Removal: After the turning process is complete, the workpiece is removed from the lathe machine.
Advantages of Turning
The turning process offers several advantages, including:
- Versatility: The lathe machine can be used to turn a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood.
- High Precision: The turning process allows for precise control over the shape and dimensions of the workpiece.
- Efficiency: Turning is a relatively fast and efficient process for removing material and creating cylindrical shapes.
- Cost-Effective: The use of lathe machines for turning is cost-effective, as it requires less manual labor compared to other machining processes.
Conclusion
The turning process in a lathe machine is a fundamental operation in the manufacturing and machining industries. It allows for the efficient and precise removal of material to create cylindrical shapes. With its versatility and cost-effectiveness, the lathe machine is a valuable tool in various industries.
Safety Measures for Lathe Machine Operation
1. Wear proper protective gear
Before operating a lathe machine, it is important to wear the appropriate protective gear to ensure your safety. This includes wearing safety glasses or goggles to protect your eyes from flying debris. Additionally, you should wear earplugs or earmuffs to protect your hearing from the loud noise produced by the machine. It is also important to wear gloves to protect your hands from sharp tools or hot materials.
2. Familiarize yourself with the machine
Prior to operating a lathe machine, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with its components and controls. Read the machine’s manual or receive proper training to understand how to operate the machine safely and effectively. Make sure you know how to start and stop the machine, change speeds, and adjust the cutting tools.
3. Keep the work area clean and organized
Maintaining a clean and organized work area is essential for safe lathe machine operation. Ensure that the area around the machine is clear of any clutter, tools, or debris that may interfere with the machine’s operation. Remove any unnecessary items from the lathe bed or carriage to avoid accidents or damage.
4. Secure the workpiece properly
When working with a lathe machine, it is important to secure the workpiece properly to prevent it from moving or becoming dislodged during operation. Use appropriate clamps, vices, or chucks to securely hold the workpiece in place. This will help ensure stability and reduce the risk of accidents or injuries.
5. Use cutting tools with caution
When using cutting tools on a lathe machine, it is crucial to use them with caution. Make sure the cutting tools are sharp and in good condition to ensure a safe and efficient cutting process. Avoid excessive force when operating the machine and take the necessary precautions to prevent any potential hazards.
6. Monitor the machine and process
During lathe machine operation, it is important to constantly monitor both the machine and the cutting process. Keep an eye on any unusual sounds or vibrations that may indicate a problem with the machine. Regularly inspect the cutting tools for any signs of wear or damage. If any issues are detected, stop the machine and address them before continuing.
7. Follow proper maintenance and servicing procedures
To ensure the safe and efficient operation of a lathe machine, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance and servicing procedures. Regularly clean and lubricate the machine to keep it in good working condition. Additionally, schedule regular inspections and servicing to catch any potential problems before they escalate.
8. Never leave the machine unattended
Leaving a lathe machine unattended is extremely dangerous and can lead to accidents or damage. Whenever the machine is in operation, always stay by its side and maintain full attention. In the event that you need to leave the machine momentarily, either turn it off or assign another trusted person to monitor it until you return.
9. Seek proper training and supervision
If you are new to operating a lathe machine or are unfamiliar with its operation, it is important to seek proper training and supervision from an experienced operator. Having someone with knowledge and experience by your side can greatly reduce the risk of accidents and help you learn the proper techniques and safety measures.
10. Know how to react in case of emergency
Even with all the necessary precautions in place, emergencies can still occur. Therefore, it is important to know how to react in case of an emergency while operating a lathe machine. Familiarize yourself with the location of emergency shut-off switches and ensure they are easily accessible. Additionally, have a clear plan for what to do in the event of an injury or machine malfunction.
By following these safety measures, you can minimize the risk of accidents and ensure a safe and efficient operation of a lathe machine.
Importance of Lubrication in Lathe Machines
In a lathe machine, lubrication plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation and prolonging the lifespan of the equipment. Proper lubrication helps in reducing friction between moving parts, preventing wear and tear, and enhancing overall performance.
Benefits of lubrication:
- Friction reduction: Lubricating the moving parts of a lathe machine helps in reducing friction and heat generated during the machining process. This prevents the parts from getting damaged due to excessive heat and friction.
- Preventing wear and tear: Lubrication creates a protective barrier between the moving components, preventing them from rubbing against each other and causing wear and tear. This improves the lifespan of the machine and its components, reducing the need for frequent repairs and replacements.
- Smooth operation: Proper lubrication ensures smooth and uninterrupted movement of the components in a lathe machine. This results in precise machining and better quality output.
- Noise reduction: Lubrication helps in reducing the noise produced during lathe machine operation. The film of lubricating oil absorbs the vibrations and minimizes the noise, creating a quieter working environment.
- Protection against corrosion: Lubricants provide a protective coating on the metal surfaces, preventing them from rusting or corroding due to exposure to moisture or contaminants present in the environment. This helps in maintaining the integrity of the machine and its components.
Types of lubricants:
There are different types of lubricants used in lathe machines, such as:
- Oil-based lubricants: These lubricants are commonly used in lathe machines. They come in various grades and viscosities, depending on the specific requirements of the machine and its components.
- Greases: Greases are semi-solid lubricants that provide long-lasting lubrication. They are suitable for applications where frequent re-lubrication is not possible or practical.
- Cutting fluids: Cutting fluids are used during the machining process to lubricate and cool the cutting tool and workpiece. They help in reducing friction, heat, and tool wear, resulting in improved efficiency and surface finish.
Lubrication schedule:
It is important to follow a regular lubrication schedule for a lathe machine to ensure optimal performance. The manufacturer’s guidelines should be followed regarding the type of lubricant, quantity, and frequency of lubrication. Over-lubrication or under-lubrication can lead to problems like excess oil buildup, poor lubrication, or component damage.
| Lubrication point | Lubricant type | Lubrication frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Headstock bearings | Oil | Weekly |
| Carriage and tailstock movement | Grease | Monthly |
| Lead screw | Oil | Monthly |
| Tool turret | Grease | Quarterly |
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of a lathe machine. Regular maintenance and lubrication help in preventing breakdowns, extending the lifespan of the machine, and ensuring high-quality machining results.
Common Issues in Lathe Machine Turning
1. Vibration
Vibration is a common issue in lathe machine turning and can occur due to various reasons. Excessive vibration can affect the accuracy and quality of the turned parts. The main causes of vibration in lathe machine turning include:
- Imbalanced workpiece
- Incorrect cutting tool setup
- Loose or worn-out machine components
- Improper machine alignment
To reduce vibration, it is important to properly balance the workpiece, ensure correct tool setup, regularly maintain and tighten machine components, and align the machine accurately.
2. Poor Surface Finish
Poor surface finish is another common issue faced in lathe machine turning. The surface finish of the turned parts may be affected by factors such as:
- Incorrect cutting speed
- Improper tool selection or geometry
- Excessive feed rate
- Worn-out cutting tool
To achieve a better surface finish, it is important to select the correct cutting speed, choose appropriate cutting tools with the right geometry, control the feed rate properly, and replace worn-out cutting tools.
3. Chatter
Chatter refers to the unwanted vibrations that occur during lathe machine turning. It can cause poor surface finish, dimensional inaccuracies, and tool wear. Some common causes of chatter in lathe machine turning include:
- Insufficient workpiece rigidity
- Excessive cutting speed or feed rate
- Poor machine condition or alignment
- Inadequate tool overhang
To eliminate chatter, it is important to ensure proper workpiece rigidity, adjust the cutting speed and feed rate appropriately, maintain the machine in good condition, and minimize the tool overhang.
4. Dimensional Inaccuracies
Dimensional inaccuracies can occur during lathe machine turning and can be caused by various factors, including:
- Thermal expansion of the workpiece
- Inaccurate machine setup or alignment
- Poor tool geometry
- Inadequate cutting tool rigidity
To achieve dimensional accuracy, it is important to consider the thermal expansion of the workpiece, properly set up and align the machine, choose cutting tools with suitable geometry, and ensure the cutting tool has sufficient rigidity.
5. Tool Breakage
Tool breakage can occur during lathe machine turning, leading to unexpected downtime and increased costs. Some common causes of tool breakage include:
- Inappropriate cutting tool material or geometry
- Excessive cutting forces
- Improper cutting parameters
- Tool wear or damage
To prevent tool breakage, it is important to select the right cutting tool material and geometry for the workpiece material, control the cutting forces within acceptable limits, choose appropriate cutting parameters, and regularly inspect and replace worn-out or damaged cutting tools.
| Issue | Main Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration | Imbalanced workpiece, incorrect cutting tool setup, loose or worn-out machine components, improper machine alignment | Properly balance the workpiece, ensure correct tool setup, regularly maintain and tighten machine components, align the machine accurately |
| Poor Surface Finish | Incorrect cutting speed, improper tool selection or geometry, excessive feed rate, worn-out cutting tool | Select the correct cutting speed, choose appropriate cutting tools with the right geometry, control the feed rate properly, replace worn-out cutting tools |
| Chatter | Insufficient workpiece rigidity, excessive cutting speed or feed rate, poor machine condition or alignment, inadequate tool overhang | Ensure proper workpiece rigidity, adjust cutting speed and feed rate appropriately, maintain the machine in good condition, minimize tool overhang |
| Dimensional Inaccuracies | Thermal expansion of the workpiece, inaccurate machine setup or alignment, poor tool geometry, inadequate cutting tool rigidity | Consider thermal expansion of the workpiece, properly set up and align the machine, choose cutting tools with suitable geometry, ensure cutting tool has sufficient rigidity |
| Tool Breakage | Inappropriate cutting tool material or geometry, excessive cutting forces, improper cutting parameters, tool wear or damage | Select right cutting tool material and geometry, control cutting forces within acceptable limits, choose appropriate cutting parameters, regularly inspect and replace worn-out or damaged cutting tools |
Tips for Effective Turning in a Lathe Machine
1. Choose the Right Tool
One of the most important factors in achieving effective turning in a lathe machine is choosing the right tool for the job. Different materials and cuts require different types of tools, so it’s important to have a variety of cutting tools on hand. Make sure to match the tool geometry to the specific material and cut you are working with.
2. Use Proper Cutting Speeds and Feeds
When turning on a lathe machine, it’s crucial to use the proper cutting speeds and feeds. Cutting speeds that are too high can cause the tool to wear out quickly, while cutting speeds that are too low can result in poor surface finish. Similarly, feeds that are too high can cause tool breakage, while feeds that are too low can result in inefficient cutting. Refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations or machining data to determine the appropriate cutting speeds and feeds for your specific application.
3. Secure the Workpiece Properly
Properly securing the workpiece is essential for effective turning in a lathe machine. Make sure to use appropriate clamps or fixtures to ensure that the workpiece is securely held in place during the turning process. This will help prevent any movement or vibrations that can negatively affect the quality of the finished product.
4. Pay Attention to Tool Geometry
The tool geometry plays a crucial role in achieving effective turning results. Ensure that the cutting edge of the tool is sharp and properly aligned. Check the tool regularly to ensure that it is not chipped or worn out, as this can affect the cutting performance. Also, make sure that the tool is properly positioned and angled to achieve the desired cutting action.
5. Use Coolant for Heat Control
When turning in a lathe machine, heat can be generated due to the cutting action. Excessive heat can lead to tool wear, poor surface finish, and other issues. To control heat, it’s important to use coolant. Coolant helps dissipate heat and lubricates the cutting process, resulting in better cutting performance and longer tool life. Use the appropriate coolant for the material being machined and ensure it is applied correctly.
6. Take Light Cuts
When turning in a lathe machine, it’s generally recommended to take light cuts rather than heavy cuts. Light cuts put less stress on the tool and machine, resulting in better surface finish and longer tool life. Heavy cuts, on the other hand, can lead to chatter, tool breakage, and poor surface finish. Gradually increase the depth of cut to achieve the desired dimensions without compromising the quality of the turning process.
7. Maintain a Clean Work Area
A clean work area is essential for effective turning in a lathe machine. Remove any chips or debris from the work area and check for any potential interferences that may affect the turning process. Keeping a clean work area not only enhances safety but also ensures optimal cutting conditions and improved overall efficiency.
8. Practice Good Machining Techniques
Finally, practicing good machining techniques is key to achieving effective turning results. This includes maintaining proper tool control, watching for any signs of tool wear or damage, and regularly inspecting the workpiece. Additionally, properly monitoring the cutting process and making any necessary adjustments will help optimize the turning operation and produce high-quality turned parts.
By following these tips, you can improve the effectiveness of turning in a lathe machine and achieve superior machining results.
FAQ
Why is turning an important process in a lathe machine?
Turning is an important process in a lathe machine because it allows the creation of cylindrical parts with a high degree of precision. This process is used in various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace, to produce parts such as shafts, gears, and bearings.
What is the purpose of a lathe machine?
The main purpose of a lathe machine is to create symmetrical cylindrical parts by rotating a workpiece against a cutting tool. It is used to perform various operations such as turning, drilling, and threading. The lathe machine is a versatile tool that can be used in a wide range of applications.
How does a lathe machine work?
A lathe machine works by rotating a workpiece on its axis and feeding a cutting tool into the workpiece to remove material and shape it. The workpiece is securely held in a chuck or a collet, and the cutting tool is mounted on a toolpost that can be moved along multiple axes to achieve the desired shape and dimensions.
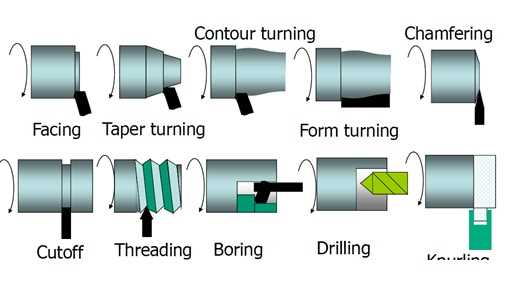
What are the different types of turning operations in a lathe machine?
There are several types of turning operations that can be performed on a lathe machine. These include facing, which is the process of removing material from the end of a workpiece to create a flat surface; taper turning, which involves creating a conical shape on a workpiece; and chamfering, which is the process of creating a beveled edge on a workpiece.
What are the advantages of using a lathe machine for turning?
Using a lathe machine for turning offers several advantages. Firstly, it allows for the creation of precise and symmetrical cylindrical parts. Secondly, it can be used to produce complex shapes and contours. Additionally, the process is efficient and can be automated, leading to increased productivity. Finally, the lathe machine is a versatile tool that can be used for various operations apart from turning.
Video











