Trepanation: What is it and why do people do it?

Trepanation is the practice of creating a hole in the skull by removing a small portion of bone. This ancient surgical technique has been documented in various cultures throughout history. The word “trepanation” comes from the Greek word “trepanon,” which means “a boring tool.”
There are several reasons why people have practiced trepanation throughout the ages. In some cases, it was believed to be a medical procedure used to treat certain conditions, such as headaches, mental disorders, and epilepsy. Others saw it as a religious or spiritual practice, believing that it could open a connection to the divine or release trapped spirits.
Trepanation has also been used as a form of self-experimentation or personal exploration. Some individuals who undergo trepanation claim that it can enhance brain function, increase creativity, or provide a greater sense of clarity. They believe that drilling a hole in the skull improves blood flow and allows for better oxygenation of the brain.
However, it’s important to note that trepanation is a controversial procedure and is not supported by modern medical science. The risks involved with trepanation are significant, including infection, hemorrhage, and damage to the brain or surrounding tissues. Additionally, there is no scientific evidence to support the claims of enhanced brain function or spiritual experiences associated with trepanation.
Despite these risks and lack of scientific validation, trepanation continues to be practiced by a small number of individuals today. It remains a topic of fascination and debate within medical, historical, and anthropological circles.
Understanding Trepanation
Trepanation, also known as trephination, is a surgical procedure that involves creating a hole in the skull for medical or cultural reasons. It is one of the oldest known surgical procedures, with evidence of trepanned skulls dating back thousands of years.
History of Trepanation

Trepanation has been practiced by various ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians, Greeks, Incas, and Mayans. The reasons for performing trepanation varied from medical treatment of head injuries and neurological disorders to religious and mystical beliefs.
Early trepanation procedures were performed using crude tools such as sharp stones, obsidian blades, and later, metal instruments. The procedure involved drilling or scraping a hole in the skull, usually over an area of trauma or pain.
Reasons for Trepanation
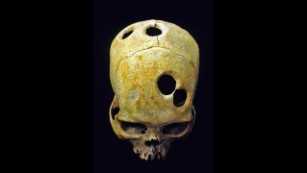
There are several reasons why people have historically practiced trepanation:
- Medical Purposes: Trepanation was used to treat head injuries, skull fractures, and conditions such as epilepsy and migraines. The hole in the skull was believed to relieve pressure, drain fluids, and allow evil spirits or demons to escape.
- Religious and Ritualistic Purposes: Some cultures believed that trepanation opened a connection to the gods or spiritual realm. They performed the procedure as a religious or ritualistic act to achieve enlightenment, enhance spiritual abilities, or release negative energy.
- Cultural Practices: Trepanation was part of cultural practices in certain societies, where it symbolized social status or initiation into adulthood.
Trepanation Techniques
Over time, trepanation techniques have evolved to become more sophisticated and less invasive.
Modern trepanation is typically performed using specialized surgical tools and techniques, ensuring the highest level of safety and effectiveness.
| Tools used in modern trepanation | Techniques used in modern trepanation |
|---|---|
| Drills and saws specifically designed for cranial surgery | Computer-guided surgical planning and navigation systems |
| Electrocautery devices to control bleeding | Minimally invasive approaches, such as burr hole trepanation |
Ethical Considerations
Trepanation is a controversial and debated practice, with concerns raised about its safety, efficacy, and cultural appropriateness. It is important to ensure that trepanation is performed by qualified medical professionals in a regulated clinical setting to minimize risks and adhere to ethical standards.
Individuals considering trepanation should consult with their healthcare providers and carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks before undergoing the procedure.
While trepanation continues to be a topic of interest and fascination, it remains a practice with historical significance and ongoing debate in the medical and cultural realms.
The Definition and History
The Definition:
Trepanation is the process of drilling or cutting a hole into the skull, usually with the intention of exposing the brain. This procedure is one of the oldest known surgical interventions in human history and has been practiced for various reasons, including medical, religious, and cultural purposes.
The History:
The origins of trepanation can be traced back thousands of years to various ancient civilizations, including ancient Egypt, ancient China, ancient Greece, and ancient America. The earliest evidence of trepanation dates back to the Neolithic period, around 10,000 BCE.
Historical records indicate that trepanation was performed for different reasons across different cultures. In ancient Egypt, for example, trepanation was often carried out as a medical procedure to alleviate head injuries or relieve intracranial pressure caused by diseases. In ancient Greece, trepanation was also practiced for medical purposes, but it was also associated with religious rituals and beliefs.
Throughout history, trepanation has been surrounded by various myths, superstitions, and cultural beliefs. In some cultures, trepanation was believed to possess mystical or magical powers, such as the ability to release evil spirits or enhance spiritual enlightenment. In others, it was considered a form of punishment or a means of proving one’s bravery.
Despite its ancient roots, trepanation continued to be practiced into modern times. During the Renaissance, for example, trepanation was still performed by some surgeons as a legitimate medical treatment for conditions such as epilepsy and mental illnesses.
Today, trepanation is considered an obsolete and highly risky procedure, with little to no medical or scientific basis. It is largely abandoned in favor of more advanced and safer surgical techniques. However, there are still rare cases of individuals who pursue trepanation for non-medical reasons, such as personal exploration or aesthetic purposes.
| Period | Significant Developments |
|---|---|
| Neolithic Period (10,000 BCE) | Earliest evidence of trepanation |
| Ancient Egypt | Medical and religious use of trepanation |
| Ancient Greece | Trepanation associated with medicine and religious rituals |
| Renaissance | Continued practice of trepanation for medical purposes |
| Modern Times | Trepanation abandoned as a medical procedure due to lack of scientific basis |
The Medical Procedure
Trepanation, also known as trephination or trephining, is a medical procedure that involves drilling or scraping a hole in the skull. This procedure has been practiced for thousands of years across various cultures and time periods.
Historical Background:
Trepanation can be traced back to ancient times, with evidence of the procedure found in prehistoric skulls. It is believed that trepanation was performed for various reasons, including as a treatment for head injuries, diseases, and mental disorders. In some cultures, it was also believed to release evil spirits or to enhance spiritual experiences.
The Procedure:
The trepanation procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The patient is positioned and prepared for the procedure. This may involve shaving the area of the scalp where the hole will be made and cleaning the area.
- Anesthesia: Depending on the circumstances, local or general anesthesia may be administered to ensure the patient’s comfort during the procedure.
- Incision: A small incision is made in the scalp to expose the skull, which is then carefully cleaned and sterilized.
- Bone Removal: Using a trepanning tool, such as a trephine or a hand drill, a hole is created in the skull. The size and location of the hole may vary depending on the reason for the procedure.
- Closure: Once the desired result is achieved, the surgeon may close the incision with sutures or leave it open to allow for drainage.
Modern Use:
In modern medicine, trepanation is rarely performed as it is considered an invasive and potentially dangerous procedure. Instead, alternative treatment options are available for conditions that were traditionally treated with trepanation.
Continued Interest:
Despite its decline in medical practice, trepanation continues to generate curiosity and interest among certain individuals. Some proponents believe that trepanation can increase blood flow and oxygen supply to the brain, leading to improved mental health and consciousness. However, these claims lack scientific evidence and have not been widely accepted by the medical community.
Ethical Considerations:
The practice of trepanation raises ethical concerns due to the potential risks involved in the procedure. It is crucial to prioritize patient safety and well-being when considering any medical intervention.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Reasons for Trepanation
1. Medical reasons
Trepanation can be performed for medical reasons, especially in cases where there is pressure or damage to the brain. By creating a hole in the skull, doctors can relieve intracranial pressure, remove blood clots or tumors, and treat certain neurological conditions.
2. Religious or spiritual beliefs
Some individuals choose to undergo trepanation due to their religious or spiritual beliefs. They believe that by opening the skull, they can achieve a higher state of consciousness, improve brain function, or unlock hidden potential. These beliefs are often rooted in ancient rituals and cultural practices.
3. Alternative therapy
Trepanation is also sometimes used as an alternative therapy or self-help technique. Proponents claim that it can alleviate chronic pain, improve mental health, enhance creativity, or increase energy levels. However, there is limited scientific evidence to support these claims, and trepanation is not recognized as a legitimate medical treatment.
4. Experimental purposes
In certain cases, trepanation may be performed for experimental purposes. Researchers might study the effects of trepanation on brain function, consciousness, or pain perception. These studies are often conducted in a controlled and ethical manner, involving consenting individuals and rigorous scientific methods.
5. Cultural practices and rituals
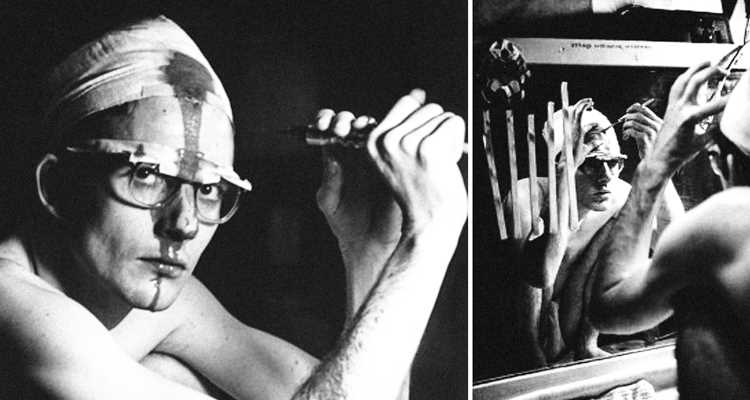

Historical evidence suggests that trepanation has been used for cultural and religious practices in various societies throughout history. It may have been performed as part of initiation rituals, healing ceremonies, or spiritual practices. These practices often have deep cultural significance and vary across different regions and time periods.
Please note that trepanation is a controversial practice and should only be performed by qualified medical professionals for legitimate medical reasons. Seeking professional advice and conducting thorough research is crucial before considering trepanation.
Exploring Ancient Beliefs
Throughout history, various cultures and civilizations have held different beliefs and practices related to trepanation. This ancient surgical procedure involved drilling or scraping a hole into the skull, often for medical or spiritual purposes.
Medical Beliefs
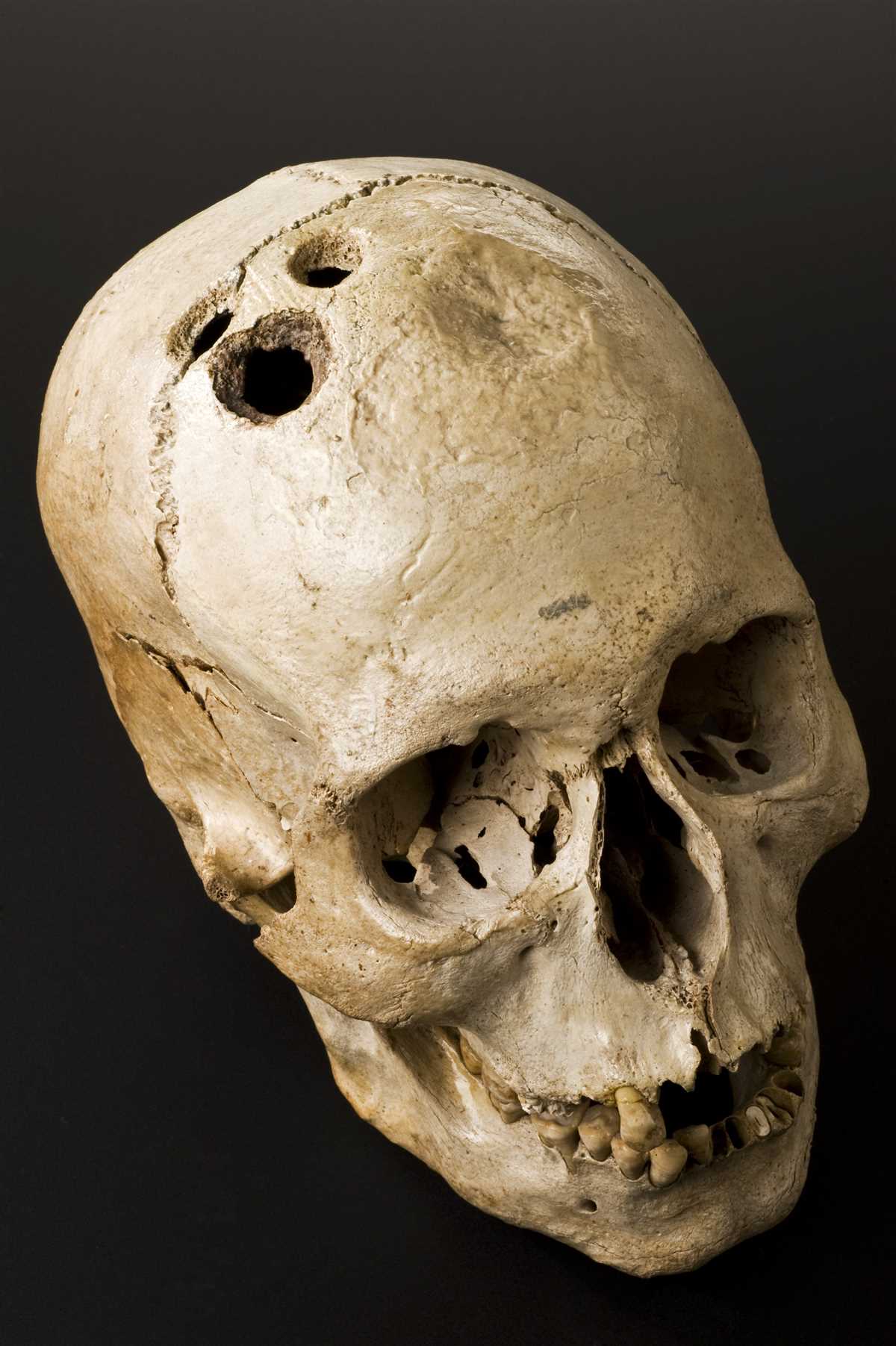
Ancient societies believed that trepanation could help treat various medical conditions. They thought that by creating a hole in the skull, they could release evil spirits or relieve pressure on the brain. It was believed to cure ailments such as headaches, epilepsy, mental illnesses, and even skull fractures.
Trepanation was performed using primitive tools such as sharpened stones, obsidian blades, or primitive drills made from animal bones. The procedure was usually done while the patient was still alive.
Spiritual Beliefs
For many ancient cultures, trepanation held strong spiritual significance. The act of creating an opening in the skull was believed to allow connection with the spirit world or the divine. Some believed that it could enhance spiritual powers, improve consciousness, and open up channels for energy flow.
Many ancient religious rituals involved trepanation, with shamans or priests performing the procedure. It was believed that by accessing the spiritual realm through the hole in the skull, individuals could gain knowledge and understanding of the universe.
Symbolism and Art
Trepanation was not only a medical or spiritual practice but also held symbolic meaning in ancient cultures. Depictions of trepanation can be found in ancient art and artifacts, showcasing the societal significance of the procedure.
Some ancient civilizations believed that trepanation symbolized rebirth or transformation. The creation of a hole in the skull represented a passage between worlds or a gateway to a new life.
Conclusion
Exploring ancient beliefs surrounding trepanation helps us understand the diverse cultural and spiritual practices of our ancestors. Whether used as a medical procedure or a spiritual ritual, trepanation played a significant role in many ancient civilizations and continues to captivate our curiosity today.
Modern Motivations
1. Spirituality and Consciousness
One modern motivation for trepanation is the belief that it can enhance spirituality and expand consciousness. Some people believe that drilling a hole in the skull can open up channels for spiritual energy to flow through, leading to greater enlightenment or a heightened sense of awareness.
2. Medical Benefits
While trepanation is not a recognized medical procedure, some individuals believe it can bring various health benefits. One theory is that it increases blood flow to the brain, potentially improving cognitive function and relieving symptoms of conditions like migraines or depression. However, there is no scientific evidence to support these claims, and trepanation can be extremely dangerous and lead to serious health complications.
3. Personal Transformation and Self-Exploration
Some individuals see trepanation as a way to undergo personal transformation or engage in self-exploration. They may view it as a form of body modification or an extreme form of expressing themselves. By undergoing trepanation, they believe they are pushing their physical and mental limits and exploring the depths of their own existence.
4. Ancient Cultural Practices
For some individuals, trepanation is seen as a way to connect with ancient cultural practices. They may be drawn to the historical significance of trepanation and believe that by experiencing it themselves, they are honoring and connecting with the past. This motivation is often rooted in a fascination with ancient civilizations and their medical practices.
5. Rebellion and Counterculture
In certain countercultural movements or subcultures, trepanation is seen as a form of rebellion against societal norms and established medical practices. Some individuals may undergo trepanation as an act of defiance, challenging the conventional views on health and exploring alternative ways of living and thinking.
Conclusion
While there are various modern motivations for trepanation, it is important to note that this procedure is not supported by medical or scientific evidence. It is considered extremely dangerous and can lead to severe health complications or even death. Anyone considering trepanation should seek professional medical advice and explore safer alternatives for personal growth or exploring spirituality.
Potential Benefits of Trepanation
1. Relief from chronic headaches and migraines
Trepanation has been reported to relieve chronic headaches and migraines in some individuals. The opening created by trepanation allows for increased blood flow and circulation to the brain, which may help to alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions. However, more research is needed to understand the effectiveness of trepanation for headache and migraine relief.
2. Enhanced cognitive function
Advocates of trepanation argue that it can lead to enhanced cognitive function. They believe that the increased blood flow to the brain and release of cranial pressure can improve mental clarity, creativity, and overall cognitive abilities. However, these claims are largely anecdotal and unsupported by scientific evidence.
3. Alleviation of psychiatric symptoms
Some proponents of trepanation believe that it can alleviate symptoms of psychiatric conditions, such as depression and anxiety. They argue that trepanation can help balance the brain’s chemical composition and improve overall mental well-being. However, there is no scientific evidence to support these claims, and trepanation is not recognized as a legitimate treatment for psychiatric disorders.
4. Improved energy and vitality
Supporters of trepanation claim that it can increase energy levels and overall vitality. They believe that the removal of a small piece of the skull allows for improved energy flow throughout the body, resulting in increased energy levels and a greater sense of well-being. However, these claims are not supported by scientific research.
5. Spiritual and metaphysical experiences
Some individuals who underwent trepanation report experiencing spiritual and metaphysical experiences. They believe that the opening in the skull allows for a greater connection with the universe and higher levels of consciousness. However, these experiences are subjective and not scientifically measurable.
6. Historical and cultural significance
Trepanation has a long history and cultural significance in various societies. Studying and understanding trepanation can provide insights into ancient medical practices, cultural beliefs, and the human fascination with altering consciousness.
7. Potential future research opportunities
Although trepanation is controversial and lacks scientific support, studying its effects and mechanisms could lead to a better understanding of the brain’s physiology and potential treatments for neurological conditions. By exploring trepanation as a historical practice, researchers may uncover valuable knowledge that can be applied to modern medicine and neuroscience.
Improving Brain Function
While trepanation is often associated with ancient civilizations and tribal rituals, some modern individuals have turned to the practice in search of improved brain function. Advocates of trepanation claim that it can increase blood flow and oxygenation to the brain, resulting in enhanced cognitive abilities and overall mental well-being.
Proponents of trepanation argue that the skull is meant to be permeable and that modern humans have lost the natural ability for the skull to expand and contract. By creating a small hole in the skull, trepanation enthusiasts believe that they can restore this natural function and facilitate better brain functioning.
Theories and Techniques
There are various theories and techniques surrounding trepanation for improving brain function. Some practitioners advocate for a small hole drilled into the skull, while others prefer a larger opening. The positioning of the hole can also vary, with some suggesting specific areas known as “Third Eye trepanation” or “Frontal trepanation.”
The procedure is typically performed using sterile surgical tools to minimize the risk of infection. Some individuals may attempt self-trepanation, although this is highly discouraged due to the potential risks involved.
Controversy and Risks
The practice of trepanation for brain function improvement remains highly controversial within the medical community. Many medical professionals argue that there is no scientific evidence to support the claims made by trepanation advocates. The risks associated with the procedure, including infection, brain damage, and death, far outweigh any potential benefits.
It is important to note that trepanation is illegal in many countries and should only be performed by trained medical professionals in a controlled and sterile environment. Seeking alternative methods for improving brain function, such as a healthy diet, exercise, and mental stimulation, is recommended instead.
Conclusion
While some individuals believe that trepanation can improve brain function, the practice remains highly controversial and risky. The lack of scientific evidence and the potential for serious harm make trepanation an unsafe and ineffective method for enhancing cognitive abilities. It is crucial to prioritize scientifically proven and safe methods for improving brain function instead.
Relieving Chronic Conditions
Trepanation, the practice of drilling or scraping a hole in the skull, has been used throughout history as a way to treat various chronic conditions. While trepanation is not a widely accepted medical procedure today, some individuals still believe in its potential benefits.
Migraines and Headaches
One of the most common chronic conditions that people seek relief from through trepanation is migraines and headaches. It is believed that by removing a small piece of the skull, pressure inside the head is relieved, leading to a reduction in the frequency and intensity of migraines and headaches.
Depression and Mental Illness
Some proponents of trepanation claim that it can help alleviate symptoms of depression and other mental illnesses. They argue that by increasing blood flow to the brain and releasing pressure, trepanation can improve overall mental health and alleviate symptoms of various conditions.
Epilepsy
Studies have suggested that trepanation may have some potential benefits for individuals with epilepsy. By reducing pressure inside the brain, trepanation could potentially decrease the frequency and severity of seizures in some individuals.
Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is another condition that some believe can be relieved through trepanation. By releasing pressure and increasing blood flow to affected areas, trepanation may provide relief from chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia or arthritis.
Caution and Consultation
While trepanation may be seen as a potential alternative treatment for chronic conditions, it is important to note that it is not recognized as a mainstream medical practice. Before considering trepanation or any other alternative treatment, it is crucial to consult with a medical professional to fully understand the potential risks and benefits involved.
| Condition | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Migraines and Headaches | Reduction in frequency and intensity |
| Depression and Mental Illness | Improved overall mental health |
| Epilepsy | Decreased frequency and severity of seizures |
| Chronic Pain | Relief from pain conditions |
Risks and Controversies
Medical Risks
- Infection: Trepanation involves drilling or cutting into the skull, which can introduce bacteria or other microorganisms into the brain and cause an infection.
- Bleeding: The procedure can lead to excessive bleeding, both during the surgery and in the post-operative period.
- Brain damage: Despite advancements in medical technology, there is still a risk of unintentional brain damage during trepanation.
- Seizures and epilepsy: Some individuals who undergo trepanation may develop seizures or epilepsy as a result of the procedure.
- Psychological effects: Trepanation can have psychological consequences, including anxiety, depression, and changes in personality.
Ethical and Cultural Controversies
Trepanation is a controversial practice that raises ethical and cultural concerns:
- Lack of scientific evidence: The efficacy and safety of trepanation have not been scientifically proven, leading many medical professionals to consider it an unproven and potentially dangerous procedure.
- Cultural appropriation: Some argue that the adoption of trepanation by non-medical communities and individuals is a form of cultural appropriation, as it undermines the significance and cultural context of the practice in ancient societies.
- Ethical considerations: Performing a surgical procedure on oneself or others without proper medical training and supervision raises ethical concerns, including the potential for harm and the violation of medical ethics.
- Social stigma: Individuals who choose to undergo trepanation often face social stigma and skepticism from the general public, as it is viewed as an unconventional and potentially dangerous practice.
- Legal restrictions: In many countries, trepanation is not regulated or legally recognized as a legitimate medical procedure, leading to potential legal consequences for those who perform or undergo it.
FAQ:
What is trepanation?
Trepanation is a surgical procedure in which a hole is drilled or scraped into the human skull. This involves removing a piece of the skull bone to expose the brain.
Why do people undergo trepanation?
People undergo trepanation for various reasons. Some believe that it can improve brain function, enhance psychological well-being, or provide spiritual enlightenment. Others do it as a form of self-experimentation or for cultural or religious reasons.
Is trepanation a safe procedure?
Trepanation can be highly dangerous and should only be performed by trained medical professionals. It carries the risk of infection, bleeding, brain damage, and even death. It is not recommended as a medical procedure and is often considered to be a controversial and risky practice.
Are there any benefits to trepanation?
The benefits of trepanation are not scientifically proven and are largely based on anecdotal evidence. Some individuals claim to have experienced improved clarity of thought, increased creativity, and reduced stress after undergoing trepanation. However, these claims have not been substantiated by medical research and should be approached with caution.
Video:










