When was the lathe invented: A historical overview

The invention of the lathe revolutionized the way people work with wood and metal. It is considered one of the oldest and most important tools in human history. The lathe is a machine that rotates a workpiece on its axis, allowing a craftsman to shape, cut, and drill with precision. Dating back to ancient times, the lathe has evolved and undergone various improvements over the centuries, creating a profound impact on industries and craftsmanship.
The origins of the lathe can be traced back to ancient Egypt, where the first lathe-like tools were used around 1300 BCE. These early lathes were powered by human or animal labor, and their purpose was mainly to turn wood and create cylindrical shapes. These simple lathes were made of two basic components: a spinning headstock and a tool rest for holding and guiding the cutting tool. They were primarily used in the production of household items, furniture, and weapons.
However, it was during the Hellenistic period that the lathe experienced significant advancements. Ancient Greek craftsmen, known for their innovation and precision, developed a more sophisticated version of the lathe. This new design featured tools mounted on a mechanical frame, allowing for greater control and precision in shaping wood and metal. The Greeks also introduced the concept of screw threads, which were used to secure the workpiece to the lathe and facilitate precise cutting and drilling.
Over the centuries, the lathe continued to evolve and improve with advancements in technology. During the Industrial Revolution in the 18th century, steam power began to replace human or animal labor, leading to the development of the steam-powered lathe. This innovation increased the efficiency and productivity of lathes, enabling the mass production of various products. Today, modern lathes are powered by electricity and equipped with advanced features, such as computer numerical control (CNC) systems, further enhancing their accuracy and versatility.
In conclusion, the invention of the lathe has had a profound impact on human civilization, transforming the way we work with wood and metal. From its humble beginnings in ancient Egypt to the advanced machines we have today, the lathe remains a crucial tool in various industries, including woodworking, metalworking, and manufacturing. It has played a significant role in the development of intricate designs, precision engineering, and mass production. As technology continues to advance, we can only imagine what further innovations and improvements will come to this essential tool in the future.
When was the lathe invented
The lathe is one of the oldest tools in human history. Its origins can be traced back to ancient Egypt around 1300 BC. However, the concept of a lathe predates this, with evidence of similar tools being used in ancient Mesopotamia and China.
In ancient Egypt, the lathe was used primarily for woodworking and turning of objects such as bowls and furniture legs. The lathe consisted of a rotating spindle, which was operated by hand or foot, and a cutting tool that was used to shape the wood.
During the Middle Ages, the lathe underwent significant improvements and became an essential tool in metalworking as well. The introduction of a mechanical drive system, known as the “spring pole lathe,” allowed for greater precision and control in shaping metal objects.
It wasn’t until the Industrial Revolution in the 18th century that the lathe underwent further advancements and became a machine tool. The invention of the steam engine led to the development of the steam-powered lathe, which greatly increased productivity and efficiency in manufacturing.
Since then, the lathe has continued to evolve with the introduction of electric and computer numerical control (CNC) technologies. These advancements have further improved precision, speed, and versatility in lathe operations.
Today, lathes are used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. They are essential tools for shaping and machining various materials, such as wood, metal, and plastic.
Summary:
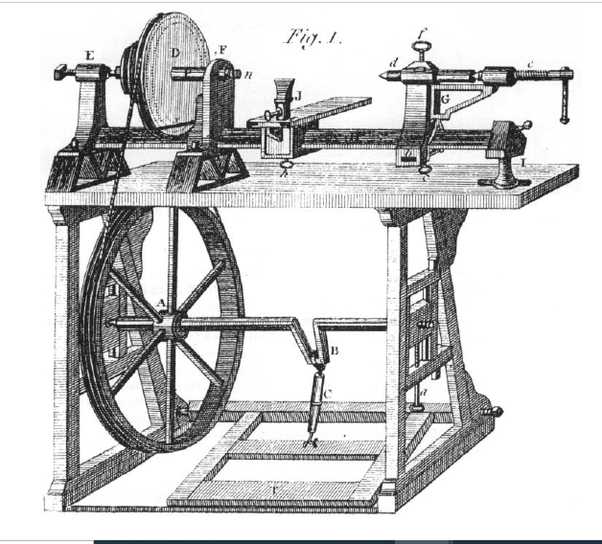
- The lathe was invented around 1300 BC in ancient Egypt but has roots in even earlier civilizations.
- It was primarily used for woodworking but later became an important tool in metalworking.
- Advancements during the Industrial Revolution led to steam-powered lathes and increased productivity.
- Modern lathes employ electric and CNC technologies for improved precision and efficiency.
- The lathe remains a crucial tool in many industries today.
The Origins of the Lathe
The lathe is one of the oldest and most important tools in human history. Its origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations that existed thousands of years ago. The lathe has played a crucial role in shaping the development of various industries and technologies.
Ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt
The early origins of the lathe can be found in ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt. In these civilizations, artisans and craftsmen used simple lathes to shape wood and stone. The lathe allowed them to create intricate designs and precise shapes that would have been impossible to achieve by hand alone.
Archaeological evidence suggests that the lathe was used in ancient Mesopotamia as early as 1300 BCE. The Egyptians also used lathes, as evidenced by the beautifully crafted pottery and stone objects that have been discovered from this period.
The Middle Ages
During the Middle Ages, the lathe reached new levels of sophistication. This was due in part to advancements in engineering and metallurgy. The introduction of iron and steel made it possible to create stronger and more durable lathe components, allowing for more precise and intricate work.
One notable development during this period was the invention of the pedal-operated lathe. This allowed craftsmen to use both hands to manipulate the workpiece while controlling the lathe’s rotation with their feet. This innovation greatly increased productivity and efficiency.
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution marked a significant turning point in the history of the lathe. The invention of steam power and the development of new machining techniques revolutionized the manufacturing process. The lathe became an essential tool in factories, enabling mass production on a scale never before seen.
During this time, lathes evolved from manual-operated machines to powered machines. The introduction of electric motors allowed for even greater precision and control over the lathe’s movements. This technological advancement paved the way for modern lathes that we use today.
In conclusion, the lathe has a rich and storied history that spans thousands of years. From its humble beginnings in ancient civilizations to its pivotal role in the Industrial Revolution, the lathe has been instrumental in shaping the course of human civilization.
Ancient Lathe Tools
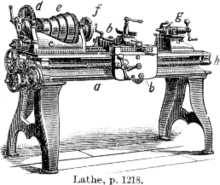
Ancient civilizations had developed a variety of lathe tools that were used for different purposes. These tools allowed craftsmen to shape and carve materials such as wood, bone, and metal with precision and detail. Here are some examples of ancient lathe tools:
Bow Lathe
The bow lathe is one of the earliest types of lathe tools, dating back to ancient Egypt around 1300 BC. It consisted of a bow-shaped piece of wood or metal, with a string attached to both ends. By pulling and pushing the string, the craftsmen could rotate the workpiece and shape it using a cutting tool.
Foot-Powered Lathe
The foot-powered lathe is another ancient lathe tool that was widely used in Roman and medieval times. This tool had a pedal operated by the craftsman’s foot, which would rotate the workpiece. This allowed the craftsmen to have both hands free to manipulate the cutting tool and create intricate designs on the workpiece.
Hand Lathe
The hand lathe was commonly used in ancient Greece and Rome. It was a lightweight and portable tool that could be operated by hand. The craftsmen would manually rotate the workpiece by turning a handle or crank. This type of lathe was suitable for smaller and more delicate tasks.
Engine Lathe (Orbital Lathe)
The engine lathe, also known as the orbital lathe, was developed in ancient China during the Han dynasty (202 BC-220 AD). It was powered by water or animal mechanisms and had a horizontal axis of rotation. This allowed craftsmen to create cylindrical shapes and spirals with greater precision and efficiency.
These ancient lathe tools played a crucial role in the advancement of craftsmanship and manufacturing techniques. They laid the foundation for the development of modern lathes and continue to inspire and influence contemporary artisans in their work.
The Renaissance and Lathe Development
During the Renaissance period, from the 14th to the 17th century, there was a significant advancement in the field of lathe development. This period witnessed a renewed interest in science, arts, and technology, which contributed to the improvements in lathe design and functionality.
Leonardo da Vinci:
One of the prominent figures during the Renaissance who made significant contributions to the development of the lathe was Leonardo da Vinci. Da Vinci, a renowned artist, engineer, and inventor, studied and sketched various machine designs, including those related to lathes.
Expanding Applications:
The Renaissance period saw an expansion in the range of applications for lathes. While lathes were primarily used for woodworking purposes in ancient times, their usage expanded to include metalworking and ornamental turning during the Renaissance. This led to innovations in lathe design and the development of specialized lathes for specific tasks.
Invention of Pedal Lathe:
One significant development during the Renaissance was the invention of the pedal lathe. This type of lathe was operated using pedals, allowing for greater ease and control in turning objects. The pedal lathe revolutionized the field of woodturning and enabled craftsmen to create more intricate and precise designs.
Lathe Artistry:
The Renaissance period was also characterized by a growing emphasis on artistic expression. This newfound focus on aesthetics influenced the development of lathes, as craftsmen strived to create intricate and visually appealing designs. Ornamental turning became a popular practice, and specialized lathes capable of producing complex patterns and shapes were developed.
Improvements in Lathe Design:
The Renaissance period witnessed numerous improvements in lathe design. These included the introduction of various accessories and attachments, such as the tool rest and the faceplate, which allowed for greater precision and control during turning. The development of screw-cutting capabilities also revolutionized lathe use, enabling the production of threads and screws.
The Influence of the Renaissance:
The Renaissance was a pivotal period in the history of lathe development. The renewed interest in science, arts, and technology paved the way for significant advancements in lathe design and functionality. The inventions and ideas from this period laid the foundation for further innovations in the centuries to come.
The Industrial Revolution and Lathe Innovation
The Industrial Revolution, which spanned from the late 18th to the early 19th century, was a period of significant technological advancement and social change. During this time, the invention and improvement of various machines revolutionized industries and manufacturing processes. The development of the lathe played a crucial role in this transformation.
The Need for Lathe Innovation
Before the Industrial Revolution, lathes were primarily operated manually and were limited in their capabilities. They were typically used for shaping wood and metal by rotating the material against a cutting tool. However, the increasing demand for precision and efficiency called for new and improved lathe designs.
In response to these needs, inventors and machinists began developing innovative lathes that could perform more complex tasks and produce higher-quality products at a faster pace.
Key Lathe Innovations During the Industrial Revolution
Several significant lathe innovations emerged during the Industrial Revolution, bringing about a paradigm shift in manufacturing processes and capabilities:
- Engine Lathe: One of the most important lathe inventions was the engine lathe. It was powered by a steam engine, allowing for automated and continuous rotational movement. This innovation greatly increased the production speed and efficiency of lathe operations.
- Turret Lathe: The turret lathe, introduced in the early 19th century, featured a movable tool head that could hold multiple cutting tools. This design enabled the lathe to perform various operations and transitions without the need for manual tool changes, saving time and effort.
- Screw-Cutting Lathe: The invention of the screw-cutting lathe revolutionized thread production. Prior to this innovation, creating screws was a labor-intensive process. The screw-cutting lathe allowed for precise and efficient production of screws and threaded parts, contributing to advancements in machinery and technology.
The Impact of Lathe Innovation
The innovations in lathe technology during the Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on manufacturing industries and the overall economy:
- Mass Production: Automated and more efficient lathe operations enabled mass production of standardized parts, contributing to the growth of industries such as textiles, transportation, and machinery.
- Improved Precision: The increased capabilities of lathes allowed for higher precision in shaping materials, resulting in the production of more accurate and better-performing components.
- Greater Versatility: With the introduction of advanced lathe designs, manufacturers were able to diversify their product offerings and explore new markets, leading to economic growth and expansion.
In conclusion, the Industrial Revolution brought about significant advancements in lathe technology, transforming manufacturing processes and revolutionizing various industries. The innovations in lathes such as the engine lathe, turret lathe, and screw-cutting lathe paved the way for mass production, improved precision, and greater versatility in manufacturing.
Lathe Innovations in the 20th Century
In the 20th century, the development of lathe machinery experienced significant advancements and innovations. These innovations revolutionized the capabilities and efficiency of lathes, enabling them to meet the demands of various industries and applications.
1. Introduction of Electric Motors
One significant innovation in the 20th century was the introduction of electric motors to power lathes. Prior to this, lathes were usually driven by belt systems connected to steam engines or other power sources. Electric motors provided a more reliable and convenient power source, allowing lathes to be used in a wider range of settings.
2. Automatic and CNC Control

Another major innovation was the introduction of automatic and computer numerical control (CNC) systems. Automatic lathes, also known as screw machines, could perform repetitive machining operations without constant manual supervision. CNC lathes, on the other hand, utilized computer control to precisely guide the cutting tools and perform complex operations with ease.
CNC lathes offered improved accuracy and repeatability, allowing for the precise production of intricate and complex parts. These machines played a crucial role in the development of industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
3. Introduction of Turret Lathes
Turret lathes, also known as capstan lathes, were another significant innovation in the 20th century. These machines featured a rotating turret that held multiple cutting tools, allowing for rapid tool changes and increased productivity. Turret lathes were especially useful for mass production, as they allowed for the simultaneous machining of multiple components.
4. Advancements in Cutting Tools and Materials
Throughout the 20th century, advancements in cutting tools and materials greatly improved the performance and versatility of lathes. The development of high-speed steel (HSS) cutting tools provided increased cutting speeds and tool life. Later, the introduction of carbide and ceramic cutting tools further enhanced cutting capabilities.
Additionally, the use of new materials such as carbide and diamond tooling inserts allowed for the effective machining of harder materials, such as alloys and hardened steels.
5. Integration of Digital Control Systems
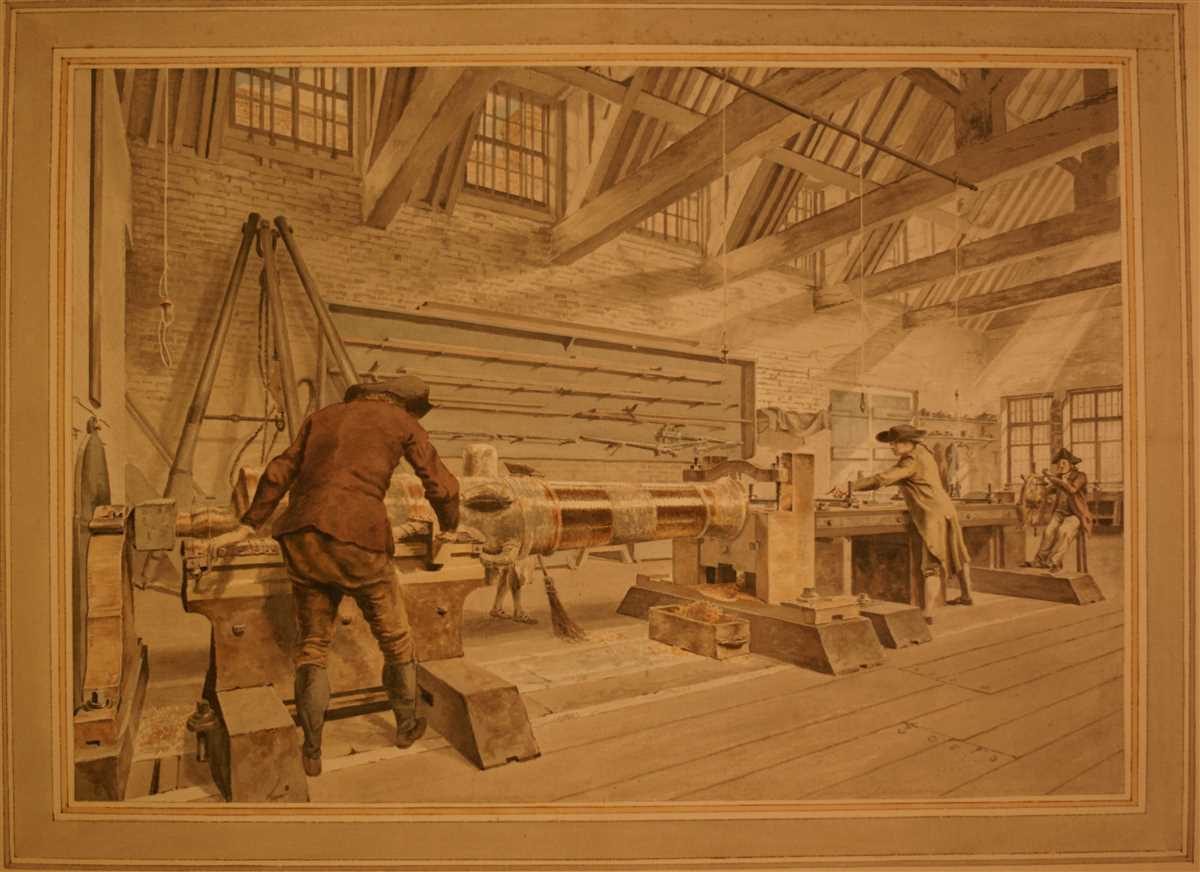

Towards the end of the 20th century, lathe machines benefited from the integration of digital control systems. These systems enabled the programming and storage of complex tool paths, further increasing productivity and accuracy. Operators could now create intricate designs and patterns on a computer, which the lathe would replicate precisely.
Conclusion
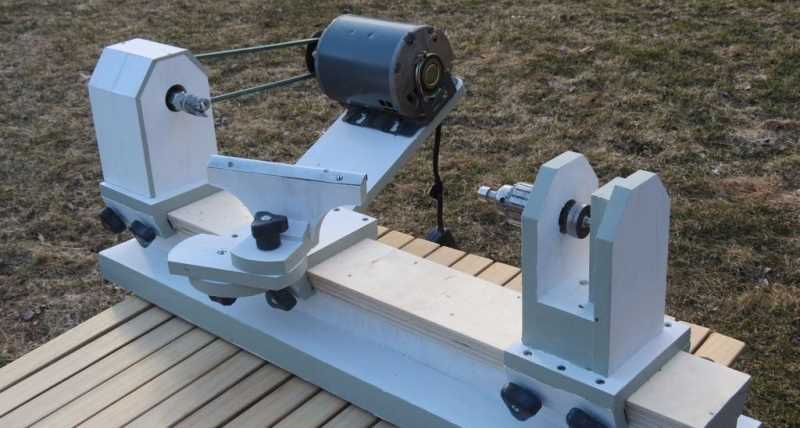

The innovations in lathe machinery in the 20th century greatly expanded their capabilities and made them indispensable tools in a wide range of industries. From the introduction of electric motors and automatic control systems to the advancements in cutting tools and materials, these innovations continue to shape and improve lathe technology to this day.
Lathe Technology Today
CNC Lathes
One of the most significant advancements in lathe technology is the introduction of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) lathes. CNC lathes use computerized systems to control the movement and operation of the lathe. This technology has greatly increased the precision and efficiency of lathe operations.
Automation and Robotics
Another major development in lathe technology is the integration of automation and robotics. Automated lathes have the ability to perform tasks without human intervention, improving productivity and reducing labor costs. Robotic systems can also be integrated with lathes to automate material handling and tool changes, further enhancing productivity.
High-Speed Machining
The advent of high-speed machining has revolutionized lathe operations. High-speed lathes are capable of rotating at much higher speeds than traditional lathes, allowing for faster cutting and improved surface finish. This technology has enabled industries to achieve higher levels of productivity and precision.
Multi-Axis Lathes
Multi-axis lathes are another notable advancement in lathe technology. These machines have the capability to simultaneously control multiple axes of movement, allowing for more complex and intricate machining operations. Multi-axis lathes offer increased flexibility and can produce parts with higher complexity and precision.
Advanced Cutting Tools
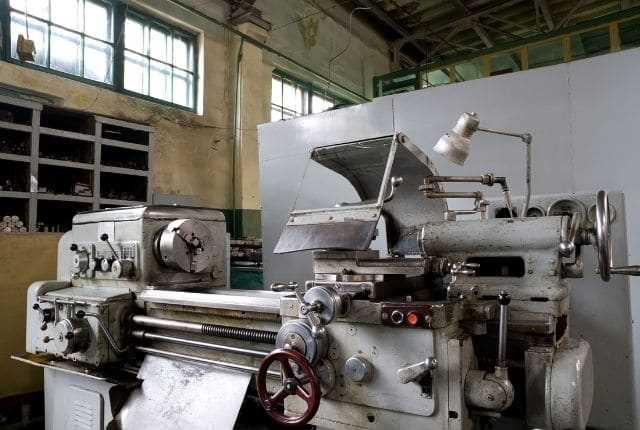

The development of advanced cutting tools has also contributed to the evolution of lathe technology. Modern lathe cutting tools are made from high-performance materials and feature advanced coatings, which enhance their durability and cutting performance. These tools allow for more efficient machining processes and extended tool life.
Integration of IoT and Data Analytics
With the emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics, lathe technology has seen further advancements. IoT-enabled lathes can collect and analyze data in real-time, providing valuable insights into machine performance, tool wear, and maintenance needs. This enables proactive maintenance, reduces downtime, and improves overall productivity.
Environmental Considerations

Modern lathe technology also takes into account environmental considerations. Many lathe machines now incorporate energy-saving features such as variable frequency drives and automatic power-off functions. Additionally, measures are taken to reduce noise and vibration levels, ensuring a safer and more comfortable working environment.
Industry 4.0 Integration
The integration of lathe technology with Industry 4.0 concepts is another trend in the field. As part of the fourth industrial revolution, lathe machines are being connected to digital networks and integrated into smart manufacturing systems. This enables real-time monitoring, remote control, and seamless communication between machines, optimizing production processes.
| Advancement | Description |
|---|---|
| CNC Lathes | Computer Numerical Control systems improve precision and efficiency. |
| Automation and Robotics | Automated lathes and robotic systems enhance productivity. |
| High-Speed Machining | High-speed lathes enable faster cutting and improved surface finish. |
| Multi-Axis Lathes | Multi-axis machines allow for complex and precise machining operations. |
| Advanced Cutting Tools | High-performance tools enhance machining efficiency and tool life. |
| Integration of IoT and Data Analytics | IoT-enabled lathes provide real-time data insights for proactive maintenance. |
| Environmental Considerations | Energy-saving features and noise reduction measures improve working conditions. |
| Industry 4.0 Integration | Lathe machines are connected and integrated into smart manufacturing systems. |
The Importance of the Lathe in Modern Manufacturing
The lathe is an essential tool in modern manufacturing processes. It allows for the production of precise and complex parts that are used in a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical.
1. Precision and Accuracy
One of the main reasons why the lathe is so important in modern manufacturing is its ability to produce parts with high precision and accuracy. The lathe uses a cutting tool to remove material from the workpiece, allowing for the creation of intricate shapes and tight tolerances.
With the lathe, manufacturers can create parts that meet the exact specifications required by their customers. This is particularly important in industries where precision is crucial, such as aerospace and medical manufacturing.
2. Versatility
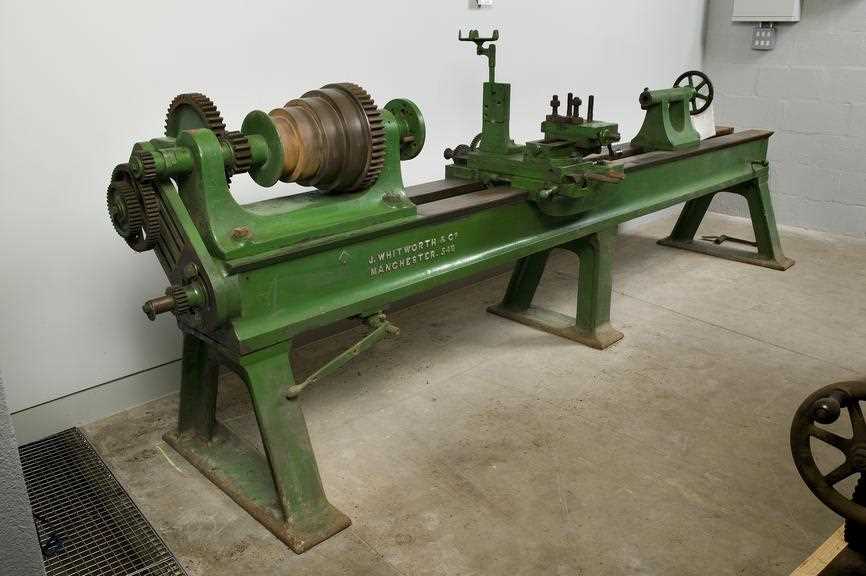

The lathe is also highly versatile, capable of producing a wide range of parts. It can be used to create cylindrical shapes, such as shafts and bolts, as well as more complex components, including gears and splines.
Furthermore, the lathe can work with various materials, such as metal, wood, and plastics. This versatility makes the lathe a valuable tool in many manufacturing processes, allowing manufacturers to produce a diverse range of products.
3. Efficiency and Productivity
Another key factor in the importance of the lathe is its ability to improve efficiency and productivity in manufacturing processes. The lathe can automate many tasks that would otherwise require manual labor, resulting in faster production times and increased output.
In addition, the lathe can perform multiple operations in a single setup, reducing the need for multiple machines and setups. This streamlines the manufacturing process, saving time and resources.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
By improving efficiency and productivity, the lathe also contributes to cost-effectiveness in modern manufacturing. The ability to produce parts with high precision and accuracy reduces waste and the need for rework.
Furthermore, the versatility of the lathe allows manufacturers to consolidate their production processes, eliminating the need for multiple machines and reducing overhead costs. This makes the lathe a cost-effective tool for businesses in various industries.
5. Innovation and Advancements
Finally, the lathe continues to drive innovation and advancements in modern manufacturing. As technology advances, lathes are equipped with more advanced features and capabilities, such as computer numerical control (CNC) systems.
CNC lathes offer increased automation, accuracy, and flexibility, further enhancing the capabilities of the lathe. These advancements enable manufacturers to push the boundaries of what is possible in terms of part complexity and precision.
In conclusion, the lathe plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing. Its precision, versatility, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and contribution to innovation make it an essential tool for the production of high-quality parts.
The Future of Lathe Technology
1. Automation and Advanced Control Systems
One of the major trends in the future of lathe technology is the increasing automation and the development of advanced control systems. As technology advances, lathe machines are becoming more automated, reducing the need for manual intervention and improving efficiency.
Advanced control systems equipped with AI algorithms and machine learning capabilities can monitor and adjust various parameters during the machining process to optimize performance. This not only improves the accuracy and precision of the lathe but also reduces the risk of errors and improves productivity.
2. Integration of IoT and Connectivity

An emerging trend in lathe technology is the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and connectivity features. IoT-enabled lathes can be connected to a network, allowing for real-time monitoring, data analysis, and remote control.
With IoT integration, operators can monitor the performance of the lathe, track maintenance needs, and perform diagnostics from anywhere, improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). The connectivity also enables seamless integration with other manufacturing systems, such as CAD/CAM software and ERP systems.
3. Additive Manufacturing and Hybrid Machines
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is rapidly advancing and has the potential to revolutionize lathe technology. Hybrid machines that combine traditional subtractive manufacturing processes with additive manufacturing capabilities are being developed.
These hybrid machines can combine the benefits of both technologies, allowing for the creation of complex geometries and the ability to build up parts layer by layer. This opens up new possibilities in terms of design flexibility and the production of customized or unique components.
4. Advanced Materials and Coatings
The future of lathe technology also involves the use of advanced materials and coatings. As industries demand higher-performance components, there is a need for materials with improved mechanical properties, such as higher strength, hardness, and heat resistance.
New materials, such as superalloys and composites, are being developed that can withstand extreme conditions and provide superior performance. Additionally, advanced coatings, such as diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings, can reduce friction and wear, extending the tool life and improving the surface finish.
5. Enhanced User Interfaces and Experience
Last but not least, the future of lathe technology focuses on improving user interfaces and overall user experience. While lathe machines have become more advanced, the interfaces and controls have often remained complex and intimidating.
Efforts are being made to create user-friendly interfaces, intuitive controls, and visual feedback systems that make it easier for operators to interact with the lathe and understand the machining process. This can help reduce operator error and shorten the learning curve for new users.
In conclusion, the future of lathe technology is filled with automation, connectivity, additive manufacturing, and advancements in materials and coatings. These developments aim to improve efficiency, accuracy, and productivity while enhancing the user experience for operators.
FAQ
Who invented the lathe?
The lathe was not invented by a single person, but its origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians and the Greeks, who used simple turning machines.
When was the lathe first invented?
The lathe can be traced back to ancient times, as early as the Egyptians in 1300 BC. However, the modern lathe as we know it today began to take shape during the Industrial Revolution in the 18th century.
What is the history of the lathe?
The history of the lathe dates back to ancient civilizations, where simple turning machines were used. Over time, the lathe evolved and became more complex. During the Industrial Revolution, the lathe underwent significant advancements, leading to the development of modern lathes with improved precision and functionality.
How has the lathe changed over time?
The lathe has undergone significant changes over time. From its humble beginnings as a simple turning machine in ancient civilizations, it has evolved into a complex tool during the Industrial Revolution. With advancements in technology, modern lathes have become more precise, efficient, and versatile, offering a wide range of capabilities for various industries and applications.













