Understanding the Basics of a Reciprocating Air Compressor

When it comes to powering many types of industrial machinery and equipment, a common and reliable option is the reciprocating air compressor. This type of compressor works by using a piston within a cylinder to compress air and deliver it at high pressure. Understanding the basics of a reciprocating air compressor can help you make informed decisions about its use in your specific applications.
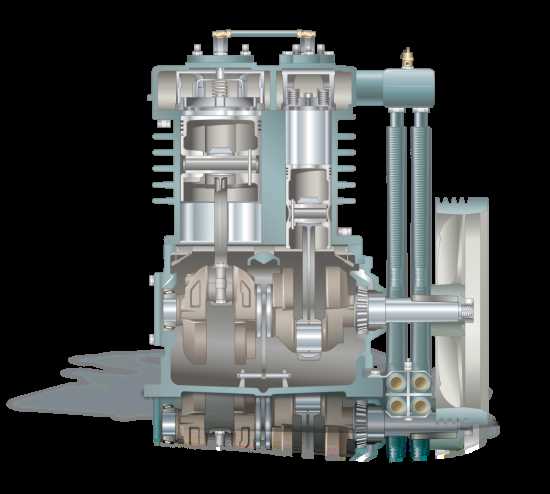
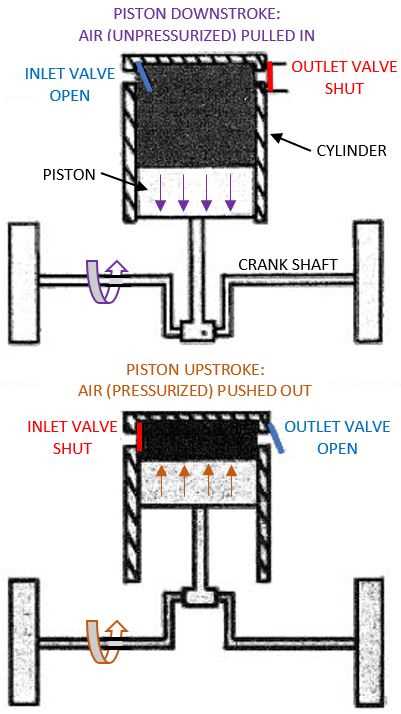
One of the key components of a reciprocating air compressor is the cylinder. This is where the compression of air takes place. The piston moves up and down inside the cylinder, creating a vacuum on the downstroke and compressing the air on the upstroke. The compressed air is then delivered through an outlet valve to the desired location.
Reciprocating air compressors can be either single-stage or two-stage. Single-stage compressors compress the air in one stroke, while two-stage compressors compress the air in two strokes. Two-stage compressors are capable of delivering higher pressures, making them ideal for applications that require more power.
It is important to consider the horsepower (hp) rating of a reciprocating air compressor when choosing the right one for your needs. The hp rating indicates the power output of the compressor and determines its ability to compress air efficiently. Selecting an air compressor with the appropriate hp rating ensures that it can meet the demands of your specific applications.
In conclusion, a reciprocating air compressor is a reliable option for powering industrial machinery and equipment. By understanding the basics of how it works, including the role of the cylinder, the types of compressors available, and the importance of the hp rating, you can make informed decisions about the best compressor for your needs.
What is a Reciprocating Air Compressor

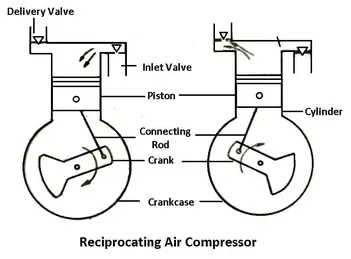
A reciprocating air compressor is a type of compressor that uses a piston and cylinder to compress air. It works by drawing in air through an intake valve, then compressing the air with a piston that moves back and forth in the cylinder. This compression process increases the pressure of the air, which can then be stored in a tank or used for various applications.
Reciprocating air compressors are commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and automotive. They are used for tasks such as powering air tools, inflating tires, and supplying pressurized air for machinery and equipment.
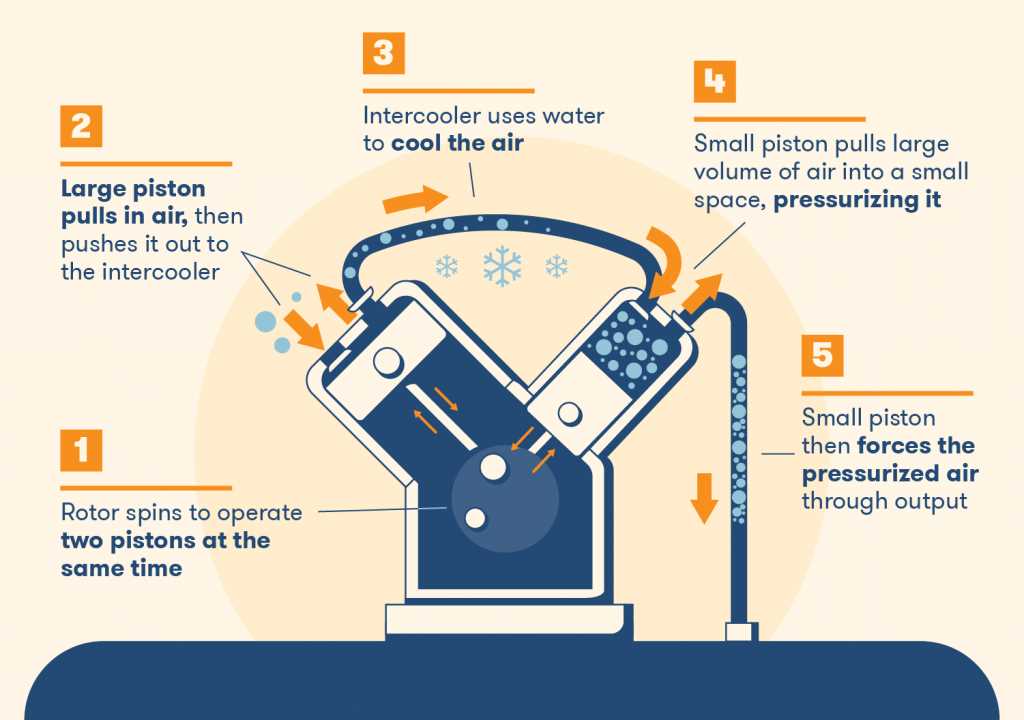
This type of compressor can come in different sizes and configurations to meet different needs. They can be powered by electricity, gasoline, or diesel, and they can have either a single-stage or two-stage compression process. Single-stage compressors compress the air in one stroke of the piston, while two-stage compressors use two pistons to further increase the pressure of the air.
Reciprocating air compressors are known for their durability and reliability. They are able to provide a steady supply of compressed air and can handle heavy-duty tasks. However, they can be noisy and require regular maintenance to ensure proper functioning.
Overall, a reciprocating air compressor is an essential tool for many industries that require compressed air. It provides a reliable source of compressed air for various applications, making it an important component in many industrial processes.
Operating Principles of Reciprocating Air Compressors

How Reciprocating Air Compressors Work

A reciprocating air compressor operates by using a piston that moves back and forth inside a cylinder. This movement creates a pressure difference that allows air to be compressed. As the piston moves downwards, the air is drawn into the cylinder through an intake valve. On the upward stroke, the air in the cylinder is compressed and forced out through a discharge valve.
Compression and Discharge Processes
During the compression process, the volume of air is reduced while the pressure increases. This is achieved by the upward movement of the piston, which decreases the volume of the cylinder. The discharge process involves expelling the compressed air from the cylinder and into a storage tank or directly into a pneumatic system. Both the compression and discharge processes are regulated by the valves, ensuring the efficient operation of the reciprocating air compressor.
Single-Stage vs. Two-Stage Compressors
Reciprocating air compressors can be classified as either single-stage or two-stage compressors. In a single-stage compressor, the air is drawn in, compressed, and then discharged in a single stroke of the piston. This type of compressor is typically used for light-duty applications where a lower pressure is required. On the other hand, a two-stage compressor uses two pistons to compress the air in two stages. This allows for higher pressure output and is commonly used in heavy-duty applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Reciprocating Air Compressors
Reciprocating air compressors offer several advantages, including their ability to generate high pressures and handle a wide range of air volumes. They are also relatively compact in size and can be easily transported. However, these compressors tend to have a higher maintenance requirement and can be noisier compared to other types of compressors. Additionally, reciprocating air compressors can have lower overall energy efficiency, especially when used for continuous operation.
Applications of Reciprocating Air Compressors
1. Industrial Manufacturing
Reciprocating air compressors are widely used in industrial manufacturing processes where compressed air is required. They play a crucial role in powering pneumatic tools, such as drills, impact wrenches, and nail guns. These tools are commonly used in various industries, including automotive, construction, and metal fabrication.
2. HVAC Systems
Reciprocating air compressors are commonly employed in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. They are used to power air conditioning units, which require compressed air to cool and dehumidify the air in buildings. The reliable and efficient performance of reciprocating air compressors ensures the effective operation of HVAC systems in a wide range of environments.
3. Refrigeration

Reciprocating air compressors are also used in refrigeration systems. These compressors play a vital role in maintaining the optimal temperature in refrigerators, freezers, and air conditioning units. By compressing the refrigerant gas, the compressor enables the cooling cycle, allowing the system to regulate the temperature and preserve perishable goods.
4. Automobile Industry
The automobile industry extensively relies on reciprocating air compressors for various applications. They are used in automotive painting processes, where compressed air is needed to power paint sprayers. Reciprocating air compressors are also utilized in tire inflation, air suspension systems, and engine combustion processes.
5. Energy Production
Reciprocating air compressors find applications in the energy production sector as well. They are used in power plants to provide compressed air for control systems, equipment operation, and the maintenance of various instruments. Additionally, reciprocating air compressors are utilized in oil and gas processing facilities for compression and transportation of gases.
6. Aerospace Industry

The aerospace industry extensively employs reciprocating air compressors for a wide range of applications. They are used in aircraft systems, such as landing gear operation, cabin pressurization, and pneumatic controls. The reliable and efficient performance of reciprocating air compressors is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of aircraft.
In conclusion, reciprocating air compressors have numerous applications across various industries. Their versatility, reliability, and efficiency make them essential tools for powering pneumatic equipment, cooling systems, refrigeration units, and more. From industrial manufacturing to aerospace, reciprocating air compressors play a vital role in ensuring smooth operations and efficient processes.
Advantages of Reciprocating Air Compressors
Reciprocating air compressors have several advantages that make them a popular choice for many applications.
1. Versatility

One of the biggest advantages of reciprocating air compressors is their versatility. They can be used in a wide range of industries and applications, from small workshops to large manufacturing plants. This versatility makes them a reliable and flexible choice for many different needs.
2. High pressure capability
Reciprocating air compressors are known for their high pressure capability. They can deliver high-pressure air, making them suitable for applications that require a significant amount of pressure, such as pneumatic tools, spray painting, and industrial processes. This high-pressure capability ensures that the compressor can handle even the toughest tasks.
3. Energy efficiency

Reciprocating air compressors are also known for their energy efficiency. They are designed to minimize energy consumption while maximizing air output. This means that they can provide a powerful air supply while using less energy, resulting in reduced operating costs and environmental impact.
4. Durability
Another advantage of reciprocating air compressors is their durability. They are built to withstand heavy use and demanding conditions, making them a reliable choice for continuous operation. The robust construction and high-quality components ensure that the compressor can withstand the rigors of daily use and provide long-lasting performance.
5. Easy maintenance
Reciprocating air compressors are relatively easy to maintain. They have a simple design with fewer components compared to other types of compressors, making maintenance and repairs more straightforward. Regular maintenance tasks, such as oil changes and filter replacements, can be easily performed, ensuring the compressor’s optimal performance and extended lifespan.
In conclusion, the advantages of reciprocating air compressors, including their versatility, high pressure capability, energy efficiency, durability, and easy maintenance, make them a reliable and practical choice for various industrial and commercial applications.
Disadvantages of Reciprocating Air Compressors
While reciprocating air compressors have many advantages, there are also some disadvantages to consider when using these types of compressors.
1. Size and Weight: Reciprocating air compressors tend to be larger and heavier than other types of compressors. This can make them more difficult to move and transport.
2. Noise Level: Reciprocating air compressors can be quite noisy when in operation. This can be a disadvantage in environments where noise levels need to be kept to a minimum.
3. Vibration: Reciprocating air compressors generate a lot of vibration during operation. This can cause damage to other equipment or structures if not properly isolated or supported.
4. Maintenance: Reciprocating air compressors require regular maintenance to keep them running smoothly. This can include oil changes, filter replacements, and general cleaning. Failure to perform regular maintenance can lead to decreased performance and potentially costly repairs.
5. Energy Efficiency: Reciprocating air compressors are not as energy efficient as some other types of compressors. They can consume more energy when running, which can result in higher operating costs over time.
While these disadvantages may be a consideration, they do not necessarily outweigh the benefits of using a reciprocating air compressor. It is important to evaluate the specific needs and requirements of your application before choosing a compressor type.
Maintenance of Reciprocating Air Compressors
Maintenance is crucial to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of reciprocating air compressors. Regular maintenance not only helps prevent unexpected breakdowns but also improves the overall efficiency of the compressor.
1. Daily Inspections
Performing daily inspections is essential to identify any potential issues before they escalate. Check for any oil or air leaks, loose bolts or belts, and abnormal noises during operation. Additionally, monitor the air pressure, temperature, and oil level regularly to ensure they are within the recommended range.
2. Lubrication

Proper lubrication is vital for the smooth operation of reciprocating air compressors. Regularly check and change the oil according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Insufficient or contaminated oil can lead to increased friction and wear, leading to decreased efficiency and potential damage to the compressor. Make sure to use the recommended oil type and level for optimal performance.
3. Air Filter Maintenance
The air filter plays a critical role in maintaining the air quality and preventing contaminants from entering the compressor. Check the air filter regularly and clean or replace it as necessary. A clogged air filter can lead to reduced airflow, strain the compressor, and decrease its efficiency.
4. Valve Maintenance
The valves in a reciprocating air compressor help control the flow of air during compression. Regularly inspect the valves for signs of wear, such as leaks or improper sealing. Clean or replace the valves if necessary to maintain optimal performance.
5. Cooling System Maintenance
The cooling system is essential to prevent the compressor from overheating. Regularly clean the cooling fins to remove any dust or debris that can hinder heat dissipation. Additionally, check the cooling fan for proper operation. Overheating can cause damage to the compressor components and reduce its lifespan.
By following these maintenance practices, you can ensure the reliable and efficient operation of your reciprocating air compressor. Remember to consult the manufacturer’s manual for specific maintenance instructions and schedules.
Choosing the Right Reciprocating Air Compressor
When it comes to selecting the right reciprocating air compressor, there are several factors to consider. One of the most important factors is the required air capacity. You need to determine the volume of air that your operations require in order to properly size the compressor. This can be calculated by considering factors such as the number of tools or equipment that will be connected to the compressor and their individual air consumption rates.
Another important factor to consider is the compressor’s horsepower (HP) rating. The HP rating will determine the compressor’s ability to deliver the required air capacity. Generally, a higher HP rating will provide a larger air capacity, but it’s important to choose a compressor that matches the specific needs of your operations. If you choose a compressor with too high of a HP rating, it may be inefficient and cost more to operate.
Pressure requirements are also an essential consideration when choosing a reciprocating air compressor. You need to determine the maximum pressure that your operations require and choose a compressor that can reliably provide that pressure. Additionally, it’s important to consider the compressor’s duty cycle, which refers to the amount of time the compressor can run continuously without overheating. Ensure that the compressor’s duty cycle matches the demands of your operations.
Other factors to consider include the compressor’s tank size and the type of drive system it uses. A larger tank size can provide a reserve of compressed air, reducing the need for the compressor to continuously run. The type of drive system, whether electric or gas-powered, will depend on the availability of power sources in your facility and the portability requirements of your operations.
- Reliability is an important consideration when choosing a reciprocating air compressor. Prioritize compressors from reputable manufacturers that have a track record of producing reliable and durable equipment. This will help ensure that your compressor will perform effectively and require minimal maintenance.
- Cost is also a factor to consider. While it’s important to choose a compressor that meets your operational needs, it’s equally important to consider your budget. Compare prices from different manufacturers and consider the long-term costs of operation, including energy efficiency and maintenance requirements.
- Noise level may be a consideration depending on the environment in which the compressor will be used. If noise is a concern, consider compressors that are designed to be quieter, such as those with noise reduction features.
By considering these factors and conducting thorough research, you can choose the right reciprocating air compressor that will meet the specific needs of your operations and provide reliable and efficient performance.
FAQ:
What is a reciprocating air compressor?
A reciprocating air compressor is a type of compressor that uses pistons to compress air. It works by drawing in air into a cylinder, then sealing the cylinder and compressing the air using a piston. It is commonly used in various industries and applications that require compressed air.
How does a reciprocating air compressor work?
A reciprocating air compressor works by using a piston and a cylinder to compress air. The piston moves back and forth inside the cylinder, drawing in air on the intake stroke and compressing it on the compression stroke. The compressed air is then stored in a tank or used directly for various applications.
What are the advantages of a reciprocating air compressor?
Reciprocating air compressors have several advantages. They are generally more affordable than other types of compressors, making them a popular choice for small businesses and individuals. They also have a high output, allowing them to provide large amounts of compressed air for various applications. Additionally, reciprocating air compressors are easy to maintain and repair.
Are there any drawbacks to using a reciprocating air compressor?
There are a few drawbacks to using a reciprocating air compressor. They tend to be louder and produce more vibrations than other types of compressors, which can be a concern in certain settings. They also require regular maintenance and lubrication to ensure proper functioning. Additionally, reciprocating air compressors are not as energy-efficient as some other types of compressors.
What are some common applications of reciprocating air compressors?
Reciprocating air compressors are commonly used in a variety of applications. They are often used in automotive shops for powering pneumatic tools such as impact wrenches and air ratchets. They are also used in industrial settings for powering equipment and machinery, as well as in construction for operating air-powered nail guns and paint sprayers. Reciprocating air compressors are also popular for home use, such as inflating tires and powering airbrushes.
How do I choose the right reciprocating air compressor for my needs?
When choosing a reciprocating air compressor, there are several factors to consider. First, determine your specific compressed air requirements, including the required pressure and airflow. Consider the power source, whether electric or gas-powered, and the available space for the compressor. Also, consider the compressor’s duty cycle, noise level, and maintenance requirements. Lastly, compare different models and brands to find the one that best fits your needs and budget.
What maintenance is required for a reciprocating air compressor?
A reciprocating air compressor requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. This includes checking and changing the oil, inspecting and replacing air filters, checking and tightening bolts and connections, and periodically draining condensate from the tank. It’s also important to keep the compressor clean and free from debris. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and schedule for maintenance is crucial to prolonging the lifespan of your compressor.
Video:













