Learn how to program a radius on a CNC lathe | Ultimate guide

Programming a radius on a CNC lathe is a crucial skill for machinists and operators. A radius is a curved feature that is commonly found in various parts and components. It allows for smoother transitions between surfaces and improves the overall appearance and functionality of a machined part.
In this ultimate guide, we will dive into the intricacies of programming a radius on a CNC lathe. We will cover the basics of G-code programming, explain the different methods of programming a radius, and provide step-by-step instructions on how to achieve accurate and precise results.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced CNC lathe operator, this guide will help you enhance your programming skills and take your machining projects to the next level. By the end of this guide, you will have the knowledge and confidence to program complex radii on a CNC lathe and create high-quality machined parts.
So, if you are ready to expand your CNC lathe programming capabilities and master the art of programming radii, let’s dive in!
Understanding the Basics of CNC Lathe
Introduction
A CNC lathe, which stands for Computer Numerical Control lathe, is a type of machine tool used for shaping and cutting various materials such as metal, wood, or plastic. It is widely used in manufacturing processes to produce precision parts with high efficiency and accuracy.
How CNC Lathe Works
A CNC lathe operates by using computerized controls to automate the machining process. The operator creates a program that specifies the tool path, machining operations, and other parameters. The program is loaded into the CNC control unit, which interprets the instructions and sends signals to the machine’s motors and actuators to execute the desired operations.
The Components of a CNC Lathe
A typical CNC lathe consists of several key components, including:
- Bed: The base of the lathe that provides support and rigidity.
- Headstock: The section of the lathe that houses the spindle and provides rotational motion to the workpiece.
- Chuck: The device used to hold the workpiece in place.
- Tool Turret: A rotating tool holder that holds various cutting tools.
- Tool Post: The component that holds the cutting tool and moves along the lathe axis.
- Tailstock: The part of the lathe that supports and centers the opposite end of the workpiece.
- Control Unit: The computerized system that controls the machine’s movements and operations.
Advantages of CNC Lathe
CNC lathes offer numerous advantages over manual lathes, including:
- Automation: The ability to automate the machining process reduces the need for manual intervention and increases productivity.
- Precision: CNC lathes are capable of producing highly precise parts with consistent accuracy.
- Efficiency: The time required to set up and machine a part is significantly reduced, improving overall production efficiency.
- Versatility: CNC lathes can perform a wide range of machining operations, allowing for the production of diverse parts.
- Flexibility: Changes to the machining process can be easily made by modifying the program, eliminating the need for manual adjustments.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of CNC lathe is crucial for anyone involved in the field of manufacturing. CNC lathes offer numerous advantages over conventional lathes and play a vital role in modern machining processes. By automating the machining process and providing precise control, CNC lathes enable the production of high-quality parts with efficiency and accuracy.
Types of CNC Lathe Machines
1. Benchtop CNC Lathe Machines
Benchtop CNC lathe machines are smaller, compact CNC lathes that are designed to be placed on a workbench or table. They are ideal for small-scale or hobbyist projects, as well as for educational purposes. Benchtop CNC lathes offer limited capabilities compared to larger machines, but they are more affordable and easier to use.
2. Toolroom CNC Lathe Machines
Toolroom CNC lathe machines are versatile machines that are used in toolrooms and small production settings. They are capable of performing a wide range of operations, including threading, drilling, facing, and turning. Toolroom CNC lathes are often equipped with live tooling, which allows for simultaneous operations and increased productivity.
3. Production CNC Lathe Machines
Production CNC lathe machines are designed for high-volume manufacturing and mass production. They are equipped with multiple tools and automatic tool changers, which enable continuous operation and reduce setup times. Production CNC lathes are used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics, where fast and efficient production is essential.
4. Slant Bed CNC Lathe Machines
Slant bed CNC lathe machines have a bed that is inclined at a certain angle, typically between 45 and 60 degrees. This design allows for better chip flow and improved tool access, resulting in higher machining accuracy and reduced tool wear. Slant bed CNC lathes are commonly used in industries that require high-quality and precision machining, such as medical device manufacturing.
5. Swiss Type CNC Lathe Machines
Swiss type CNC lathe machines, also known as Swiss screw machines, are specialized machines used for high-precision and small-diameter machining. They are particularly suitable for long and slender workpieces. Swiss type CNC lathes feature a sliding headstock and a guide bushing, which provide better support and stability during machining. They are widely used in industries like watchmaking, jewelry, and electronics.
| Type | Size | Capability | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benchtop | Small | Limited | Small-scale, hobbyist, educational |
| Toolroom | Medium | Versatile | Toolrooms, small production |
| Production | Large | High-volume | Mass production |
| Slant Bed | Medium to large | Precision | High-quality machining |
| Swiss Type | Small to medium | High-precision | Small-diameter machining |
Each type of CNC lathe machine has its own advantages and is suitable for specific applications. When choosing a CNC lathe machine, it is important to consider factors such as the size of the workpiece, required machining capabilities, and production volume.
Importance of Programming a Radius on a CNC Lathe
When using a CNC lathe, it is important to understand and be able to program a radius. A radius is a curved shape that is commonly used in machining and can greatly affect the final outcome of a part.
Accuracy and Precision
Programming a radius allows for greater accuracy and precision in the machining process. By specifying the desired radius in the program, the CNC lathe can precisely control the tool movement to create the desired curve. This ensures that the final part meets the required dimensions and specifications.
Improved Surface Finish
Using a radius instead of a sharp corner can also improve the surface finish of the part. Sharp corners can cause stress concentration and potential failure points, especially in materials with low ductility. By using a radius, the stress is distributed more evenly, resulting in a smoother and more reliable surface finish.
Reduced Tool Wear
Programming a radius can also help reduce tool wear. Sharp corners can cause excessive tool wear as the tool has to change direction suddenly. By using a radius, the tool can smoothly transition from one direction to another, reducing the stress on the tool and prolonging its lifespan.
Increased Efficiency
Efficiency is another key benefit of programming a radius. By eliminating the need for manual post-processing or additional operations, the machining time can be significantly reduced. This not only saves time but also increases productivity and reduces costs.
Versatility
Programming a radius on a CNC lathe enables greater versatility in part design. With the ability to create curved shapes, designers have more flexibility to create complex geometries and achieve the desired aesthetic or functional outcome. This versatility opens up new possibilities for innovation and creativity.
Conclusion
Programming a radius on a CNC lathe is of utmost importance to ensure accuracy, precision, improved surface finish, reduced tool wear, increased efficiency, and design versatility. By understanding and utilizing radius programming, machinists can achieve better results in their machining operations.
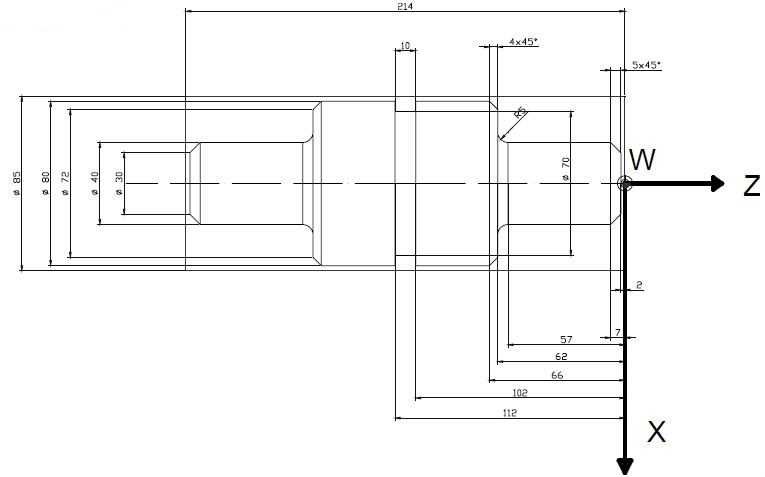
Step-by-Step Guide to Programming a Radius
1. Set up your CNC lathe
Make sure your CNC lathe is in proper working order and all necessary tools and materials are available.
2. Understand the geometry of the radius
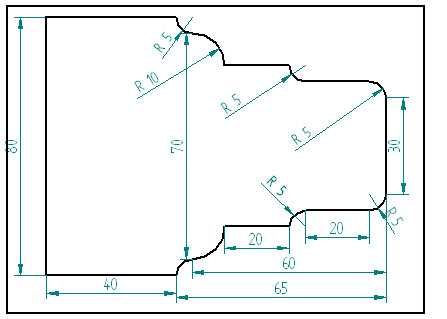
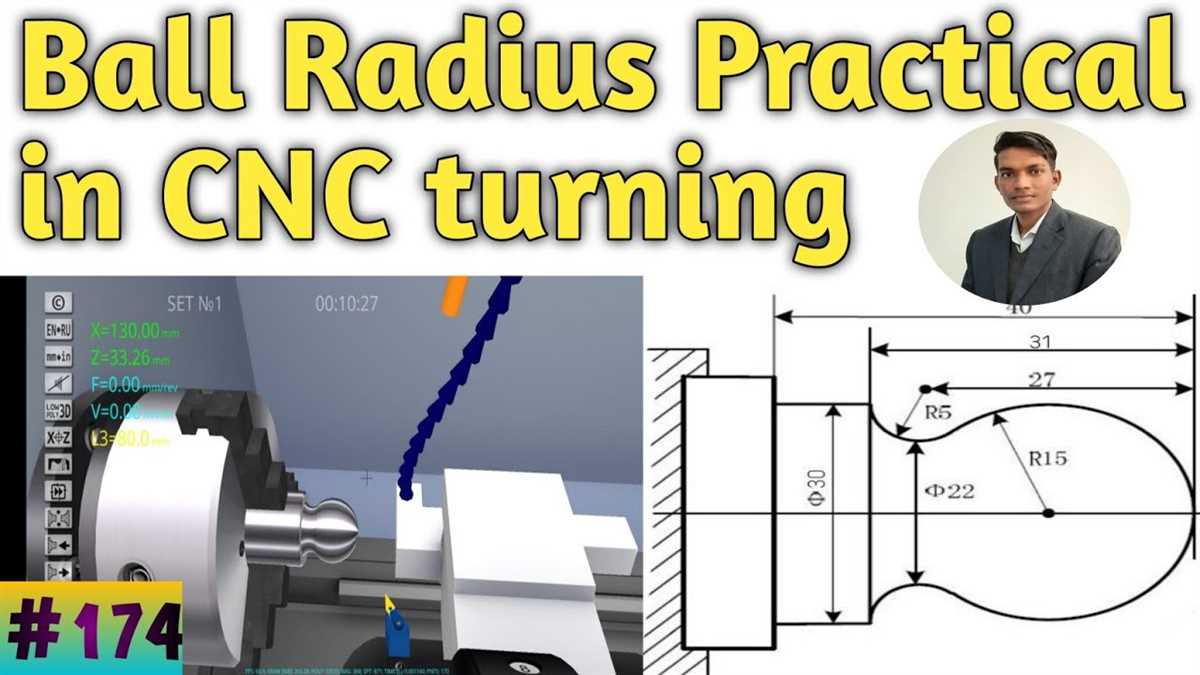
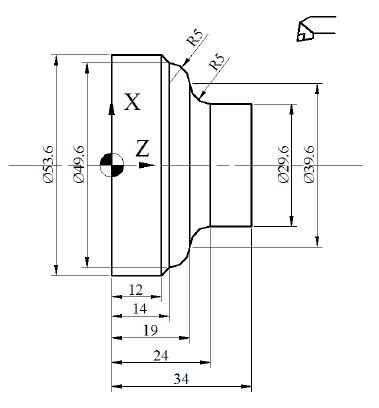
Before programming the radius, it is important to understand its geometry. A radius is a curved shape that connects two straight lines by forming a smooth transition between them.
3. Determine the radius dimensions
Measure the dimensions of the desired radius, including the radius length and the angle of curvature.
4. Calculate the tool path
Based on the radius dimensions, calculate the tool path that the lathe will follow to create the radius. This involves determining the starting point, the cutting depth, and the arc length.
5. Prepare the lathe program
- Open the CNC lathe programming software.
- Create a new program or open an existing one.
- Specify the necessary parameters, such as the starting point, cutting speed, and tool selection.
- Enter the tool path calculations into the program.
6. Test the program
Before running the program on the actual lathe, it is recommended to run a simulation or test the program on a virtual lathe. This will help identify any errors or issues before the actual machining process.
7. Load the program onto the CNC lathe
Once the program is thoroughly tested, load it onto the CNC lathe. Ensure that all safety protocols are followed and the lathe is properly set up for operation.
8. Run the program
- Start the lathe and let it reach the desired speed.
- Initiate the program on the lathe’s control panel.
- Monitor the lathe’s operation and make any necessary adjustments during the machining process.
- Once the program is completed, stop the lathe and inspect the final result.
9. Make any necessary modifications
If the final result is not satisfactory, make any necessary modifications to the program or adjust the lathe’s settings to achieve the desired outcome. Iterate the process until the desired radius is achieved.
10. Document the program
Document the final program for future reference. This should include all the parameters, tool paths, and any modifications made during the process.
11. Repeat the process for additional radii

If you need to program multiple radii on the CNC lathe, repeat the above steps for each radius.
A well-programmed radius on a CNC lathe can greatly enhance the precision and quality of your work. Following this step-by-step guide will help you achieve accurate and consistent results.
Common Challenges in Programming a Radius
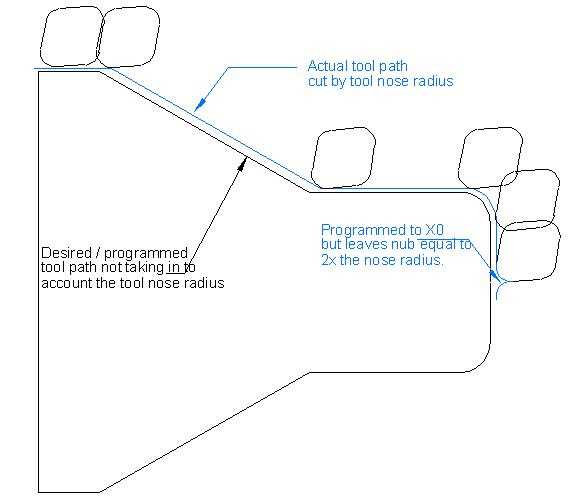
Programming a radius on a CNC lathe can be a complex task, and there are several common challenges that programmers may face. These challenges include:
- Calculating the correct radius: Calculating the correct radius for the desired shape can be challenging. It requires knowledge of the geometry of the part and the cutting tools being used. The incorrect calculation of the radius can result in a part that does not meet the required specifications.
- Selecting the appropriate tool: Choosing the right tool for programming a radius is crucial. Different tools have different capabilities and limitations when it comes to cutting radii. It is important to select a tool that can achieve the desired radius accurately and efficiently.
- Determining the cutting path: Programming the tool’s cutting path to achieve the desired radius can also be a challenge. The cutting path must be precise and efficient, taking into account factors such as tool clearance, material type, and the desired surface finish.
- Handling tool wear: Tool wear is another challenge that programmers must consider when programming a radius. As the tool wears down over time, it may affect the accuracy and quality of the programmed radius. Monitoring tool wear and adjusting the program accordingly is essential to maintaining consistent results.
- Dealing with machine limitations: CNC lathes may have limitations in terms of their capabilities and programming options. These limitations may affect the programmer’s ability to accurately program a radius. Understanding the machine’s limitations and working within them is crucial to achieving the desired results.
Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of technical knowledge, experience, and attention to detail. It is important for programmers to continuously learn and improve their skills to successfully program complex radii on CNC lathes.
By understanding and addressing these common challenges, programmers can increase their efficiency and accuracy when programming radii, resulting in better quality parts and improved overall productivity.
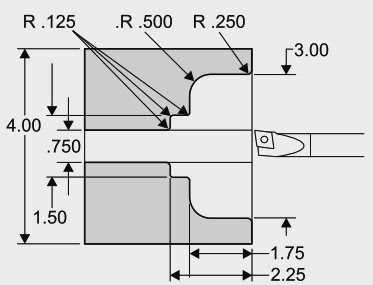
Best Practices for Programming a Radius
1. Understand the Basics
Before you start programming a radius on a CNC lathe, it’s important to have a solid understanding of the basics. Familiarize yourself with the different types of radii, such as concave and convex, and know how to calculate their dimensions. Additionally, learn how to program tool offsets and compensate for tool wear for accurate results.
2. Use Appropriate G-Codes
When programming a radius, use the appropriate G-codes for your CNC lathe. G01 is used for linear interpolation, G02 for clockwise circular interpolation, and G03 for counterclockwise circular interpolation. These G-codes allow you to specify the direction and arc size of the radius.
3. Break the Radius into Segments
Instead of programming a large radius as a single arc, it’s best to break it into smaller segments. This allows for better control and precision. Determine the number of segments based on the desired smoothness of the radius and the capabilities of your CNC lathe.
4. Define the Start and End Points
When programming a radius, define the start and end points of each segment. This ensures smooth transitions between segments and avoids abrupt changes in direction. Use G28 or G00 to position the tool at the start point of each segment before starting the machining operation.
5. Pay Attention to Tool Selection
Choosing the right cutting tool is crucial for programming a radius. Use a tool with a nose radius that matches the desired radius dimension. This ensures that the tool can accurately machine the contour without leaving any rough edges or excess material.
6. Use Proper Feeds and Speeds
Optimize the feeds and speeds for machining the radius to achieve the best results. Use appropriate cutting speeds, feed rates, and depths of cut to prevent tool wear, maintain accuracy, and reduce overall machining time. Experiment and make adjustments as needed.
7. Test and Debug the Program
Before running the program on the CNC lathe, it’s important to thoroughly test and debug it. Use simulation software or a CNC lathe with a testing mode to check for any programming errors or potential issues. Make any necessary adjustments to the program to ensure a successful machining process.
8. Document and Save Programs
Once you have successfully programmed a radius, it’s important to document and save the program for future use. This allows you to easily reproduce the same radius in the future without starting from scratch. Keep a detailed record of the program, including the tooling, feeds and speeds, and any specific parameters used.
9. Continuous Improvement
Don’t be afraid to continuously improve your programming skills for radii on a CNC lathe. Stay updated with the latest technologies, techniques, and software. Learn from your mistakes and successes to continually refine your programming techniques and achieve better results.
10. Seek Expert Guidance
If you’re just starting out or facing challenges with programming a radius on a CNC lathe, don’t hesitate to seek expert guidance. Join online forums, attend training sessions, or consult with experienced machinists to gain valuable insights and advice.
Conclusion
Programming a radius on a CNC lathe requires a solid understanding of the basics, careful planning, and attention to detail. By following these best practices, you can ensure accurate and efficient machining results while minimizing errors and rework.
Tips and Tricks for Efficient Programming
1. Plan your programming ahead of time
Before starting the programming process, it is important to plan out your steps and approach. This will help you determine the most efficient way to program and minimize errors.
2. Utilize canned cycles
Canned cycles are pre-programmed sequences of codes that simplify the programming process. They can be used for common operations like drilling, tapping, and facing, saving you time and effort.
3. Use subprograms for repeated tasks

If you have a series of repeated tasks in your program, consider using subprograms. Subprograms allow you to define a set of instructions that can be called multiple times, reducing the amount of code you need to write and maintain.
4. Group similar operations together
To improve efficiency, group similar operations together in your program. This can help minimize tool changes and reduce the time it takes to complete a job.
5. Optimize tool paths
Take time to optimize your tool paths to minimize unnecessary movements and reduce cycle times. This can be achieved by using contouring and adaptive machining techniques.
6. Use variables and parameters
Utilize variables and parameters in your programming to make it more flexible and adaptable. This allows you to easily modify values and dimensions without rewriting the entire program.
7. Comment your code
Adding comments to your code is essential for easier understanding and maintenance. Comments provide explanations for specific sections of code and can be helpful for others who may need to review or modify your program.
8. Test and simulate your program
Before running your program on the CNC lathe, make sure to test and simulate it using software or virtual machines. This can help identify any errors or issues before they occur on the actual machine.
9. Keep your programming skills up to date
Continuous learning is key to efficient programming. Stay updated with the latest techniques, tools, and software in the CNC lathe programming field, as this can help improve your efficiency and productivity.
10. Document your programming knowledge
Keep a record of your programming knowledge and experiences. This can include notes, tutorials, and examples that you can refer back to for future projects. Having a comprehensive documentation can save you time and help you avoid repeating the same mistakes.
11. Seek assistance and collaborate
If you encounter challenges or face difficulties in CNC lathe programming, don’t hesitate to seek assistance or collaborate with others. This can be through online communities, forums, or networking with other professionals in the field. Sharing knowledge and experiences can lead to more efficient programming techniques.
FAQ
What is a CNC lathe?
A CNC lathe is a machine tool used in the manufacturing industry to shape metal or other materials. It is controlled by a computer program, which allows for precise and repetitive machining operations.
Why is it important to learn how to program a radius on a CNC lathe?
Knowing how to program a radius on a CNC lathe allows you to create rounded or curved shapes on a workpiece. This is essential for many manufacturing applications, such as creating pipes, cylinders, or rounded edges on parts.
Video











