What is a Swiss Lathe: Understanding the Basics

In the world of machining, there are many types of lathes that are used to shape and cut materials. One such type is the Swiss lathe, also known as a Swiss screw machine. This type of lathe is unique in its design and functionality, making it a popular choice for precision machining.
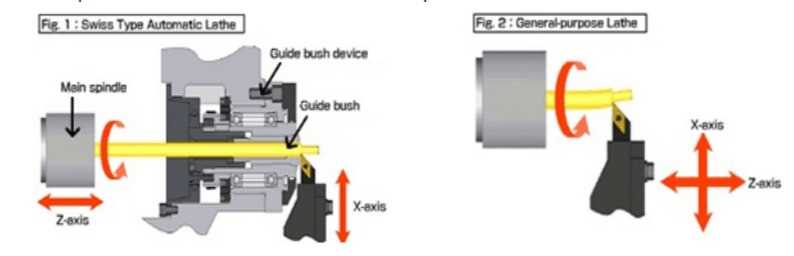
So, what exactly is a Swiss lathe? Unlike traditional lathes, which hold the workpiece in a fixed position and rotate the cutting tool, a Swiss lathe holds the cutting tool in a fixed position and rotates the workpiece. This design allows for more precise and intricate machining, especially for small, complex parts.
The Swiss lathe was first developed in the late 19th century in Switzerland, hence its name. It revolutionized the machining industry with its ability to produce complex parts with high precision. Since then, the design and capabilities of Swiss lathes have evolved, incorporating advanced technology and features.
How Swiss Lathe Works
1. Introduction
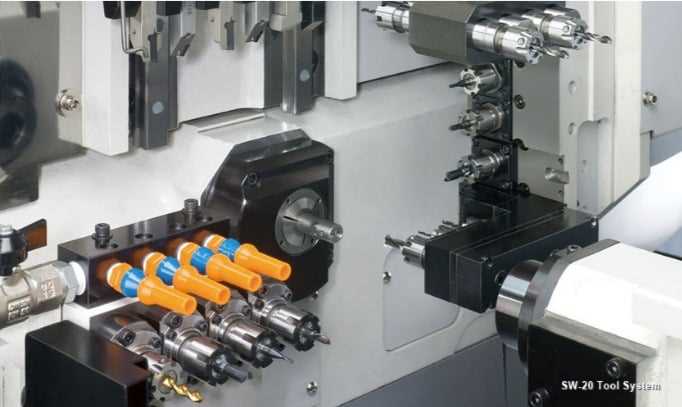

A Swiss lathe, also known as a Swiss-type lathe or Swiss screw machine, is a type of lathe that is specifically designed for high-precision machining. It is widely used in the manufacturing industry for producing small and complex parts with tight tolerances.
2. Operation
The main characteristic of a Swiss lathe is its sliding headstock. Unlike a traditional lathe, where the workpiece rotates and the cutting tools are stationary, in a Swiss lathe, the cutting tools are held by the headstock and the workpiece is stationary. The headstock slides along the Z-axis and moves the cutting tools into the workpiece to perform the machining operations.
This setup provides several advantages:
- Greater precision: The stationary workpiece and moving cutting tools allow for more accurate machining, resulting in parts with tighter tolerances.
- Reduced vibration: By keeping the workpiece stationary, the Swiss lathe minimizes the vibration during the machining process, leading to improved surface finish.
- Increased productivity: The simultaneous machining of multiple parts and the ability to perform multiple operations in a single setup increase the production efficiency.
3. Guide Bushing
Another important component of a Swiss lathe is the guide bushing. It is a cylindrical bushing that acts as a support for the workpiece during machining. The guide bushing is positioned close to the cutting area and provides stability and rigidity, reducing deflection and ensuring precision.
4. Bar Feeder

To feed the workpiece into the machine, Swiss lathes are equipped with a bar feeder. The bar feeder holds a long bar stock, typically of round shape, and feeds it through the guide bushing into the lathe. This allows for continuous and uninterrupted machining, as the lathe can automatically grab and release the bar stock as needed.
5. CNC Control
Most modern Swiss lathes are equipped with computer numerical control (CNC) systems, which provide precise control over the machining process. The CNC control allows for the programming of complex tool paths, automatic tool changes, and real-time monitoring of the machining operations.
6. Applications
The Swiss lathe is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics, where small and intricate parts with high precision are required. It is especially suitable for manufacturing components such as screws, bolts, pins, and other small cylindrical parts.
7. Conclusion
The Swiss lathe is a specialized machine tool that offers exceptional precision and productivity for the machining of small and complex parts. Its unique design and features make it an essential tool in various industries where precision and efficiency are paramount.
Main Components of a Swiss Lathe
1. Headstock
The headstock is an essential component of a Swiss lathe. It houses the main spindle that rotates the workpiece. The headstock is responsible for providing the required power and speed to the spindle for cutting and machining operations. It also helps in maintaining the accuracy and stability of the lathe.
2. Guide Bushing
A guide bushing is a critical component that is used in Swiss lathes. It is located close to the cutting tools and is responsible for guiding the bar stock material while it is being machined. The guide bushing helps in reducing the vibrations and deflections, resulting in improved precision and surface finish of the machined parts.
3. Bar Stock Material
The bar stock material is the raw material used in Swiss lathes. It is a long, cylindrical metal rod that is fed through the guide bushing and clamped in the headstock for machining. The Swiss lathe uses the bar stock material to produce high-precision turned parts with tight tolerances.
4. Cutting Tools
The cutting tools are mounted on the tool holders and are responsible for cutting and shaping the bar stock material. Swiss lathes use various types of cutting tools, such as turning tools, boring tools, threading tools, and grooving tools, to perform different machining operations.
5. Tool Holders
Tool holders are used to secure and position the cutting tools in the Swiss lathe. They provide stability and allow for quick tool changes when different machining operations are required. The tool holders are designed to accommodate different types and sizes of cutting tools.
6. Sub-Spindle
The sub-spindle is an additional spindle that is located opposite the main headstock. It allows for simultaneous machining on both ends of the workpiece, reducing the need for multiple setups. The sub-spindle can hold and rotate the workpiece independently, enabling complex machining operations.
7. Live Tooling
Live tooling refers to the rotary tooling attachments that are mounted on the tool holders. These tools can rotate and perform various operations, such as drilling, milling, and tapping, while the workpiece is being machined. Live tooling adds versatility to the Swiss lathe, allowing for more complex and multi-tasking machining operations.
8. Control Panel
The control panel is where the operator can control and monitor the Swiss lathe’s operation. It includes buttons, knobs, and displays that allow the operator to set the desired parameters, such as spindle speed, feed rate, and tool movement. The control panel is essential for programming and operating the Swiss lathe efficiently.
9. Coolant System
A Swiss lathe requires a coolant system to remove heat and lubricate the cutting area during machining. The coolant system helps in maintaining the temperature of the cutting tools and workpiece, preventing any damage or tool wear. It also helps in flushing away chips and swarf from the machining area to ensure smooth and efficient operations.
Advantages of Using a Swiss Lathe
The use of Swiss lathes in the manufacturing industry offers several advantages over conventional lathes. These advantages make Swiss lathes a popular choice for precision machining applications. Here are some of the key benefits of using a Swiss lathe:
1. High Precision
A Swiss lathe is designed to provide exceptional precision during machining operations. The machine’s sliding headstock design allows for precise and accurate turning of small diameter workpieces. It can hold tight tolerances and produce complex shapes with ease, making it ideal for manufacturing components that require high accuracy.
2. Increased Productivity
The Swiss lathe’s ability to perform multiple operations simultaneously greatly enhances productivity. With the integration of various tooling stations, a Swiss lathe can perform turning, drilling, milling, and tapping operations in a single setup. This reduces the need for multiple machines and setups, saving time and increasing throughput.
3. Cost Efficiency
The combination of high precision and increased productivity makes Swiss lathes a cost-effective solution. The ability to produce complex parts in a single setup reduces production time and eliminates the need for additional finishing processes. This leads to significant cost savings and improved overall efficiency.
4. Versatility
Swiss lathes are known for their versatility. They can handle a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, allowing for flexibility in manufacturing various components. The ability to machine small, intricate parts with precision makes Swiss lathes suitable for industries such as medical, aerospace, and electronics.
5. Reliability and Durability
Swiss lathes are built to be robust and durable. They are designed to handle high-speed operations and heavy workloads while maintaining accuracy. This ensures the longevity of the machine and reduces the risk of unexpected downtime or maintenance, resulting in improved reliability and uninterrupted production.
6. Time Savings
The Swiss lathe’s ability to perform multiple operations in one setup not only increases productivity but also saves valuable time. The reduced setup time and quick changeover between different tooling stations enable faster machining of complex parts. This can lead to shorter lead times, giving manufacturers a competitive edge in delivering products to the market.
7. Enhanced Tool Life
Swiss lathes are equipped with high-quality cutting tools and advanced tooling systems. These systems are designed to optimize tool life and performance, resulting in reduced tooling costs. The machine’s ability to handle small workpieces with precision also reduces tool wear, further extending tool life and improving overall cost-effectiveness.
In conclusion, the advantages of using a Swiss lathe include high precision, increased productivity, cost efficiency, versatility, reliability, time savings, and enhanced tool life. These benefits make Swiss lathes an excellent choice for manufacturers who require precision machining capabilities and improved efficiency.
Applications of Swiss Lathe
The Swiss lathe, also known as a Swiss-type lathe or Swiss screw machine, is a specialized type of lathe used for precision machining. Its unique design and functionality make it well-suited for a variety of applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics.
1. Precision Turning
- The Swiss lathe is capable of producing small, complex parts with high precision and accuracy.
- It is commonly used for turning operations, such as creating shafts, pins, and screws, with tight tolerances.
- Its ability to perform multiple operations in a single setup reduces the need for additional machining processes.
2. Micro Machining
- The Swiss lathe excels at micro machining, which involves the fabrication of extremely small parts with dimensions in the micrometer range.
- It is used for producing intricate components used in electronics, optical devices, and medical devices.
- The machine’s high precision and stability allow for the creation of miniaturized parts with complex geometries.
3. High Volume Production
- The Swiss lathe is well-suited for high volume production due to its rapid machining capabilities.
- It can efficiently produce large quantities of small parts with minimal setup time.
- Its automatic bar feed system facilitates continuous production, reducing the need for manual intervention.
4. Medical Industry

- The medical industry extensively uses Swiss lathes for manufacturing precision components used in surgical instruments, implants, and medical devices.
- These machines can produce complex medical parts with tight tolerances, ensuring compatibility and reliability.
- Materials commonly machined include titanium, stainless steel, and various biocompatible alloys.
5. Aerospace Industry
- The aerospace industry utilizes Swiss lathes for manufacturing critical components, such as turbine blades, fuel system parts, and connectors.
- These machines are capable of machining tough materials, including high-performance alloys, that are used in aerospace applications.
- Swiss lathes are suitable for producing complex geometries and achieving the required surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
6. Electronics Industry
- In the electronics industry, Swiss lathes are used for producing small parts such as connectors, pins, and terminals.
- These machines can manufacture components with high precision and repeatability, ensuring proper electrical connections.
- Swiss lathes also enable cost-effective production of complex parts used in electronic devices.
Overall, the Swiss lathe offers versatility and precision, making it a popular machine for a wide range of applications. Its ability to handle small, complex parts with high accuracy and efficiency makes it an indispensable tool in industries that require precision machining.
Choosing the Right Swiss Lathe
When it comes to choosing the right Swiss lathe, there are several factors to consider. The Swiss lathe is a versatile and precision machine that can handle a wide range of manufacturing tasks. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind when selecting a Swiss lathe:
1. Size and Capacity
One important factor to consider is the size and capacity of the Swiss lathe. Depending on your specific needs, you may require a larger or smaller machine. Consider the maximum bar diameter and length that the lathe can handle, as well as the maximum swing over the bed and the maximum length of the workpiece.
2. Tooling Options
Another crucial factor to consider is the tooling options available for the Swiss lathe. Different machines may have different tooling configurations and options. It’s important to choose a lathe that offers the right tooling options to meet your specific machining requirements. Consider the number of tool positions available and the types of tools that can be used.
3. Control System
The control system of the Swiss lathe is another important consideration. There are different types of control systems available, including manual, semi-automatic, and fully-automatic. Think about the level of automation and precision you require for your machining tasks and choose a lathe with a suitable control system.
4. Accuracy and Precision
For precision machining tasks, accuracy and precision are of utmost importance. When selecting a Swiss lathe, consider the machine’s accuracy and precision specifications. Look for features such as high spindle accuracy, minimal runout, and tight tolerances to ensure that the lathe can deliver the level of precision you need.
5. Maintenance and Support
Lastly, it’s important to consider the maintenance and support options available for the Swiss lathe. Look for a reliable manufacturer or supplier that offers good customer support and maintenance services. Regular maintenance and support are essential for keeping the lathe in optimal condition and minimizing downtime.
By considering these factors, you can choose the right Swiss lathe that meets your specific manufacturing needs and helps you achieve high-quality and precise machining results.
Tips for Operating a Swiss Lathe
Operating a Swiss lathe can be a complex task, but with some practice and knowledge, you can become proficient in using this type of machine. Here are some tips to help you operate a Swiss lathe effectively:
1. Understand the Machine’s Functions
Before operating a Swiss lathe, take the time to familiarize yourself with its various functions and features. This includes understanding the different controls, tooling options, and how to properly set up the machine for specific tasks. Refer to the machine’s manual or seek guidance from experienced operators if needed.
2. Choose the Right Tooling
The selection of tooling plays a crucial role in the performance and accuracy of a Swiss lathe. Ensure that you choose the appropriate cutting tools, inserts, and holders for the material you are working with. Using the right tooling will improve your productivity and reduce the chances of tool breakage.
3. Set Up the Machine Correctly
Proper setup is essential for achieving accurate and consistent results with a Swiss lathe. Make sure the workpiece is securely clamped in the machine’s collet or chuck and that the machine is properly aligned. Use dial indicators and other measuring tools to ensure the workpiece is correctly positioned before starting the machining process.
4. Pay Attention to Chip Control
Effective chip control is crucial for maintaining the quality of the machined parts and preventing damage to the machine. Use appropriate cutting speeds, feed rates, and coolant or lubrication to ensure chips are effectively removed from the cutting zone. Regularly inspect and clean the chip conveyor to prevent chip buildup that can cause tooling issues.
5. Monitor and Adjust Cutting Parameters
During operation, it is important to monitor the cutting parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut. Pay attention to tool wear and make necessary adjustments to maintain the desired cutting performance. Use tool life management systems or software to track tool usage and schedule timely tool changes.
6. Practice Good Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for a Swiss lathe to operate at its best. Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance recommendations for lubrication, cleaning, and inspection of critical components. Keep an eye out for signs of wear or damage and address any issues promptly to prevent costly breakdowns and ensure accuracy.
7. Seek Continuous Learning
Operating a Swiss lathe is a skill that can be continuously improved. Stay updated with the latest advancements in machining technology and attend training programs or workshops to enhance your knowledge and skills. Networking with other Swiss lathe operators or joining online communities can also provide valuable insights and tips.
By following these tips and continuously refining your skills, you can become a proficient operator of a Swiss lathe and achieve high-quality machining results.
FAQ
What is a Swiss lathe?
A Swiss lathe, also known as a Swiss-type lathe or a sliding headstock lathe, is a type of lathe machine that is specifically designed for precision machining of small, complex parts. It is named after the country of Switzerland, where it was originally developed.
How does a Swiss lathe work?
A Swiss lathe works by using a sliding headstock that provides support for the workpiece while it is being machined. The workpiece is held firmly in a collet and is rotated by a main spindle. It is the cutting tools that move and perform the machining operations, while the headstock remains stationary.
What are the advantages of using a Swiss lathe?
There are several advantages of using a Swiss lathe. Firstly, it is capable of achieving high levels of precision and accuracy, making it ideal for machining intricate parts. Secondly, it has the capability to perform multiple operations in one setup, reducing the need for multiple machines and setups. Lastly, it is highly efficient and can improve productivity and throughput.
What types of parts can be machined using a Swiss lathe?
A Swiss lathe is commonly used for machining small, high-precision parts such as medical components, watch parts, and electronic components. It is capable of machining parts with complex geometries, tight tolerances, and fine surface finishes.
Are Swiss lathes only used in Switzerland?
No, Swiss lathes are not only used in Switzerland. They are widely used in industries all over the world, especially in the precision machining and manufacturing sectors. However, they were originally developed in Switzerland and the name “Swiss lathe” has stuck.
What are some other names for a Swiss lathe?
A Swiss lathe is also commonly referred to as a Swiss-type lathe, a sliding headstock lathe, or a CNC Swiss lathe. These names are often used interchangeably to refer to the same type of lathe machine.
Video











