Understanding the Role of a Compressor in an Air Conditioner

The compressor is a vital component in an air conditioner, playing a crucial role in the cooling process. It is responsible for pressurizing and circulating the refrigerant within the system, allowing the air conditioner to remove heat from the indoor environment and maintain a comfortable temperature.
The compressor works by drawing in low-pressure refrigerant vapor from the evaporator coil and compressing it using a piston or scroll mechanism. This compression raises the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant, transforming it into a high-pressure gas. As the gas travels to the condenser coil, it releases heat and condenses back into a liquid state.
The compressed refrigerant then moves through the expansion valve, where it undergoes a pressure drop, resulting in a decrease in temperature. This cold liquid is then sent back to the evaporator coil, where it absorbs heat from the indoor air, cooling it in the process. The cycle continues as the refrigerant returns to the compressor and the process repeats.
The role of the compressor in an air conditioner is vital, as it is responsible for maintaining the necessary pressure and flow of refrigerant throughout the system. Without a properly functioning compressor, the air conditioner would not be able to effectively cool the indoor space, leading to discomfort and potentially damaging the unit.
The Function of an Air Conditioner
An air conditioner is a vital device for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature. It performs the crucial task of cooling the air to remove heat and humidity, creating a pleasant environment for occupants. The primary function of an air conditioner is to extract warm air from the indoor space and replace it with cool air, enhancing the overall comfort level.
Air Circulation: By circulating the air within a room or building, air conditioners ensure consistent cooling throughout the space. The air conditioner’s fan draws in the warm air from the room and passes it over cold evaporator coils. As a result, heat is absorbed from the air, causing it to cool down. The cooled air is then released back into the room, while the heat extracted from the air is transferred to the condenser coils for release to the outside.
Humidity Regulation: In addition to cooling the air, air conditioners also help regulate humidity levels. As warm air passes over the evaporator coils, moisture in the air condenses onto the coils and is collected in a drip pan or drained away. This process effectively reduces the humidity in the room, providing a drier and more comfortable environment.
Temperature Control: Air conditioners provide precise temperature control by using a thermostat. The thermostat allows users to set their desired temperature, and the air conditioner works to achieve and maintain that temperature. Once the desired temperature is reached, the compressor cycles on and off to maintain a consistent and comfortable indoor climate.
Eco-Friendliness: Modern air conditioners often come with energy-saving features to reduce environmental impact. These features include programmable settings, timers, and sensors that optimize energy usage while still providing the desired level of cooling. By using energy-efficient technologies, air conditioners can cool spaces effectively while minimizing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential to keep an air conditioner functioning optimally. This includes cleaning or replacing air filters, inspecting and cleaning coils, checking refrigerant levels, and ensuring proper airflow. Proper maintenance not only helps extend the lifespan of the air conditioner but also ensures efficient performance, improved indoor air quality, and lower energy costs.
Components of an Air Conditioner
An air conditioner consists of several key components that work together to cool and regulate the temperature of a room or space. These components include:
- Compressor: The compressor is an essential component of an air conditioner. It is responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas, increasing its pressure and temperature.
- Condenser: The condenser is located outside the building and is responsible for releasing heat from the refrigerant gas. It helps to cool the gas into a liquid state.
- Evaporator: The evaporator is located inside the building and is responsible for absorbing heat from the air. It is where the liquid refrigerant evaporates and cools the air.
- Expansion Valve: The expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant from the condenser to the evaporator. It helps to regulate the pressure of the refrigerant and control its cooling effect.
- Air Filter: The air filter is responsible for removing dust, pollen, and other particles from the air before it is cooled and circulated in the room. It helps to improve indoor air quality.
- Thermostat: The thermostat is the control unit of the air conditioner. It allows the user to set the desired temperature and controls the operation of the compressor and other components.
In addition to these components, an air conditioner may also have other features such as a fan, a drain pan, and a duct system for distributing the cooled air. Understanding the role of each component and how they work together can help in troubleshooting and maintaining the air conditioner for optimal performance.
How Does an Air Conditioner Work?
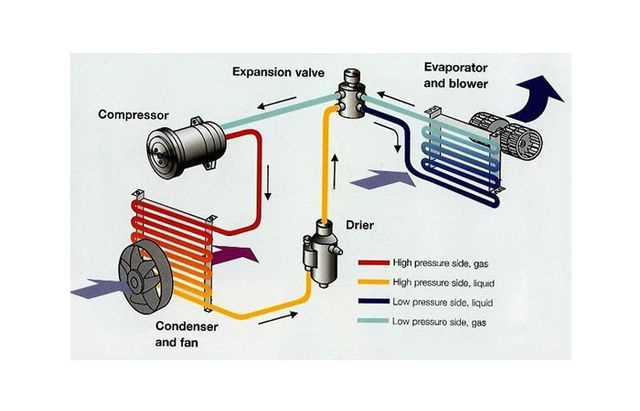
An air conditioner is a system that is used to cool down the temperature and improve the air quality in a room or building. It works by removing the heat from the air and circulating cool air back into the room. The main components of an air conditioner are the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. Each of these components plays a crucial role in the cooling process.
Compressor
The compressor is the heart of an air conditioner. It is responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas and raising its temperature and pressure. The compressor takes in the low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant gas from the evaporator and compresses it into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas. This compressed gas then moves to the condenser.
Condenser
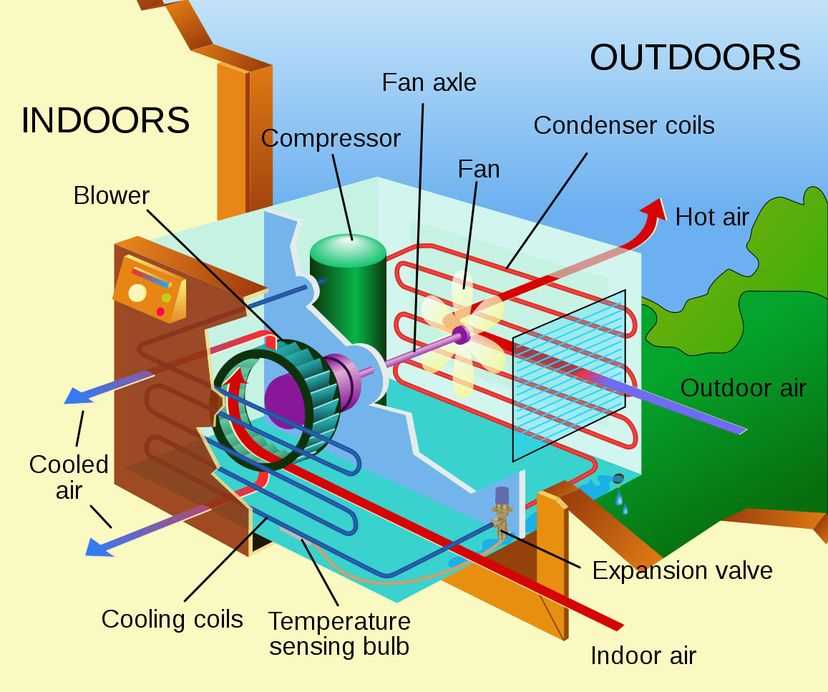
The condenser is where the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant gas is cooled down and condensed into a liquid. Heat is released from the refrigerant as it circulates through the condenser coils, which are usually located outside the building. The heat is transferred to the surrounding air, and the refrigerant is cooled down and liquefied. The condensation process helps to release the heat from the air conditioner system.
Expansion Valve and Evaporator
The expansion valve is located between the condenser and the evaporator. It acts as a metering device that controls the flow of the refrigerant into the evaporator. The expansion valve restricts the flow of the refrigerant, causing a drop in pressure. As a result, the refrigerant expands and evaporates, absorbing heat from the air in the process. This cooled air is then blown into the room through the air conditioner’s vents.
The evaporator is the final component in the air conditioning process. It consists of a series of coils that are filled with the cold refrigerant. As warm air from the room passes over the evaporator coils, the heat is absorbed by the refrigerant, causing the air to cool down. The cool air is then recirculated back into the room, while the refrigerant, now in its gaseous state, returns to the compressor to start the cycle again.
The Role of the Compressor
The compressor is a vital component in an air conditioner, serving the purpose of increasing the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant. This plays a crucial role in the cooling process, as it allows the refrigerant to absorb heat from the indoor air and release it to the outdoor environment.
1. Compression: The compressor takes in low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant vapor and compresses it, resulting in an increase in both its temperature and pressure. This compression process is achieved through the use of a motor-driven piston or a rotating scroll.
2. Heat transfer: Once the refrigerant is compressed, it becomes high-pressure, high-temperature gas. This hot gas then enters the condenser coil, where it releases heat to the surrounding environment. As a result, the refrigerant changes from a gas to a liquid state.
3. Pressure regulation: The compressor plays a critical role in regulating the pressure within the air conditioning system. It ensures that the refrigerant flows properly through the different components, facilitating the refrigeration cycle and optimizing cooling efficiency.
4. Energy consumption: The compressor consumes a significant amount of energy in an air conditioner. It requires a motor to drive its operation, which increases the overall energy consumption of the system. Therefore, ensuring the compressor operates efficiently is important for energy savings.
5. Maintenance and repairs: Proper maintenance and timely repairs of the compressor are crucial for the smooth operation of an air conditioning system. Regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspection of the compressor can help prevent breakdowns and prolong its lifespan.
Overall, the compressor plays a vital role in the cooling process of an air conditioner, transforming the refrigerant from a low-pressure gas to a high-pressure liquid, facilitating heat transfer, and regulating pressure within the system, contributing to efficient and effective cooling.
Types of Compressors Used in Air Conditioners
Reciprocating Compressor
A reciprocating compressor is one of the most common types of compressors used in air conditioners. It uses a piston and cylinder arrangement to compress the refrigerant gas. When the piston moves down, it creates a vacuum, drawing in the refrigerant gas. As the piston moves up, it compresses the gas, raising its pressure.
Reciprocating compressors are known for their high efficiency and reliability. They are commonly used in smaller air conditioning units and refrigerators.
Rotary Compressor
A rotary compressor is another type of compressor used in air conditioners. It has a rotating mechanism that compresses the refrigerant gas. The most common type of rotary compressor used in air conditioners is the scroll compressor.
Scroll compressors have two spiral-shaped components, known as scrolls, that interlock to compress the gas. They are known for their quiet operation and high efficiency. Rotary compressors are often used in larger air conditioning units and commercial HVAC systems.
Centrifugal Compressor
A centrifugal compressor is a type of compressor that uses centrifugal force to compress the refrigerant gas. It has an impeller with blades that rotate at high speeds, creating a centrifugal force that pushes the gas towards the outer edge of the impeller.
Centrifugal compressors are known for their high capacity and ability to handle large volumes of air. They are commonly used in industrial air conditioning and refrigeration systems.
Screw Compressor
A screw compressor is a type of compressor that uses rotating screws to compress the refrigerant gas. It has a pair of helical rotors that interlock and push the gas towards the outlet. As the rotors rotate, the volume between them decreases, causing the gas to be compressed.
Screw compressors are known for their high capacity and efficiency. They are often used in large-scale air conditioning and refrigeration systems, such as those found in commercial buildings and industrial facilities.
Turbocompressor
A turbocompressor is a type of compressor that uses a turbine to compress the refrigerant gas. It has a turbine wheel that is driven by a high-speed motor or engine. As the gas passes through the turbine, it gains speed and pressure.
Turbocompressors are known for their high efficiency and reliability. They are commonly used in large-scale air conditioning and refrigeration systems, as well as in gas turbine power plants.
In summary, there are several types of compressors used in air conditioners, each with its own advantages and applications. Reciprocating compressors are commonly used in smaller units, while rotary compressors, such as scroll compressors, are used in larger units. Centrifugal compressors are used in industrial systems, while screw compressors are used in large-scale systems. Turbocompressors are used in high-capacity applications. Understanding the different types of compressors can help in choosing the right air conditioner for a particular application.
Reciprocating Compressors
A reciprocating compressor is one of the most common types of compressors used in air conditioning systems. It works by using a piston that moves back and forth in a cylinder to compress the refrigerant. This type of compressor is often referred to as a piston compressor.
Working Principle: The reciprocating compressor works on the principle of positive displacement. When the piston moves down, it creates a vacuum in the cylinder, which draws in the refrigerant gas from the evaporator. As the piston moves up, it compresses the gas and forces it into the condenser. This process creates a high-pressure, high-temperature gas that can be cooled and condensed.
Advantages: One of the main advantages of reciprocating compressors is their ability to handle high-pressure and high-load conditions. They are also known for their efficiency and reliability. Additionally, reciprocating compressors are relatively compact and can be easily integrated into air conditioning systems.
- Compact size
- High-pressure and high-load capacity
- Efficiency and reliability
Disadvantages: Despite their advantages, reciprocating compressors have a few disadvantages. They tend to be noisier compared to other types of compressors and can produce vibrations. They also require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Applications: Reciprocating compressors are commonly used in small-scale air conditioning systems, such as window air conditioners and residential split air conditioning units. They are also used in refrigeration systems for commercial and industrial applications.
Rotary Compressors
Rotary compressors are a type of compressor commonly used in air conditioning systems. They are designed to compress refrigerant gas and circulate it through the air conditioner, playing a crucial role in the cooling process. Unlike other types of compressors, rotary compressors use a rotating mechanism to compress the refrigerant gas.
The main advantage of rotary compressors is their compact size and energy efficiency. They are generally smaller and more lightweight than other compressor types, making them ideal for space-limited installations. Additionally, rotary compressors operate with minimal vibration and noise, providing a quieter and more comfortable environment.
There are two main types of rotary compressors: rotary vane compressors and rotary scroll compressors. Rotary vane compressors consist of a rotor with vanes that rotate and slide against the walls of a cylinder, compressing the gas. On the other hand, rotary scroll compressors use two spiral-shaped scrolls that interlock and create pockets of trapped gas, which are then compressed as the scrolls rotate.
Both types of rotary compressors offer efficient and reliable performance. They can handle a wide range of operating conditions and provide consistent cooling output. The choice between rotary vane compressors and rotary scroll compressors depends on factors such as the specific cooling requirements, installation space, and budget.
In summary, rotary compressors play a vital role in air conditioning systems by compressing refrigerant gas and circulating it for cooling. Their compact size, energy efficiency, and quiet operation make them a popular choice in various applications. Whether it’s a rotary vane compressor or a rotary scroll compressor, both offer reliable performance and contribute to optimal cooling performance in air conditioners.
Screw Compressors

A screw compressor is a type of compressor commonly used in air conditioning systems. Unlike other types of compressors, a screw compressor uses two rotating screws to compress the refrigerant gas. These screws are referred to as the male and female rotors.
One of the main advantages of using a screw compressor is its high efficiency. The design of the screws allows for a continuous and smooth compression process, resulting in minimal energy loss. This makes screw compressors more energy-efficient compared to other types of compressors, such as reciprocating compressors.
Another advantage of screw compressors is their ability to provide a higher volume flow rate. The screw design allows for a larger refrigerant flow, making screw compressors suitable for larger air conditioning systems that require a higher cooling capacity.
Screw compressors are also known for their quiet operation. The design of the screws reduces noise and vibrations, resulting in a quieter and more comfortable environment for users. This makes screw compressors ideal for applications where noise reduction is important, such as in office buildings or residential areas.
In summary, screw compressors are an efficient and reliable option for air conditioning systems. Their unique screw design allows for high efficiency, increased volume flow rate, and quiet operation. Screw compressors are widely used in various industries where cooling is required, providing effective and efficient cooling solutions.
Centrifugal Compressors
A centrifugal compressor is a type of compressor commonly used in air conditioning systems. It utilizes centrifugal force to increase the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant in the system. The compressed refrigerant is then passed through a series of heat exchange coils to cool down before it is circulated back into the space being cooled.
Unlike other types of compressors, such as reciprocating compressors or scroll compressors, centrifugal compressors have a rotating impeller that is used to increase the pressure of the refrigerant. The impeller is housed in a casing and spins at a high speed, creating a centrifugal force that pushes the refrigerant towards the outside of the impeller.
Advantages of Centrifugal Compressors:
- High efficiency: Centrifugal compressors are known for their high efficiency and ability to compress large volumes of air or refrigerants. They are capable of handling large cooling loads and can provide high-quality air conditioning.
- Compact design: Centrifugal compressors have a compact design compared to other types of compressors. This makes them ideal for installations where space is limited.
- Low maintenance: Centrifugal compressors require less maintenance compared to other types of compressors. They have fewer moving parts, which reduces the chances of mechanical failure or breakdowns.
Disadvantages of Centrifugal Compressors:
- Higher cost: Centrifugal compressors tend to be more expensive than other types of compressors. The advanced technology and design required for their operation contribute to their higher cost.
- Higher noise levels: Centrifugal compressors can be noisier compared to other types of compressors due to their high rotational speed. This may be a concern in residential or noise-sensitive areas.
- Lower capacity range: Centrifugal compressors are not suitable for applications with low cooling loads. They perform best when handling large cooling loads and may not be efficient for smaller air conditioning systems.
Overall, centrifugal compressors are a reliable and efficient option for air conditioning systems that require high cooling capacity. However, they may not be suitable for all applications due to their higher cost and noise levels. It is important to consider the specific requirements and limitations of the air conditioning system before choosing a compressor type.
Importance of Compressor Maintenance
1. Prolongs the Life of the Compressor
Maintaining the compressor of an air conditioner is crucial for extending its lifespan. Regular maintenance helps to prevent the accumulation of dirt, debris, and other contaminants that can cause damage to the compressor. By cleaning or replacing filters, inspecting and cleaning coils, and ensuring proper lubrication, the compressor can operate efficiently and avoid unnecessary strain.
2. Improves Energy Efficiency
A well-maintained compressor is essential for maximizing the energy efficiency of an air conditioner. Dirty or clogged filters and coils can restrict airflow, leading to reduced efficiency and increased energy consumption. Maintaining the compressor by cleaning or replacing filters and performing regular coil cleaning can help to improve the airflow, allowing the unit to operate more efficiently and consume less energy.
3. Prevents Costly Repairs
Regular maintenance of the compressor can help to identify and address potential issues before they become major problems. By inspecting and lubricating moving parts, checking refrigerant levels, and detecting any abnormal noises or vibrations, technicians can catch and resolve minor issues early on. This preventive maintenance can save homeowners from expensive repairs or even the need for a complete compressor replacement.
4. Ensures Optimal Cooling Performance
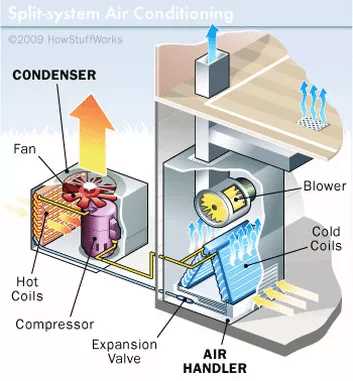
The compressor plays a crucial role in the cooling process of an air conditioner. It is responsible for compressing the refrigerant, which removes heat from the indoor air. If the compressor is not properly maintained, it can lead to inadequate cooling performance, reduced airflow, or even complete system failure. Regular maintenance of the compressor helps to ensure optimal cooling performance, keeping the indoor space comfortable during hot weather.
5. Promotes Indoor Air Quality

A properly maintained compressor can help to improve indoor air quality. Regular maintenance includes cleaning or replacing filters, which helps to remove dust, pollen, and other airborne contaminants from the air. This can prevent the circulation of pollutants and allergens, ensuring that the air conditioner contributes to a healthier indoor environment.
FAQ:
What is the role of a compressor in an air conditioner?
The role of a compressor in an air conditioner is to compress the refrigerant gas and increase its temperature and pressure. This high-pressure gas then flows to the condenser where it gets cooled down and converted back into a liquid state before being sent to the evaporator.
Why is the compressor considered an important component of an air conditioner?
The compressor is considered an important component of an air conditioner because it is responsible for pressurizing the refrigerant gas, which is essential for the cooling process. Without a properly functioning compressor, the air conditioner would not be able to effectively cool the air.
What happens if the compressor in an air conditioner fails?
If the compressor in an air conditioner fails, the cooling process will be affected. The air conditioner may blow warm air instead of cool air, or it may not work at all. In some cases, a faulty compressor can also cause the air conditioner to make strange noises or leak refrigerant. In any case, it is recommended to have a professional technician inspect and repair the compressor.
Can a compressor be repaired or does it need to be replaced?
Whether a compressor can be repaired or needs to be replaced depends on the extent of the damage. In some cases, minor issues like leaks or faulty electrical connections can be repaired. However, if the compressor is severely damaged or worn out, it may need to be replaced. A professional technician will be able to assess the condition of the compressor and recommend the appropriate course of action.
Is it normal for a compressor to make noise?
It is normal for a compressor to produce some noise during operation, but excessive or unusual noise can be a sign of a problem. If the compressor is making loud banging, rattling, or grinding noises, it may indicate a mechanical issue. It is best to have a professional technician inspect the compressor to determine the cause of the noise and perform any necessary repairs.
How often should a compressor in an air conditioner be serviced?
A compressor in an air conditioner should be serviced regularly to ensure its proper functioning and longevity. It is recommended to have the air conditioner professionally serviced at least once a year. During the service, the technician will inspect and clean the compressor, check for any leaks or damage, and perform any necessary maintenance tasks to keep the compressor in optimal condition.
Can a faulty compressor affect the energy efficiency of an air conditioner?
Yes, a faulty compressor can affect the energy efficiency of an air conditioner. If the compressor is not functioning properly, it may require more energy to compress and cool the refrigerant gas. This can lead to higher energy consumption and increased electricity bills. Additionally, a faulty compressor may cause the air conditioner to run longer and work harder to maintain the desired temperature, further decreasing its energy efficiency.
Video:













