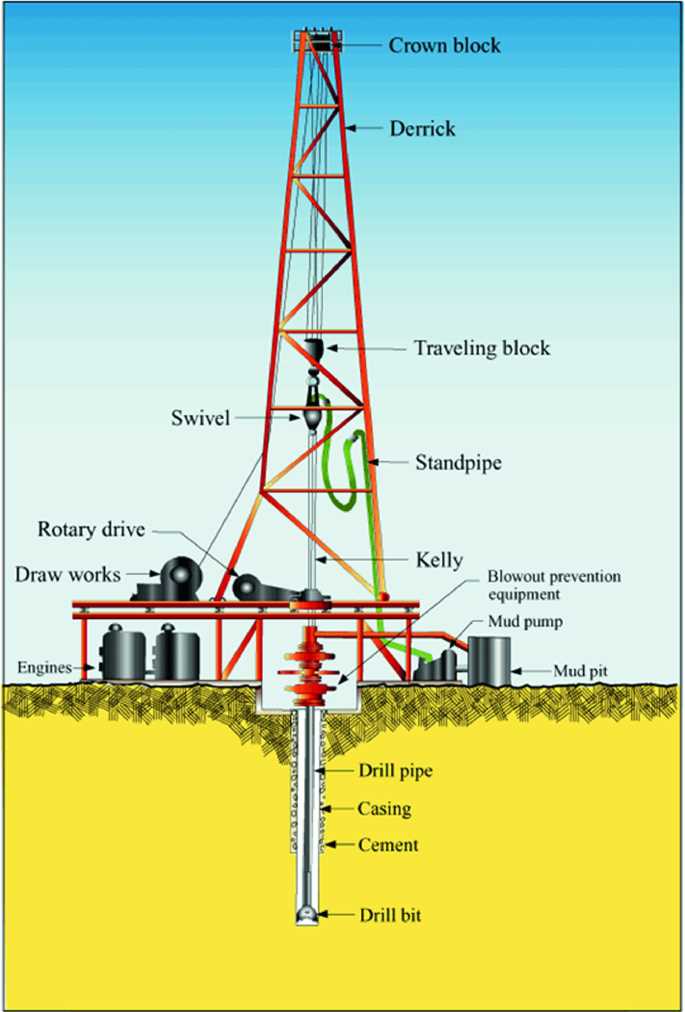
How Does a Drill Rig Work: Everything You Need to Know

A drill rig is a powerful machine used in various industries, including oil and gas exploration, mining, and construction. It is designed to bore deep holes into the earth’s surface to extract resources or gather geological information. Understanding how a drill rig works is crucial for anyone involved in these industries or interested in learning more about the drilling process.
At the heart of a drill rig is the drilling mechanism, which typically consists of a drilling bit and a rotary system. The drilling bit, usually made of tungsten carbide or diamond, is attached to the bottom of a drill string. When the drill string rotates, the drilling bit cuts through the earth’s layers, creating a hole.
To generate the rotary motion, drill rigs are equipped with a power source, such as an engine or an electric motor. This power source drives a series of gears and the rotary table, which transfers the rotation to the drill string. The rotary table can rotate the drill string at high speeds, allowing the drilling bit to penetrate the ground efficiently.
In addition to the drilling mechanism, a drill rig also includes other important components, such as a mast or derrick, a hoisting system, and a mud circulation system. The mast provides support for the drill string and allows it to be raised or lowered as needed. The hoisting system, typically consisting of a winch or a drawworks, is responsible for raising and lowering the drill string and other heavy equipment. The mud circulation system, on the other hand, helps to cool and lubricate the drilling bit and carry the drilled cuttings to the surface.
Overall, a drill rig is a complex machine that requires skilled operators and careful planning to ensure efficient and safe drilling operations. By understanding how a drill rig works, we can appreciate the engineering and technology that goes into the extraction of valuable resources from deep below the earth’s surface.
In conclusion, a drill rig is an essential tool used in various industries for drilling deep holes into the earth’s surface. It consists of a drilling mechanism, a power source, and other important components that work together to penetrate the ground and extract resources. By learning about the inner workings of a drill rig, we can gain a better understanding of the drilling process and its role in industries such as oil and gas exploration, mining, and construction.
Types of Drill Rigs
There are several types of drill rigs that are used for various drilling applications. Each type of drill rig is designed to perform specific tasks and is suited for different geological conditions.
1. Rotary Drill Rigs
Rotary drill rigs are the most common type of drill rigs used in the industry. They work by rotating a drill bit to break through the ground and create a hole. Rotary drill rigs are versatile and can be used for a wide range of drilling tasks, including water well drilling, oil and gas exploration, and geotechnical drilling.
2. Percussion Drill Rigs
Percussion drill rigs use a piston-driven mechanism to deliver the force needed to break through tough rock formations. These drill rigs are commonly used in mining and construction projects. The piston strikes the drill bit, causing it to break the rock into small pieces.
3. Auger Drill Rigs
Auger drill rigs are used for drilling holes in soil and soft rock formations. These drill rigs feature a helical screw-like bit, called an auger, that helps in cutting through the ground. Auger drill rigs are commonly used for environmental drilling, foundation drilling, and soil sampling.
4. Diamond Drill Rigs
Diamond drill rigs are specifically designed for drilling through hard rock formations. These drill rigs use a diamond-impregnated drill bit to cut through the rock. Diamond drill rigs are commonly used in mineral exploration and mining projects.
5. Directional Drill Rigs
Directional drill rigs are used to drill horizontally or at various angles. These drill rigs are commonly used in oil and gas exploration, as they allow for drilling multiple wells from a single location. Directional drill rigs use specialized tools and equipment to control the direction and angle of the drill hole.
6. Crawler Drill Rigs
Crawler drill rigs are mounted on a tracked crawler platform, which allows them to maneuver in difficult terrains. These drill rigs are commonly used in geological surveying, geotechnical drilling, and slope stabilization projects.
| Type of Drill Rig | Common Applications |
|---|---|
| Rotary Drill Rigs | Water well drilling, oil and gas exploration, geotechnical drilling |
| Percussion Drill Rigs | Mining, construction |
| Auger Drill Rigs | Environmental drilling, foundation drilling, soil sampling |
| Diamond Drill Rigs | Mineral exploration, mining |
| Directional Drill Rigs | Oil and gas exploration |
| Crawler Drill Rigs | Geological surveying, geotechnical drilling, slope stabilization |
These are just a few examples of the types of drill rigs available in the industry. The choice of drill rig depends on the specific drilling requirements and the geological conditions of the site.
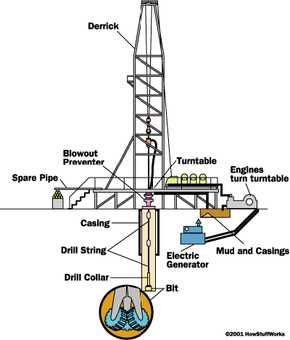
Components of a Drill Rig
A drill rig is a complex machine that consists of various components. Each component plays a crucial role in the drilling process. Here are some of the main components of a drill rig:
1. Derrick
The derrick is a tall structure that supports the entire drill rig and provides stability during the drilling process. It is usually made of steel and stands vertically, allowing the drill string to be raised and lowered.
2. Drill String
The drill string is a series of connected pipes and tools that extend from the surface to the drilling point. It is used to transmit drilling fluids, provide the necessary torque and rotation, and support the weight of the drilling tools.
3. Drill Bit
The drill bit is the cutting tool attached to the end of the drill string. It is designed to crush and break the rock formations, allowing for the extraction of resources. Drill bits come in various shapes and sizes depending on the type of rock being drilled.
4. Drill Pipe
The drill pipe is a hollow tube that connects the drill bit to the surface. It is responsible for transmitting the drilling fluid and torque from the surface to the drill bit. Drill pipes are typically made of steel and come in standard lengths.
5. Drill Collars
Drill collars are heavy, thick-walled tubes placed between the drill pipe and the drill bit. They provide weight on the drill bit, which helps to facilitate drilling and prevent buckling or wobbling of the drill string.
6. Rotary Table
The rotary table is a large turntable that rotates the drill string and provides the necessary torque and rotation for drilling. It is usually powered by an electric motor or hydraulic system, allowing for controlled and precise drilling.
7. Mud Pump
The mud pump is a device that pumps drilling fluid, also known as mud, into the drill string. This pressurized mud helps to cool and lubricate the drill bit, remove cuttings from the borehole, and maintain stability of the wellbore during drilling.
8. Blowout Preventer (BOP)
The blowout preventer is a safety device that is installed at the top of the wellbore. It is designed to prevent the uncontrolled release of fluids or gases during drilling or well control operations. BOPs are crucial for maintaining wellbore integrity and preventing blowouts.
9. Mud Tanks
Mud tanks are large containers used to store and circulate drilling fluid during the drilling process. They are typically located near the drill rig and connected to the mud pump and other drilling equipment. Mud tanks help to control the properties and volume of the drilling mud.
10. Control Panel
The control panel is the central hub of the drill rig. It is where the driller operates and monitors the various components and systems of the rig. The control panel allows for the control of drilling parameters, such as the speed and torque of the rotation, pump pressure, and mud flow rate.
11. Power System
The power system of a drill rig provides the necessary energy to operate the various components. It typically consists of diesel engines or electrical motors for power generation. The power system is crucial for the functioning of the drill rig, as it powers the drilling operations and other auxiliary systems.
12. Safety Equipment
A drill rig is equipped with various safety devices and equipment to ensure the safety of the operators and the drilling operation. This includes fire suppression systems, emergency shut-off valves, first aid kits, safety harnesses, and other personal protective equipment.
13. Ancillary Equipment
In addition to the main components, a drill rig may also have various ancillary equipment depending on the specific drilling requirements. This may include casing and tubing, wellheads, drilling fluid additives, and other tools and instruments.
Overall, the components of a drill rig work together to facilitate the drilling process and extract valuable resources from the Earth’s subsurface. Each component has its specific function and plays a critical role in the success and efficiency of the drilling operation.
Drill Bit and Drill String
The drill bit is a crucial component of the drill rig that is responsible for creating the hole in the ground. It is typically made of hardened steel and comes in various shapes and sizes depending on the specific drilling requirements. The drill bit is attached to the bottom of the drill string, which is a series of connected metal pipes that transmit the drilling torque from the rig to the drill bit.
The drill string consists of several key components, including the drill pipe, drill collars, and the drilling tool itself. The drill pipe is a long, hollow tube that serves as the conduit for drilling fluid and provides structural support to the drill bit. It is typically made of steel and is threaded at both ends to allow for easy connection and disconnection.
Drill Collars
Drill collars are heavyweight steel pipes that are placed between the drill pipe and the drill bit. Their primary function is to add weight to the drill bit, which helps to maintain downward pressure and stability during drilling. Drill collars are often made of solid steel and are thicker and heavier than the drill pipe. They are also designed with spiral grooves or “slick” surface to provide a smooth rotation and reduce friction.
Drilling Tool
The drilling tool is the part of the drill string that is directly above the drill bit. It is a specialized tool that is designed to provide additional force and control to the drill bit. The drilling tool can vary depending on the specific drilling operation but may include components such as stabilizers, reamers, or even mud motors. These tools help to stabilize the drill string and improve the drilling efficiency.
Drilling Fluid
One important aspect of the drill string is the drilling fluid or mud. The drilling fluid serves several purposes, including cooling and lubricating the drill bit, carrying the cuttings to the surface, and providing hydrostatic pressure to prevent the collapse of the wellbore. The drilling fluid is pumped down through the drill pipe and returns to the surface through the annular space between the drill pipe and the wellbore, where it is then filtered and recirculated.
In summary, the drill bit and drill string are essential components of a drill rig. The drill bit is responsible for creating the hole, while the drill string transmits torque and provides stability. The drill string consists of the drill pipe, drill collars, and the drilling tool, and is used in conjunction with drilling fluid to ensure efficient and safe drilling operations.
Drilling Process and Techniques
A drilling rig is used to create holes in the ground for various purposes, such as mining, oil extraction, water well drilling, and construction. The drilling process involves several stages and techniques, which vary depending on the type of drilling rig and the purpose of the drilling operation.
1. Site Preparation
Prior to starting the drilling process, site preparation is necessary. It includes clearing the area of any obstructions, such as trees, rocks, or debris. The site is leveled and a stable platform is created to support the drilling rig.
2. Drilling Fluid
The drilling fluid, also known as mud, is a mixture of water, clay, and additives. It serves several purposes during the drilling process. Firstly, it helps in cooling and lubricating the drill bit and the drill string, reducing friction and preventing overheating. Secondly, it carries the drilled cuttings to the surface, allowing continuous drilling. Lastly, the drilling fluid provides stability and prevents the collapse of the borehole walls.
3. Drill Bit Selection
The type of drill bit used depends on the purpose of the drilling operation. There are various types of drill bits, such as roller cone bits, polycrystalline diamond compact (PDC) bits, and diamond core bits. The choice of drill bit is determined by factors such as the geological formation, the desired hole diameter, and the drilling method employed.
4. Drilling Techniques
There are several drilling techniques that can be used, depending on the type of drilling rig and the geological conditions. Some common drilling techniques include:
- Rotary Drilling: This technique involves rotating the drill bit to create a hole. It is commonly used in mineral exploration, oil and gas drilling, and water well drilling.
- Percussion Drilling: In this technique, the drill bit is repeatedly raised and lowered to create a hole. It is commonly used in geotechnical investigations, foundation drilling, and shallow water well drilling.
- Diamond Core Drilling: This technique uses a diamond-impregnated drill bit to create a cylindrical core sample. It is commonly used in mineral exploration and geological research.
5. Depth Control and Monitoring
During the drilling process, depth control and monitoring are crucial. Various tools and techniques, such as depth sensors, pressure gauges, and drilling recorders, are used to ensure accurate drilling depth and to monitor the drilling parameters.
6. Casing and Cementing
Once the desired depth is reached, a casing is installed to provide structural integrity and prevent the collapse of the borehole. The casing is then cemented in place to create a seal and to prevent the migration of fluids between different geological formations.
7. Well Completion
After the drilling process is completed, additional steps are taken to complete the well, depending on its purpose. These may include well testing, installation of production equipment, and connecting the well to the appropriate infrastructure.
In conclusion, the drilling process involves various stages and techniques, starting from site preparation to well completion. It requires careful planning, monitoring, and the use of appropriate equipment and techniques to ensure successful drilling operations.
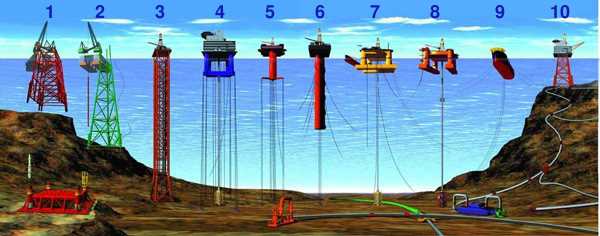
Applications of Drill Rigs
1. Mineral Exploration
Drill rigs are commonly used in mineral exploration to extract samples of rock and soil from the ground. These samples are then analyzed to determine the presence of valuable minerals and metals. This information is crucial for mining companies, as it helps them identify potential mining sites and estimate the potential value of the reserves.
2. Oil and Gas Exploration
Drill rigs are also used in the exploration and extraction of oil and gas reserves. They are often used in offshore drilling operations where they can drill deep into the ocean floor to access oil and gas deposits. Drill rigs can also be used on land to drill exploratory wells and monitor production wells.
3. Geotechnical Investigations
Drill rigs play a crucial role in geotechnical investigations, which involve studying the properties of soil and rocks for construction and engineering purposes. The rigs are used to collect samples and gather data about the soil composition, stability, and load-bearing capacity. This information helps engineers design foundations, roads, bridges, and other structures that can withstand the natural forces acting on them.
4. Environmental Monitoring and Remediation
In environmental applications, drill rigs are used for monitoring and remediation activities. They can be used to monitor groundwater contamination by drilling wells and collecting water samples for testing. Drill rigs are also used in remediation projects, where they are used to extract and remove contaminated soil and groundwater.
5. Water Well Drilling
Drill rigs are commonly used in the drilling of water wells for residential, commercial, and agricultural purposes. These rigs are designed to penetrate the earth’s surface and reach underground water sources. Once the well is drilled, pumps are installed to extract water for various uses such as drinking, irrigation, and industrial purposes.
6. Construction and Infrastructure Development
Drill rigs are used in construction and infrastructure development projects for various purposes. They can be used to drill holes for the installation of foundation piers, utility poles, fences, and signs. They are also used in the construction of tunnels, dams, and bridges to gather geological data and stabilize the ground before construction.
7. Scientific Research and Exploration
Drill rigs are used in scientific research and exploration projects to gather samples and study the Earth’s crust. These rigs are often used in projects such as ice core drilling, where they are used to extract samples from ice sheets to study climate change and geological history. They are also used in studies of geothermal energy, volcanism, and other geological phenomena.
8. Mining Operations
Drill rigs are an integral part of mining operations, where they are used to extract minerals and metals from the earth’s crust. These rigs are used to drill blast holes for explosives, which are then used to break up the rock and extract the desired materials. Drill rigs are also used for dewatering operations to remove excess water from mines and improve safety conditions.
9. Well Maintenance and Rehabilitation
Drill rigs are used for well maintenance and rehabilitation activities in various industries. They can be used to clean and repair existing water wells, oil wells, and geothermal wells. Drill rigs are also used to install pumps, casings, and other equipment to optimize well performance and extend the lifespan of wells.
10. Scientific and Geographical Surveys
Drill rigs are used in scientific and geographical surveys to collect samples and gather data about the Earth’s crust. They are used to extract core samples from rock formations, which are then studied to understand geological processes, landforms, and resources. These surveys help scientists and geographers gain insights into the Earth’s history and ecosystems.
Safety Precautions for Drill Rig Operation
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
When operating a drill rig, it is crucial to wear appropriate personal protective equipment to ensure your safety. This includes:
- Hard hat: Protects your head from falling objects or overhead hazards.
- Safety glasses or goggles: Shields your eyes from debris, flying particles, or chemical splashes.
- Earplugs or earmuffs: Reduces noise exposure and prevents hearing damage.
- Steel-toed boots: Offers protection against heavy objects that may fall on your feet.
- Gloves: Protects your hands from sharp objects, pinch points, or chemical exposure.
- High-visibility vest: Makes you more visible to others on the site.
2. Equipment Inspection
Before starting the drill rig, it is essential to inspect the equipment thoroughly. This should include checking for any loose or damaged parts, ensuring that all safety features are in place and functioning correctly. If any issues are detected, they should be reported to the supervisor or maintenance personnel immediately.
3. Proper Training and Certification
Operating a drill rig requires specific skills and knowledge. It is crucial to undergo proper training and obtain the necessary certifications before operating the equipment. This training should cover both the basics of drill rig operation and the specific procedures and safety measures relevant to the site where you will be working.
4. Communication and Warning Signs
Communication and clear warning signs are vital on a drill rig site to avoid accidents and ensure everyone’s safety. All personnel involved should understand and follow the designated communication protocols. Additionally, warning signs should be prominently displayed to warn of potential hazards such as high voltage areas, sharp machinery, or restricted access zones.
5. Proper Use of Tools and Equipment
Always use the tools and equipment provided for their intended purpose. Using tools incorrectly or attempting to modify them can lead to accidents or equipment failure. If you are unsure how to use a particular tool or piece of equipment, consult with a supervisor or experienced operator before proceeding.
6. Emergency Procedures
Familiarize yourself with the site’s emergency procedures and escape routes. Know the locations of fire extinguishers, first aid kits, and emergency shutdown switches. In the event of an emergency, remain calm, follow the established procedures, and evacuate the area if necessary.
7. Adhere to Safe Working Practices
Always follow safe working practices while operating a drill rig. This includes maintaining a clean and organized work area, keeping walkways clear and free from obstructions, and using proper lifting techniques when handling heavy objects. By adhering to these practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
8. Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection of the drill rig are crucial for safe operation. This includes checking and servicing the equipment as recommended by the manufacturer or supervisor. Proper maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they become safety hazards.
9. Follow Site-Specific Safety Guidelines
Each drill rig site may have additional safety guidelines or rules specific to that location. It is essential to be aware of and adhere to these guidelines to ensure the highest level of safety. Familiarize yourself with any additional precautions, procedures, or hazards unique to your worksite.
10. Reporting Incidents and Near Misses
It is vital to report any accidents, incidents, or near misses immediately, regardless of how minor they may seem. Reporting incidents helps identify potential hazards and allows for corrective actions to be taken to prevent future incidents. Maintaining a culture of reporting and learning from incidents is crucial for continuous improvement and preventing accidents.
Maintenance and Repair of Drill Rigs
Maintenance and repair are essential aspects of keeping drill rigs in optimal working condition. Regular maintenance can help prevent breakdowns, extend the lifespan of the equipment, and ensure the safety of the operators. This section will discuss the key maintenance and repair tasks associated with drill rigs.
1. Regular Inspections
Regular inspections should be conducted to identify any signs of wear and tear, damage, or malfunctioning components. Inspect the drill rig thoroughly, including the hydraulic system, electrical system, engine, drilling tools, and safety devices. Any issues should be promptly addressed to prevent further damage or accidents.
2. Lubrication
Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation of a drill rig. Bearings, gears, and other moving parts should be lubricated regularly to reduce friction, prevent overheating, and minimize wear. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the type and frequency of lubrication required.
3. Filter and Fluid Changes
Filters and fluids, such as hydraulic oil, engine oil, and coolant, should be regularly checked and replaced as needed. Dirty or contaminated fluids can cause equipment malfunction and decrease performance. Regularly changing filters and fluids ensures the drill rig operates efficiently.
4. Belt and Chain Tension
Check and adjust the tension of belts and chains in the drill rig. Loose or tight belts and chains can affect the performance and efficiency of the equipment. Improper tension can result in excessive wear or slippage. Ensure the belts and chains are properly tensioned according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
5. Electrical System Maintenance
The electrical system should be inspected for any loose connections, damaged wires, or faulty switches. Proper electrical maintenance is crucial for the safe operation of the drill rig. Any electrical issues should be resolved immediately by a qualified technician.
6. Drill Bit Replacement
Regularly inspect the drill bit for signs of wear. Worn-out drill bits can lead to decreased drilling efficiency and increased drilling time. Replace the drill bit as needed to maintain optimal drilling performance.
7. Operator Training and Safety

Regular training sessions for drill rig operators should be conducted to promote safety and proper equipment operation. Operators should be familiar with all safety procedures and protocols. Promoting a culture of safety can help minimize accidents and equipment damage.
8. Repair and Replacement
In the event of any major equipment damage or failure, contact a qualified technician or the manufacturer for repair or replacement. Attempting to repair complex equipment without proper expertise can lead to further damage or safety hazards. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for repairs or replacements.
By following these maintenance and repair guidelines, drill rig owners and operators can ensure their equipment remains in optimal working condition, maximize its lifespan, and minimize downtime.
FAQ:
What is a drill rig and what is its purpose?
A drill rig is a machine used in construction and mining operations to create holes in the ground. Its purpose is to extract valuable resources such as oil, gas, or minerals, or to create holes for various construction purposes.
How does a drill rig work?
A drill rig works by using various components to drill into the ground. It typically consists of a drill bit that rotates and cuts into the ground, a drill string that transfers the rotational force from the drill bit, and a power source such as an engine or electric motor that provides the necessary power to drive the drill bit. The drill rig also includes other components such as a mast or tower to support the drill string, a hoisting system to raise and lower the drill string, and a control panel to operate the rig and monitor drilling operations.
What are the different types of drill rigs?
There are several types of drill rigs, each designed for specific drilling applications. Some common types include rotary drill rigs, which use a rotating drill bit to cut into the ground; percussion drill rigs, which use a hammering action to break through rocks; directional drill rigs, which allow for drilling in a specific direction; and exploration drill rigs, which are used to explore and extract minerals and resources.
What are the advantages of using a drill rig?
Using a drill rig offers several advantages in construction and mining operations. It allows for efficient and precise drilling, reducing the time and effort required compared to manual drilling methods. Drill rigs also offer greater safety as they can be operated remotely, keeping workers away from potentially hazardous drilling areas. Additionally, drill rigs are highly versatile and can be used in various terrains and conditions, making them suitable for a wide range of drilling applications.
Video:











