What Does CFM Mean on an Air Compressor?

When shopping for an air compressor, you may come across the term CFM. But what does CFM actually mean? CFM stands for cubic feet per minute, and it is a unit of measurement used to describe the volume of air flow that an air compressor can deliver. In simple terms, CFM tells you how much air the compressor can pump out in one minute. Understanding CFM is crucial when choosing the right air compressor for your specific needs.
CFM is an important factor to consider because it determines the power and efficiency of an air compressor. The CFM rating of a compressor directly correlates to its ability to power pneumatic tools and equipment. If the CFM rating of the compressor is too low, it won’t be able to deliver enough air pressure to operate certain tools effectively. On the other hand, if the CFM rating is too high, the compressor may be too powerful for your needs, resulting in wasted energy and increased costs.
In addition to CFM, there are other factors to consider when choosing an air compressor, such as the tank size, horsepower, and PSI (pounds per square inch). These factors work together to determine the overall performance and capabilities of the compressor. However, CFM is a critical measurement that directly impacts the compressor’s ability to deliver a sufficient volume of air to power your tools and equipment.
When selecting an air compressor, it’s important to match the CFM rating to the requirements of the tools and equipment you plan to use. Different tools have different CFM requirements, so you’ll need to check the specifications of each tool to ensure compatibility. If you’re unsure about the CFM requirements of your tools, it’s best to consult the manufacturer or a knowledgeable professional who can help you make an informed decision.
Understanding CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) in Air Compressors
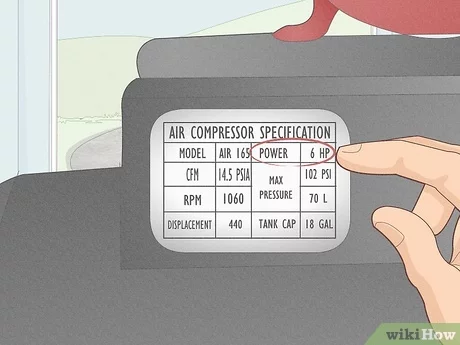
CFM, or Cubic Feet per Minute, is a measurement of the volume of air that an air compressor can deliver per minute. It is an important factor to consider when choosing an air compressor, as it determines how quickly the compressor can inflate tires, power tools, or run pneumatic machinery.
How CFM is Measured:
CFM is measured by filling a container with a known volume of compressed air at a certain pressure and timing how long it takes to fill the container. The resulting measurement represents the amount of compressed air that the air compressor can deliver in one minute.
Factors Affecting CFM:
Several factors can affect the CFM rating of an air compressor. One of the most important factors is the compressor’s motor horsepower. Generally, higher horsepower motors can deliver higher CFM ratings. Another factor is the size and design of the compressor’s storage tank. A larger tank can hold more compressed air and deliver a higher CFM. Additionally, the efficiency of the compressor’s air intake and discharge valves, as well as the compressor’s overall design, can also impact its CFM rating.
Importance of CFM:
Understanding CFM is crucial because it determines whether the air compressor can meet the demands of the tools or machinery you plan to use it with. If the CFM rating of the compressor is too low, it won’t be able to supply enough air to power the tools effectively. On the other hand, if the CFM rating is too high, you may be wasting energy and money on a compressor that is larger than what you actually need.
To determine the required CFM for your specific applications, you should consider the CFM requirements of the tools or machinery you plan to use. Each tool typically has a recommended CFM range that it requires to operate optimally. By adding up the CFM requirements of all the tools, you can determine the minimum CFM rating your air compressor should have to meet your needs.
Overall, understanding CFM is essential for selecting the right air compressor for your needs. Whether you’re inflating tires, running power tools, or operating pneumatic machinery, knowing the CFM rating of the compressor ensures that you have enough air supply for efficient and effective operations.
Importance of CFM Ratings in Air Compressors
The CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) rating is a crucial specification to consider when choosing an air compressor. It indicates the amount of air that the compressor can deliver per minute, which directly impacts the performance and efficiency of various pneumatic tools and equipment.
Accuracy in Air Tool Performance: CFM rating is essential for ensuring that the air compressor can supply enough air to keep the pneumatic tools operating at their optimal performance levels. Different tools require different amounts of airflow, and using an air compressor with a CFM rating that matches or exceeds the tool’s requirements guarantees accurate and reliable operation.
Preventing Air Flow Restrictions: Having a lower CFM rating on an air compressor can result in restricted air flow, leading to decreased efficiency and even damage to the tools. Insufficient airflow can cause tools to underperform, overheat, and wear out more quickly. By choosing an air compressor with an adequate CFM rating, users can prevent these issues and ensure longer tool lifespan.
Faster Task Completion: Air tools require a continuous supply of compressed air to function properly. If the CFM rating of the air compressor is too low, it may not be able to keep up with the tool’s demand, causing delays in completing tasks. Opting for an air compressor with a higher CFM rating translates to faster task completion and increased productivity.
Versatility and Compatibility: Different applications and tools require specific CFM ratings to operate efficiently. By understanding the CFM requirements of different tools, users can choose an air compressor that offers sufficient airflow to accommodate a wide range of applications. This versatility allows for compatibility with various tools, eliminating the need for multiple compressors.
Consistent Air Pressure: Adequate CFM rating ensures consistent air pressure throughout the operation of pneumatic tools. Insufficient airflow can cause pressure drops, resulting in reduced performance and inconsistent results. Having an air compressor with a suitable CFM rating helps maintain steady and reliable air pressure, improving the overall performance of the tools.
Considering the CFM rating of an air compressor is vital for ensuring optimal performance, preventing equipment damage, and maximizing efficiency. It allows users to select an air compressor that meets the specific requirements of their pneumatic tools, leading to enhanced productivity and reliable operation.
CFM and Air Tools: Choosing the Right Compressor for Your Needs
Understanding CFM

CFM, or cubic feet per minute, is a measurement of the volume of air that an air compressor can deliver. It indicates how much air the compressor can provide in one minute.
When it comes to air tools, CFM is an important factor to consider. Different air tools require different amounts of air, and if your compressor does not provide enough CFM, the tools may not function at their optimal level.
Matching CFM to Your Air Tools

To choose the right compressor for your air tools, you need to know the CFM requirements of those tools. This information is usually provided by the manufacturer of the air tools.
Make a list of all the air tools you plan to use and their CFM requirements. Add up the CFM requirements of all the tools to determine the minimum CFM rating that your air compressor should have.
Additional Considerations
While CFM is an important factor, there are other considerations to keep in mind when choosing an air compressor. One of these is the pressure rating of the compressor. It should meet or exceed the pressure requirements of your air tools.
You may also want to consider the tank size of the compressor. A larger tank can provide a reserve of air, which can be useful for tools that require short bursts of high-volume air.
Another factor to consider is the duty cycle of the compressor. This refers to the amount of time the compressor can operate continuously before it needs to cool down. If you plan on using your air tools for extended periods, you’ll want a compressor with a high duty cycle.
Conclusion
When choosing an air compressor for your air tools, it’s important to consider the CFM requirements of those tools. Be sure to match the CFM rating of the compressor to the total CFM requirements of your tools. Additionally, consider other factors such as pressure rating, tank size, and duty cycle to ensure that you choose the right compressor for your needs.
How CFM Affects Performance and Efficiency of Air Compressors
CFM, or cubic feet per minute, is a unit that measures the airflow of an air compressor. It represents the volume of air that the compressor can deliver per minute.
Airflow and Power: CFM plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of an air compressor. The CFM rating of a compressor determines its ability to power air tools and equipment. Higher CFM values indicate that the compressor can deliver more air, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications and tools that require a continuous flow of air.
Matching CFM with Tools: It is essential to match the CFM rating of the air compressor with the requirements of the tools or equipment being used. If the CFM rating is too low, the compressor may not be able to supply enough air, resulting in reduced performance and inefficiency. On the other hand, if the CFM rating is too high, it can lead to excessive energy consumption and unnecessary wear and tear on the compressor.
Efficiency and Duty Cycle: The CFM rating also affects the efficiency and duty cycle of an air compressor. Duty cycle refers to the amount of time a compressor can run continuously without overheating. If the CFM rating is not adequate, the compressor may have to run for longer periods to meet the airflow demands, leading to increased heat build-up and decreased efficiency.
Considerations for Different Applications: Different applications require different CFM ratings. For example, automotive repair shops may require compressors with higher CFM ratings to power air tools such as impact wrenches and spray guns. Conversely, a smaller CFM rating may be sufficient for home use or light-duty tasks. It is crucial to consider the specific requirements of the intended application when choosing an air compressor.
Conclusion: In summary, CFM is a key factor in the performance and efficiency of air compressors. It determines the compressor’s ability to deliver air, power air tools, and meet the airflow demands of different applications. Matching the CFM rating with the tools and considering the duty cycle are important considerations to ensure optimal performance and efficiency of an air compressor.

Factors Influencing CFM Requirements for Different Applications
Type of Equipment:
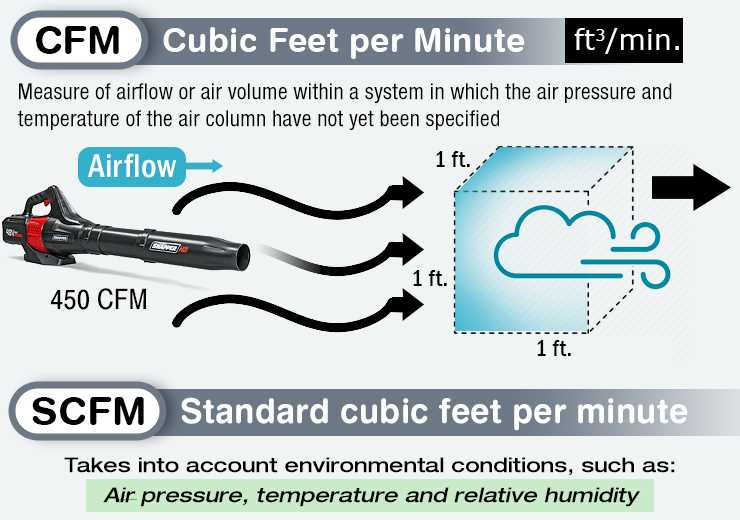
The type of equipment being used is one of the main factors influencing the required CFM (cubic feet per minute) for different applications. Each equipment has its own CFM requirement based on its design and function. For example, a pneumatic drill may require a higher CFM compared to a paint sprayer.
Workload Intensity:
The intensity of the workload also affects the CFM requirement. Applications that involve heavy-duty work, such as sandblasting or cutting metal, require a higher CFM to deliver the necessary power and airflow. On the other hand, applications with lighter workloads, such as inflating tires or operating small tools, may require a lower CFM.
Operating Pressure:
The operating pressure is another critical factor that influences CFM requirements. Higher pressure applications require a higher CFM to maintain the desired airflow and power output. This is particularly important for applications where a consistent pressure is needed, such as spray painting or operating pneumatic machinery.
Environmental Conditions:
The environmental conditions in which the equipment will be used also play a role in determining the required CFM. For example, operating in a high altitude environment or in extreme temperatures may require a higher CFM to compensate for the reduced air density or increased air resistance. Additionally, applications that involve working in dusty or humid environments may require a higher CFM to ensure proper operation and prevent clogging or moisture damage.
Number of Tools:
The number of tools or devices that will be operated simultaneously is another factor influencing CFM requirements. If multiple tools are used at the same time, the CFM requirement will be higher to provide enough airflow and power for each tool. It is important to consider the total CFM requirement when planning to use multiple tools simultaneously to ensure that the air compressor can handle the load.
Additional Features and Attachments:
In some cases, additional features or attachments may increase the CFM requirement. For example, using an air dryer or filtration system may increase the CFM needed to compensate for the additional pressure drop. Similarly, using longer hoses or attachments with smaller diameters may require a higher CFM to overcome the increased resistance and deliver the necessary airflow.
It is important to consider these factors when determining the CFM requirements for different applications. Choosing an air compressor with the appropriate CFM rating ensures that the equipment operates efficiently and effectively for the specific task at hand.
Understanding the Relationship Between CFM and PSI in Air Compressors
CFM (cubic feet per minute) and PSI (pounds per square inch) are both important measurements when it comes to air compressors. The CFM rating of an air compressor indicates the amount of air the compressor can deliver in a minute, while the PSI rating indicates the maximum pressure the compressor can generate. Understanding the relationship between CFM and PSI is crucial in choosing the right air compressor for your needs.
CFM Rating
The CFM rating of an air compressor is a measure of its ability to deliver a certain volume of air in a specified amount of time. It determines how quickly the compressor can fill a tank or deliver air to pneumatic tools. It is important to choose an air compressor with a CFM rating that meets or exceeds the requirements of the tools or equipment you plan to use.
PSI Rating

The PSI rating of an air compressor indicates the maximum pressure the compressor can generate. This pressure is measured in pounds per square inch and determines the force with which the air is delivered. The PSI rating is important when it comes to applications that require high pressure, such as operating pneumatic tools or inflating tires.
It is worth noting that while the CFM rating determines the amount of air delivered, the PSI rating determines the force with which the air is delivered. These two factors work together to determine the overall performance of an air compressor.
Relationship Between CFM and PSI
The relationship between CFM and PSI depends on the specific application. In general, a higher CFM rating is desirable when using tools that require a continuous supply of air, such as grinders or sanders. These tools consume more air and require a higher CFM rating to maintain optimal performance. On the other hand, tools that require higher pressure, such as impact wrenches or nail guns, benefit from a higher PSI rating.
Understanding the relationship between CFM and PSI is essential to ensure that you choose the right air compressor for your specific needs. A compressor with a higher CFM rating might not be suitable if it doesn’t provide enough pressure, while a compressor with a higher PSI rating might not be able to deliver enough air for certain tools or equipment.
CFM and Tank Size: Finding the Right Balance for Optimal Performance
In the world of air compressors, CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) and tank size play a crucial role in determining the performance of the compressor. CFM refers to the amount of air that the compressor can deliver per minute, while tank size refers to the storage capacity of the compressor. Both factors are important in determining the efficiency and effectiveness of the air compressor.
The Importance of CFM
The CFM rating of an air compressor is a measure of its ability to deliver a constant supply of compressed air. This rating determines the power and speed at which the compressor can effectively perform tasks such as powering air tools, inflating tires, or running pneumatic machinery. It is crucial to choose an air compressor with a CFM rating that meets the requirements of your specific application.
For example, if you plan to use the compressor for light household tasks such as inflating tires or operating small air tools, a lower CFM rating may be sufficient. However, for heavy-duty applications such as powering a sandblaster or running industrial machinery, a higher CFM rating is essential to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
The Role of Tank Size
The tank size of an air compressor determines its storage capacity, allowing it to store compressed air for later use. A larger tank size ensures a more constant supply of air, reducing the need for the compressor to constantly cycle on and off. This results in a more efficient and consistent delivery of compressed air, particularly for tasks that require a continuous and uninterrupted flow of air.
However, it is important to find the right balance between CFM and tank size. While a large tank can provide a steady supply of compressed air, it does not necessarily increase the CFM rating of the compressor. In fact, using a larger tank with a lower CFM rating can result in longer refill times and decreased overall performance.
Finding the Right Balance
When choosing an air compressor, it is essential to consider both the CFM rating and the tank size to find the right balance for optimal performance. Determine the specific requirements of your application and choose a compressor that meets those needs. If you require a higher CFM rating, it may be more beneficial to invest in a compressor with a larger tank size to ensure a consistent and reliable supply of compressed air.
In summary, CFM and tank size are two important factors to consider when choosing an air compressor. Finding the right balance between these two factors will ensure optimal performance and efficiency for your specific application. Take the time to carefully evaluate your needs and choose a compressor that meets your requirements.
Tips for Increasing CFM in Air Compressors and Maximizing Output
Increasing CFM (cubic feet per minute) in air compressors is essential for maximizing output and efficiency. By increasing CFM, you can operate more tools simultaneously, improve productivity, and complete tasks faster. Here are a few tips to help you increase CFM in your air compressor:
1. Upgrade to a larger tank size
One way to increase CFM in your air compressor is to upgrade to a larger tank size. A larger tank can store more compressed air, allowing you to use it for longer periods without the need to constantly refill. This leads to increased CFM and a more consistent airflow to your tools.
2. Invest in a higher horsepower motor
To increase CFM, consider investing in an air compressor with a higher horsepower motor. A more powerful motor can generate greater air pressure, resulting in higher CFM output. This allows you to operate air tools that require a larger volume of air, such as sanders, grinders, and pneumatic drills, with ease.
3. Use larger diameter air hoses and fittings
Using larger diameter air hoses and fittings can help increase CFM by reducing air resistance and pressure drops. When air flows through smaller hoses and fittings, friction and turbulence can reduce the overall CFM output. By using larger diameter components, you can minimize these losses and optimize the airflow to your tools.
4. Regularly clean and maintain your air compressor
Air compressors that are clogged with dirt, dust, or debris may struggle to deliver their maximum CFM output. Regularly cleaning and maintaining your air compressor can help improve its efficiency and increase CFM. This includes cleaning air filters, checking for leaks, and lubricating moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
5. Consider a two-stage air compressor
If you require a significantly higher CFM output, consider upgrading to a two-stage air compressor. Two-stage compressors utilize two cylinders to compress air, resulting in higher pressures and CFM. This type of compressor is ideal for heavy-duty applications where a single-stage compressor may not provide enough CFM.
By following these tips, you can increase CFM in your air compressor, maximize its output, and ensure optimal performance for your pneumatic tools and equipment. Remember to consider your specific needs and requirements when selecting an air compressor to ensure it can deliver the necessary CFM for your projects.
FAQ:
What does CFM stand for?
CFM stands for Cubic Feet per Minute.
Why is CFM important for an air compressor?
CFM is important for an air compressor because it measures the amount of air the compressor can deliver in a minute, which determines its ability to power tools and equipment that require a specific volume of air.
How is CFM calculated?
CFM is calculated by multiplying the air compressor’s displacement in cubic inches by the compressor’s revolutions per minute (RPM), and then dividing the result by 1,728 (the number of cubic inches in a cubic foot).
What happens if the CFM rating of an air compressor is too low?
If the CFM rating of an air compressor is too low for the tools or equipment being used, the compressor will not be able to provide enough air flow to power them properly. This can cause a decrease in performance, reduced productivity, and even damage to the tools or equipment.
Video:












