Choosing the Right Location: A Guide to Drilling a Well

Drilling a well is a complex and important process that requires careful planning and consideration. One of the first and most critical steps in drilling a well is choosing the right location. The location of a well can have a significant impact on its productivity, longevity, and overall success. It is essential to choose a location that is suitable for drilling a well to ensure that you have access to clean and reliable water for years to come.
When it comes to selecting the right location for drilling a well, there are several factors to consider. Firstly, geological conditions play a crucial role in determining the potential success of a well. The geology of an area can affect the permeability of the ground, which can impact the flow and accessibility of water. It is important to conduct thorough research and consult with experts to identify areas with favorable geological conditions for drilling a well.
In addition to geological considerations, it is important to assess the proximity to potential sources of contamination. A well should be located away from sources of pollution, such as septic tanks, industrial facilities, or agricultural fields, to prevent the risk of water contamination. It is also important to consider the topography of the area, as wells located in low-lying areas may be at risk of flooding, which can affect water quality and accessibility.
Furthermore, it is essential to consider accessibility when choosing the location for drilling a well. The location should be easily accessible for drilling equipment and maintenance purposes. In rural areas, it is important to consider the distance to nearby roads and infrastructure to ensure that drilling and maintenance operations can be carried out efficiently. Additionally, it is important to consider any legal requirements, permits, or regulations that may affect the location of the well.
Choosing the right location for drilling a well is a critical step in ensuring a reliable water source. By carefully considering geological conditions, proximity to potential sources of contamination, topography, and accessibility, you can increase the chances of drilling a successful and long-lasting well. Consultation with experts and thorough research is key to making an informed decision and ensuring that your well provides clean and reliable water for years to come.
Factors to Consider when Choosing a Well Drilling Location
1. Water Availability
One of the most important factors to consider when choosing a well drilling location is the availability of water. Conduct a thorough hydrogeological survey to determine the presence and capacity of underground water sources in the area. It is crucial to ensure a sustainable and abundant water supply to meet your needs.
2. Geology and Soil Composition
The geology and soil composition of the area play a significant role in well drilling. Certain types of rocks and soils can impede the drilling process or result in poor water quality. Conduct a geotechnical investigation to determine the suitability of the soil and rock formations for drilling a well.
3. Proximity to Contaminants
When selecting a well drilling location, it is important to consider the proximity to potential sources of contamination. Be aware of any industrial sites, landfills, or agricultural activities nearby that may pose a risk of water pollution. Selecting a location away from these potential contaminants is crucial for ensuring the safety and quality of your water supply.
4. Depth of the Water Table
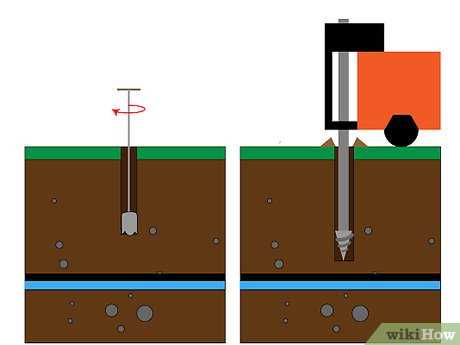
The depth of the water table will affect the cost and feasibility of drilling a well. Conduct a groundwater exploration to determine the depth at which you can access water. If the water table is too deep, it may be more expensive to drill a well, and the pumping costs may be higher.
5. Accessibility and Legal Considerations
Consider the accessibility of the drilling site, both during the drilling process and for future maintenance. Ensure that there are no legal restrictions or regulations that prevent drilling in the chosen location. Check with local authorities and obtain any necessary permits or approvals before starting the drilling process.
6. Topography and Drainage
The topography and drainage of the area can affect the water quality and the stability of the well. Avoid locations that have poor drainage or areas prone to flooding. It is important to choose a location with suitable topography to ensure proper water flow and drainage around the well.
7. Distance from Other Wells
Consider the proximity of existing wells in the area. Drilling a well too close to another source may cause interference and potentially affect the water quality or yield. Maintain a safe distance from neighboring wells to ensure the reliability and efficiency of your own well.
8. Cost and Budget

The cost of drilling a well can vary depending on various factors such as depth, soil conditions, and equipment required. Consider your budget and determine the feasibility of drilling a well in the chosen location. It is important to balance the costs with the expected benefits and long-term savings from having a reliable water source.
9. Future Growth and Expansion
When selecting a well drilling location, it is important to consider future growth and expansion plans. Ensure that the chosen location can meet the water demands of your current and future needs. Choosing a location with sufficient capacity for future expansion will save you from the hassle of drilling additional wells in the future.
In conclusion, choosing the right location for drilling a well involves considering factors such as water availability, geology, proximity to contaminants, water table depth, accessibility, topography, distance from other wells, cost, and future growth. Taking these factors into account will help you ensure a successful and sustainable well drilling project.
Geographical Features and Climate
Geographical Features
When choosing the location for drilling a well, it is important to consider the geographical features of the area. Some factors to take into account include the topography, soil composition, and proximity to water sources. Areas with flat or gently sloping terrain are generally more suitable for drilling a well, as they allow for easier access and installation. It is also important to assess the soil composition, as certain types of soil, such as sandy or loamy soil, may be more conducive to drilling.
Furthermore, the proximity to water sources, such as rivers, lakes, or underground aquifers, can also impact the feasibility of drilling a well. Being close to a reliable water source can make the drilling process easier and ensure a sustainable supply of water in the long term.
Climate
The climate of the chosen location is another crucial factor to consider. Different regions have varying levels of precipitation and temperature patterns, which can influence the availability and quality of groundwater. Areas with high levels of rainfall tend to have a higher water table, making it easier to access water through drilling. On the other hand, regions with low rainfall may have a lower water table and require deeper drilling.
Temperature is also an important consideration, as it can affect the overall demand for water. In hot and arid climates, water usage tends to be higher, necessitating a reliable and sustainable water source. Additionally, extreme temperature fluctuations can also impact the durability of the well equipment and infrastructure.
Impact of Geographical Features and Climate on Well Placement
Considering the geographical features and climate of the chosen location is crucial for determining the ideal placement of a well. By assessing the topography, soil composition, and proximity to water sources, it is possible to identify areas that are more suitable for drilling. Similarly, understanding the climate and its impact on groundwater availability and demand can help in selecting the right spot for the well.
Ultimately, a thorough evaluation of the geographical features and climate is necessary to ensure the successful drilling and long-term sustainability of a well. This information can guide the decision-making process and lead to a reliable and efficient water supply for years to come.
Groundwater Availability and Quality
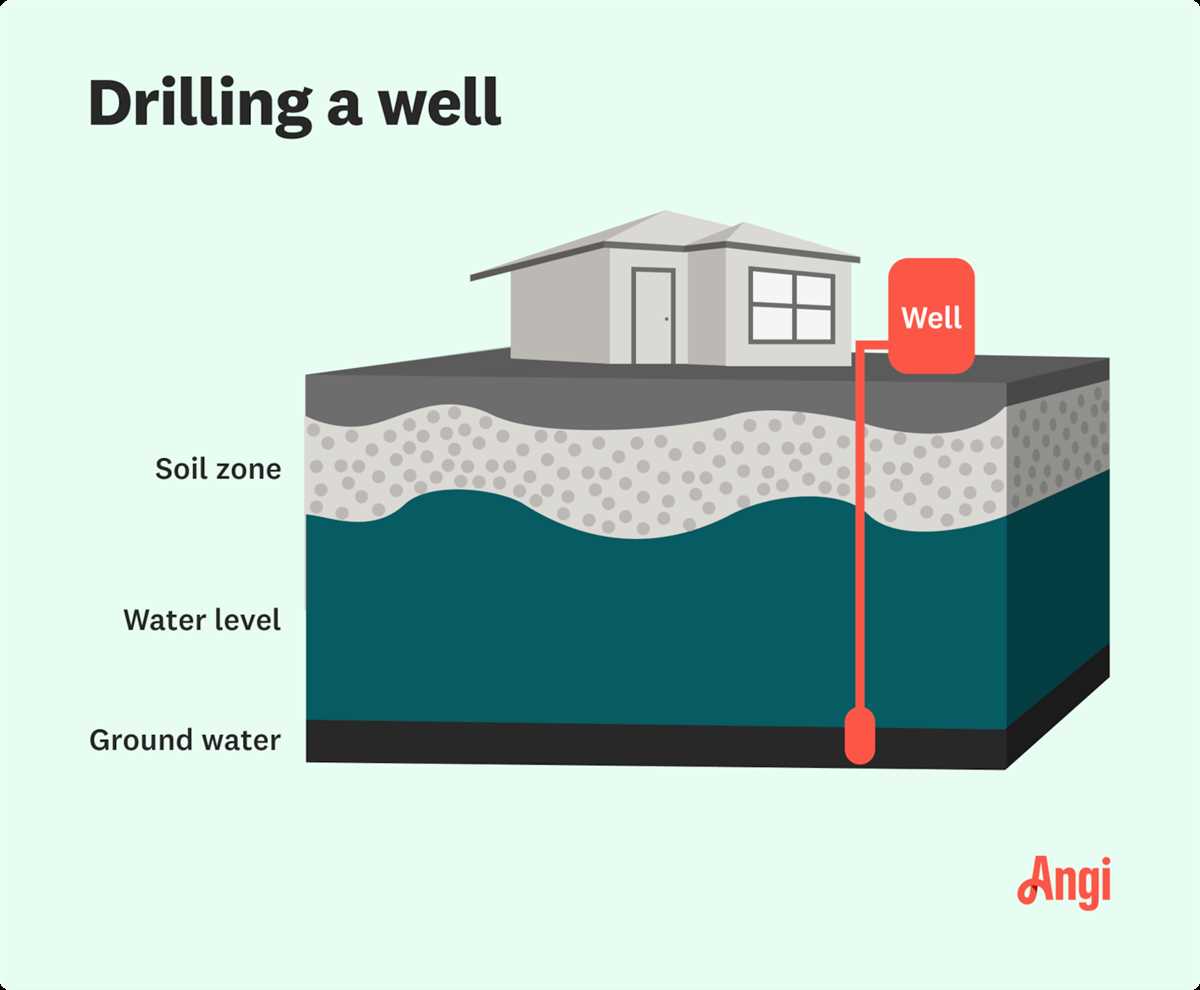
When drilling a well, it is important to consider both the availability and quality of groundwater in the location. Groundwater is the water that is stored beneath the Earth’s surface, in spaces between rocks and soil particles. It is a crucial source of water for both drinking and irrigation purposes.
Groundwater Availability
The availability of groundwater can vary depending on the geological characteristics of the area. Some areas may have abundant groundwater resources due to factors like high rainfall or porous rock formations that allow water to seep through. On the other hand, certain areas may have limited groundwater resources due to factors like low rainfall or impermeable rock formations that prevent water from infiltrating into the ground.
It is important to assess the groundwater availability in the desired location before drilling a well. This can be done by consulting local hydrogeological surveys, geological maps, and well records. These sources of information can provide valuable insights into the depth and quantity of groundwater in the area, helping determine the feasibility of drilling a well.
Groundwater Quality
The quality of groundwater refers to its chemical composition and suitability for various uses. It is important to assess the groundwater quality before drilling a well to ensure that the water extracted will be safe for consumption or irrigation purposes.
Groundwater quality can vary depending on various factors such as the geological composition of the area, the presence of pollutants from human activities, and natural processes like mineral dissolution. Common contaminants found in groundwater include heavy metals, pesticides, nitrates, and bacteria.
An analysis of groundwater quality should be conducted to determine if any potential contaminants are present and if the water meets the required standards for its intended use. This analysis can be done by collecting water samples and sending them to a certified laboratory for testing.
Conclusion
Considering both the availability and quality of groundwater is crucial when choosing a location for drilling a well. By understanding the groundwater resources in the area, it is possible to make informed decisions about the feasibility of drilling and ensure that the extracted water will be safe for use.
Depth and Yield Potential
The depth at which you drill your well can greatly affect its yield potential. The yield potential refers to the amount of water that can be extracted from the well.
Deeper wells tend to have higher yield potential because they tap into underground water sources that are more abundant. However, drilling a deeper well also comes with higher costs and may require more advanced drilling equipment.
Factors to Consider
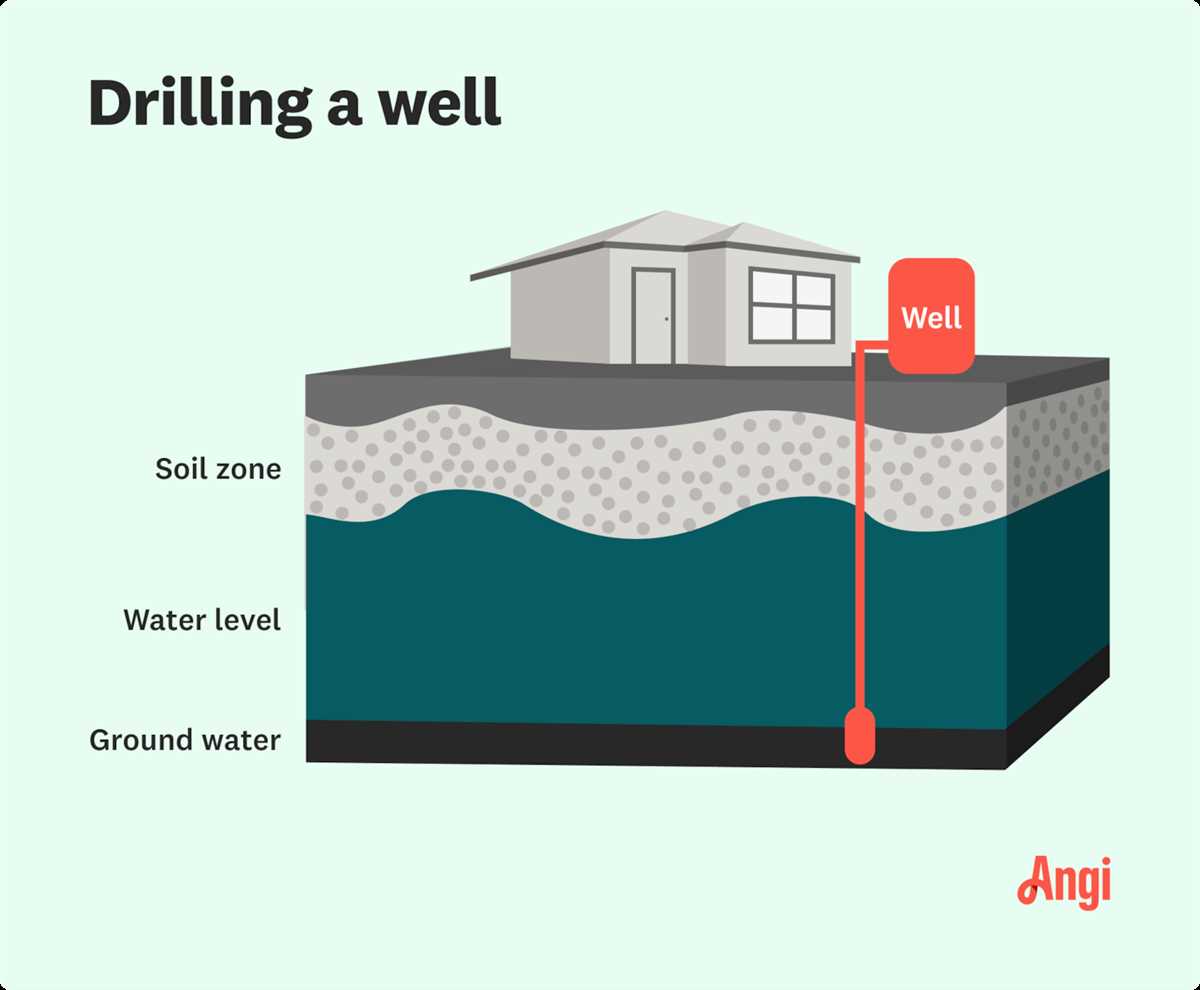
When deciding on the depth of your well, there are several factors to take into consideration:
- Geological Formation: Different geological formations may have varying water-holding capacities. Conducting a geological study of the area can help determine the potential yield at different depths.
- Water Table: The depth of the water table is an important factor to consider. If the water table is close to the surface, a shallower well may be sufficient. However, if the water table is deeper, you may need to drill a deeper well.
- Population and Usage: Consider the size of the population you plan to serve and their water usage needs. If the population is large and has high water demand, a deeper well with a higher yield potential may be necessary.
- Local Regulations: Check with local authorities regarding any regulations on well depth. Some areas may have specific requirements or restrictions on the depth of wells.
Yield Potential Testing
Before finalizing the depth of your well, it is recommended to conduct a yield potential test. This involves drilling a test well at the desired depth and measuring the amount of water that can be pumped out within a specific time frame.
The yield potential test helps to determine the productivity of the well and ensures that an adequate water supply can be obtained. It is essential to conduct this test before drilling the actual well to avoid any surprises or disappointments.
Consultation with Experts
When deciding on the depth of your well and assessing its yield potential, it is advisable to consult with drilling experts or hydrogeologists. They can provide valuable insights and help ensure that you make the right decisions based on the specific characteristics of your drilling location.
By considering all these factors and seeking expert advice, you can maximize the yield potential of your well and ensure a reliable water supply for your needs.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Permits and Licensing
Before drilling a well, it is important to obtain the necessary permits and licenses required by local authorities. This typically includes applying for a drilling permit, water rights permit, and complying with environmental regulations.
A drilling permit is necessary to ensure that the drilling operation meets safety standards and adheres to local regulations. In addition, a water rights permit is required to legally access and use water from underground sources.
It is important to consult with local authorities, such as the Department of Water Resources or the Environmental Protection Agency, to understand the specific permits and licenses required for drilling a well in your area.
Location Restrictions
There may be location restrictions that limit where a well can be drilled. These restrictions are in place to protect sensitive ecosystems, water sources, or existing infrastructure.
For example, wells may be prohibited near bodies of water, wetlands, or areas with low water tables. Additionally, there may be setback requirements to ensure that wells are a specified distance away from roads, buildings, and property lines.
It is important to research and understand any location restrictions in your area before drilling a well. Violating these restrictions can result in fines and legal consequences.
Water Usage and Stewardship
When drilling a well, it is important to consider the responsible use and stewardship of water resources. This includes complying with water usage restrictions, monitoring water levels, and implementing measures to prevent contamination.
Some areas have restrictions on water usage for irrigation, livestock, or residential purposes. It is important to be aware of these restrictions and use water resources responsibly to avoid depleting groundwater reserves.
Additionally, proper well construction and maintenance is essential to prevent contamination of underground water sources. This may include installing protective casings, regularly testing water quality, and properly disposing of drilling waste.
Consulting Professionals
Given the complexity of legal and regulatory considerations, it is advisable to consult with professionals who specialize in well drilling and permitting. These professionals can provide guidance and ensure compliance with all relevant laws and regulations.
They can assist in navigating the permit application process, analyzing location restrictions, and recommending best practices for water usage and stewardship. Their expertise can help avoid costly legal issues and ensure a successful drilling operation.
Nearby Contaminant Sources
When choosing the right location for drilling a well, it is important to consider nearby contaminant sources. Contaminants can pose a serious threat to the quality and safety of the water drawn from the well. Here are some nearby contaminant sources to be aware of:
- Industrial Facilities: Industrial facilities, such as factories and plants, can release various chemicals and pollutants into the surrounding soil and groundwater. These contaminants can seep into nearby wells and contaminate the water supply.
- Agricultural Areas: Farms that use fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides can also contribute to groundwater contamination. These chemicals can leach into the soil and find their way into nearby wells.
- Gas Stations: Gasoline and diesel fuel can leak from underground storage tanks at gas stations, contaminating the soil and groundwater. Wells located near gas stations may be at risk of contamination.
- Waste Disposal Sites: Landfills and waste disposal sites can release hazardous substances into the surrounding environment. These contaminants can migrate through the soil and contaminate groundwater, posing a risk to nearby wells.
- Septic Systems: When not properly maintained or located too close to a well, septic systems can contaminate groundwater with bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. It is important to ensure that wells are not located too close to septic systems.
It is vital to conduct a thorough assessment of potential nearby contaminant sources before drilling a well. This can involve researching the history of the area, consulting with local authorities, and conducting site assessments. By understanding the potential sources of contamination, you can choose a location that minimizes the risk of water contamination and ensures a safe water supply.
Accessibility and Proximity to Utilities
When choosing the location for drilling a well, it is important to consider the accessibility of the site and its proximity to utilities. These factors can have a significant impact on the drilling process and the overall cost and convenience of operating the well.
Accessibility
Accessible sites are generally easier to reach and require less effort and resources to transport equipment and materials. When assessing the accessibility of a potential drilling location, consider the following:
- Distance from main roads or highways: The closer the site is to a main road or highway, the easier it will be to transport heavy machinery and materials.
- Type of terrain: Flat or gently sloping terrain is generally more accessible than steep or rugged terrain, which may require specialized equipment or additional time and effort to access.
- Clearance for equipment: Ensure that there is enough space to maneuver and position drilling equipment without any obstructions or obstacles.
Proximity to Utilities
The proximity to utilities is another important factor to consider when choosing a drilling location. Being close to utilities can offer several advantages:
- Access to electricity: Drilling and operating a well often requires electricity to power equipment and tools. Being close to an electrical source can minimize the need for long electrical cables or generators.
- Availability of water: Having a nearby water source can be beneficial during the drilling process, as it can be used for drilling, cleaning equipment, or mixing drilling fluids.
- Connection to roads and infrastructure: Being located near existing infrastructure, such as roads, can make it easier to transport equipment, materials, and personnel to and from the drilling site.
It is important to note that the accessibility and proximity to utilities should be considered in conjunction with other factors, such as the geological characteristics of the site and any legal or regulatory requirements. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a drilling location that offers the best balance of accessibility, convenience, and cost-effectiveness for your well project.
Construction and Maintenance Requirements
Proper Construction
When drilling a well, it is crucial to undertake proper construction practices to ensure the longevity and efficiency of the well. The following guidelines should be followed:
- Use high-quality materials: High-grade steel casings should be used to prevent corrosion and ensure the structural integrity of the well.
- Seal the well properly: Well sealing ensures that surface water or contaminants do not enter the well. A proper seal should be applied to the annular space between the casing and borehole wall.
- Install a well cap or seal: A well cap or seal prevents foreign materials, debris, and small animals from entering the well. It also protects the well from surface water and potential contamination.
- Proper well padding: Adequate padding should be used to prevent damage to the well casing and to stabilize the well during drilling and subsequent maintenance activities.
Maintenance Practices
To ensure a well continues to function effectively, regular maintenance is required. Here are some essential maintenance practices:
- Regular testing: Periodically test the well water quality to check for any changes or contamination. This will help identify any potential issues early on.
- Well cleaning: Cleaning the well periodically will remove sediment, scale, and other accumulated debris that may affect the well’s performance. Consider hiring a professional if necessary.
- Inspecting well components: Regularly inspect the wellhead, casing, and seals for any signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Address any issues promptly to prevent further deterioration.
- Pump maintenance: Maintain and service the well pump regularly to ensure proper functioning. This includes checking pressure settings, lubricating components, and replacing worn-out parts.
Recordkeeping
Keeping thorough records is essential for well owners. It helps track maintenance activities, water quality tests, and any changes observed over time. Maintain records of:
- Well construction details: Record the well’s location, depth, casing material, and construction date.
- Maintenance and repairs: Document all maintenance activities, repairs, and any upgrades made to the well system.
- Water quality tests: Keep a record of water quality tests, including dates, results, and any deviations from the desired standards.
- Well inspections: Record the dates and findings of regular well inspections.
Compliance with Regulations
It is important to comply with any local, state, or national regulations regarding well construction and maintenance. Familiarize yourself with the specific requirements in your area to ensure that your well meets all necessary standards.
Professional Assistance
If you are unsure about drilling a well or maintaining an existing one, consider hiring a licensed well drilling professional or seeking guidance from local authorities. They can provide expert advice and ensure that all construction and maintenance activities adhere to the appropriate standards and regulations.
Cost and Return on Investment
Drilling a well can be a significant investment, but it can also provide long-term cost savings and a return on investment. Here are some factors to consider when evaluating the cost and potential return on investment of drilling a well:
Initial Cost
The initial cost of drilling a well can vary widely depending on various factors such as the location, depth, and type of well. On average, the cost can range from $5,000 to $15,000 or more, with deeper wells costing more. It is important to factor in not only the drilling cost but also the cost of permits, equipment, and hiring professionals.
Operational Cost
Once the well is drilled, there are ongoing operational costs to consider. These include regular maintenance, water treatment, and energy costs for pumping. The operational cost will depend on factors such as the depth of the well, the amount of water needed, and the quality of the water.
Water Savings
One of the main advantages of drilling a well is the potential for significant water savings. By having a well, you can eliminate or reduce your dependence on a municipal water supply, which can be expensive. The amount of water and cost savings will depend on factors such as the size of your property and the water consumption needs of your household or business.
Property Value
Having a well on your property can increase its value. Many homebuyers and businesses are attracted to properties with a reliable and independent water source. This can make your property more marketable and potentially increase its resale value.
Environmental Impact
Drilling a well can have positive environmental impacts. By using groundwater as a water source, you can reduce the strain on local water supplies and promote water conservation. It can also reduce the energy required for water treatment and transportation, resulting in lower carbon emissions.
Long-Term ROI
The return on investment for drilling a well is a long-term consideration. It may take several years to recoup the initial investment costs through water savings and increased property value. However, over time, having a well can provide significant cost savings and financial benefits.
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Drilling cost, permits, equipment, professionals |
| Operational Cost | Maintenance, water treatment, energy costs |
| Water Savings | Reduction in municipal water expenses |
| Property Value | Increase in property value and marketability |
| Environmental Impact | Water conservation, lower carbon emissions |
| Long-Term ROI | Cost savings and financial benefits over time |
FAQ:
Can I drill a well anywhere on my property?
No, you cannot drill a well anywhere on your property. There are certain factors that need to be considered when choosing the location for drilling a well.
What are the factors to consider when choosing the location for drilling a well?
There are several factors to consider when choosing the location for drilling a well. These include the geology of the area, water table level, proximity to potential sources of contamination, and accessibility for drilling equipment.
How can I determine the geology of the area before drilling a well?
To determine the geology of the area before drilling a well, you can consult geological maps or hire a professional geologist to conduct a site assessment. They will analyze the composition of the soil and rocks to determine the suitability of the location for drilling a well.
What is the water table level and why is it important?
The water table level refers to the depth at which underground water is located. It is important to consider the water table level when drilling a well because you need to ensure that the well is deep enough to reach the water source. A well that is too shallow may not provide an adequate water supply.
What are potential sources of contamination that should be avoided when drilling a well?
When drilling a well, it is important to avoid potential sources of contamination such as septic systems, underground fuel storage tanks, and industrial sites. These can pose a risk to the quality of the water extracted from the well. It is advisable to consult with local authorities or hire a professional to assess the potential sources of contamination in the area.
Is it necessary to have easy access for drilling equipment when choosing a location for drilling a well?
Yes, it is necessary to have easy access for drilling equipment when choosing a location for drilling a well. Drilling equipment is large and heavy, and it requires a clear path to the drilling site. If the location is difficult to access, it may increase the cost and time required for drilling.
Video:












